What is a Current Transformer? Understand its Importance in Power Systems
Author:admin Date: 2025-05-29 10:01 Views:974
- Introduction
- Parts of a Current Transformer
- How a Current Transformer Works
- Electrical Characteristics of Current Transformers
- Types of Current Transformers
- Current Transformers Precision/Accuracy Levels
- Where to Use Current Transformers
- Advantages of Current Transformers
- Downsides of Current Transformers
- Features to Consider When Selecting a Current Transformer
- Safety Tips of Current Transformers
- Conclusion
Introduction
Transformers remain important in how power systems work. There are various types of transformers available. They are mostly categorized based on how they work. Today, we focus more on the current transformer, how it works, applications, and much more.
A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that converts high alternating current into lower and manageable alternating current. This is primarily so that it can be measured using standard ammeters.
Such a system comes with many uses thanks to its functionality. Examples include data loggers, metering devices, and more.
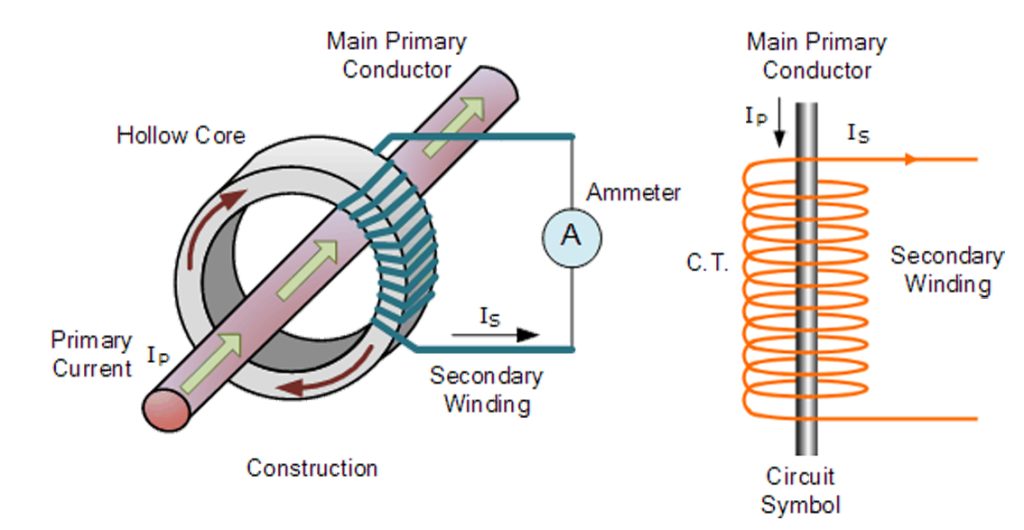
Parts of a Current Transformer
Like any other transformer type, the portable current transformer features several components that make it work as expected. The main components include a magnetic core, primary winding, and secondary winding.
- The magnetic core is made of iron or similar materials, which are good at providing a low-reluctance path for the flow of magnetic flux.
- The primary winding can have one or several windings. It is usually made of thick wire connecting to the measured current.
- The secondary winding provides the output current, which is a scaled-down version of the measured current in the primary windings. The number of windings is usually more in the secondary windings so that you can get the right transformation ratio.
- Insulation is a good addition to the donut current transformer. It is essential to prevent possible short circuits and ensure the right electrical safety while using the transformer.
- The enclosure is also vital to mention as it houses the components of the current transformer and protects them from external factors. The same enclosure also ensures structural support.
- Some models have cooling systems. This might include the current transformer cost, but it is crucial for performance depending on some applications.
How a Current Transformer Works
Current transformers work like any other transformers. In this case, the primary winding is connected to a high current source, while the secondary winding is connected to the measuring device.
When you pass the high current in the primary windings, it creates a magnetic flux in the core. This results in a magnetic field that induces an electromotive force (EMF) and current in the secondary winding.
This induced current is proportional to the primary current, only scaled down depending on the transformer ratio. To understand the amount of current in a circuit, this scaled-down current can now be measured using standard ammeters.
You will encounter various types of current transformers, each operating differently, but the overall principle is the same.
Electrical Characteristics of Current Transformers
In a current transformer simulation, you should know a few electrical characteristics to understand how it works. Below are some of them.
Current Ratio – This ratio shows the relationship between the primary and secondary current. The windings of both the primary and secondary sides lead to this ratio. The secondary current is expected to be much less than the primary current.
Polarity – The polarity of the core current transformer is based on the windings around the magnetic core. It is important to understand the polarity of the current transformer, especially during the installation and maintenance phase. Proper installation and connecting to the current transformers determine their working.
Accuracy Class — Yes, accuracy is important when dealing with current transformers as it determines various performance features. These include the maximum burden, class rating, and rated ratio accuracy rating.
Rated Primary Current – This is the maximum current that the current transformer can handle.
Burden Power – This is the maximum power the secondary windings will supply to the measuring instruments without affecting the accuracy.
Types of Current Transformers
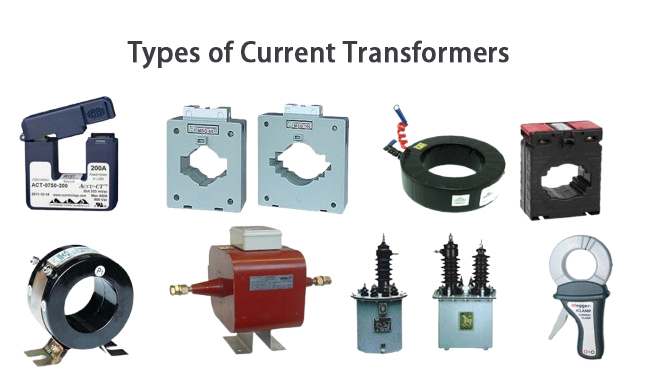
The current transformer design gives us three main types of CT available in the market. Choosing the right one largely depends on your needs. Let us look at the various types of CTs and how they work.
Wound Current Transformer
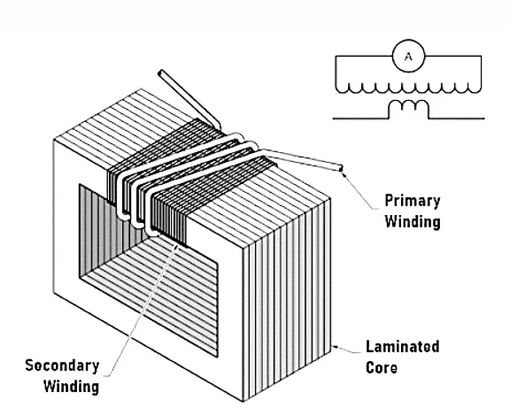
This is the standard structure of a current transformer where the primary and secondary windings are wrapped around a magnetic core. The primary windings are usually less than the secondary windings. The number of secondary windings is based on the desired transformer ratio so that the current in the secondary windings is within the right range.
Toroidal Current Transformer
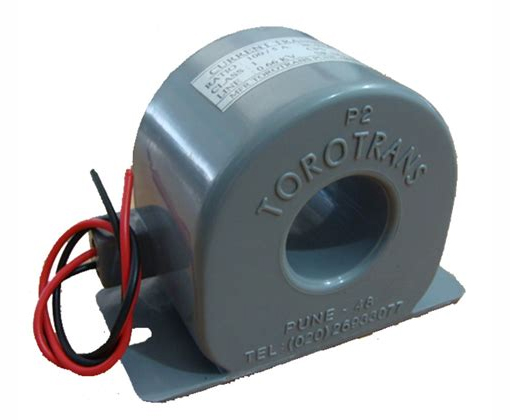

This type involves having a core shaped like a ring. It contains a conductor carrying the primary current passing through the core. This is what acts as the primary winding, which is now 1. The secondary winding is wound around the ring core, and the secondary current is measured across it.
Bar Current Transformer
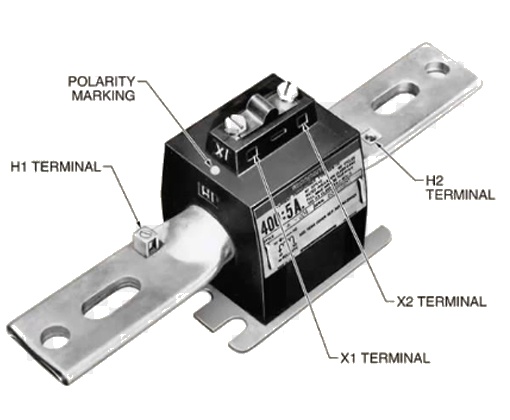
This one works just like the toroidal CT. However, the bar with the primary current is fixed in position and passes through the secondary winding. Such a CT can be considered for high-voltage applications.
Current Transformers Precision/Accuracy Levels
The precision or accuracy level of the current transformer is important in its operations. The accuracy class is the allowable error limit when using the CT under specific conditions. A CT’s accuracy class is expressed as a percentage of the primary current.
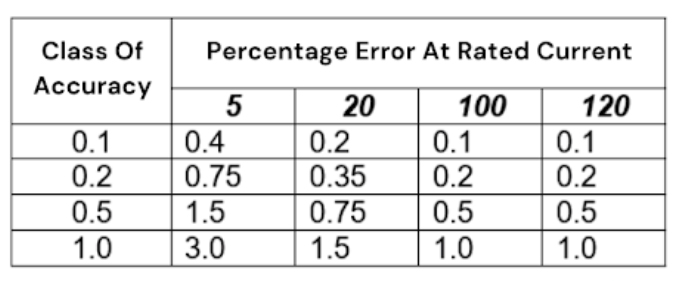
Accuracy Class of CT(Current Transformer)
So, how do you interpret the accuracy levels? A lower accuracy class means the current transformer is highly accurate.
The common CT accuracy levels include:
– 0.1 level
This one has a percent error of 0.1%. It is commonly used in high-precision metering and measuring applications, including precision instruments and energy measurement. Since it provides the highest accuracy level, it is often encountered in applications with very tight tolerances.
– 0.2 level
With a percent error of 0.2%, it is still a suitable option for high-accuracy applications. They are commonly found in commercial and industrial applications.
– 0.5 level
The percent error for this one is 0.5%, which is good for applications where accuracy requirements are not strict. This includes metering and protection applications. So, you can use it for general protection and related applications.
– Level 1
For a percent error of 1%, it is expected that its applications will have low accuracy needs. We may find such units being used for protection relays since the high accuracy will not be the primary need for such a transformer.
Where to Use Current Transformers
Now that you know more about a current transformer and how it works, next is to find out its applications. Here are the notable uses of current transformers.
- Used in measuring of current levels in high-voltage lines
- They can help protect electrical equipment from faults or overcurrents
- The current transformers offer control of power systems through relays and circuit breakers
- Expect to come across them in metering and billing by power companies to measure consumer power consumption
- They can also be used for industrial applications that involve large motor starters and power systems
Advantages of Current Transformers
Safety and Isolation
The current transformer construction makes it quite good in terms of performance including providing safety and isolation. This is because it protects the measuring instruments from the high currents.
Accuracy
Expect high accuracy when measuring with current transformers, even with varying loading conditions. They can measure both high and low currents, thus making them suitable for multiple types of applications.
System Control
Besides providing overcurrent protection, the current transformer can offer better circuit control. For example, it can be used in relay operations, initiating tripping to protect equipment connected to it.
Ease of Integration
The current transformers are built to be cost-effective compared to some other current measurement methods. Even though they are affordable, they still provide high accuracy. Expect these transformers to withstand long-term use, even in harsh environmental conditions.
Downsides of Current Transformers
Complexity
Current transformers are generally cost-effective when they are simple. However, depending on the application, sometimes more components are needed, which leads to more complexity and cost.
Accuracy Degradation
Though not common, if the current transformer design is exposed to high currents for a long time, it may become saturated, which may lead to inaccuracies and performance issues.
Burden Power Loss
This is the power the secondary circuit consumes because of the measuring equipment. This can be an issue, especially when you need to minimize power consumption in an application.
Features to Consider When Selecting a Current Transformer
Now that you know what is a current transformer, we can shift to choosing the right one for your needs. Here is how to pick the best CT in the market.
Current Ratings
The current transformer description will indicate the current ratings of the transformer so that you can get it right. Check the current ratings for both the primary and secondary sides, as it helps you work with a transformer that can handle high or low currents.
Accuracy Class
The accuracy class can also determine which unit you get. Some applications might need more accuracy while others not so much. The higher lower the accuracy level, the more precise the readings you get from a transformer. For example, a transformer with an accuracy level of 0.1 is more accurate than one with a 0.5 level.
The Frequency Range
Having a good range makes it suitable for various applications. Expect most current transformers to work with frequencies of 50 or 60Hz power systems. However, others might be specialized to handle more types of frequency ranges.
Insulation
You may also want to consider the type of insulation available with the cable current transformer. This should help determine the voltage level such a current transformer can handle without issues.
Burden Rating
This is also crucial as it can affect the accuracy and reliability of the readings. Check this information on the datasheet of your current transformer to see if it will be suitable for your application or you need something better.
Cost
The overall cost can also be a determinant. As much as you might be looking for affordability, you also want a reliable unit. Look into the different reviews about a model before buying to ensure you always get the right one.
Safety Tips of Current Transformers
Several recommendations must be considered while using current transformers so that they can operate as expected. Such include:
- Avoid overloading the primary windings. Make sure you stick to the rated primary current. When you overload, it can cause damage and inaccurate readings.
- The primary side of the CT needs the right short-circuit protection to prevent having overcurrent flowing in case of a fault.
- Never leave the secondary circuit open. This is because it can lead to very high voltage, which can be a safety hazard. Shorting the secondary or connecting a load is best when not in use.
- Proper grounding is also recommended. This is key to preventing ground faults and ensuring the current follows a safe path in case of electrical hazards.
- The insulation integrity is also vital for the operation of the current transformer. Inspect regularly to check for signs of wear or damage to the insulation.
- Training and creating awareness are recommended for the personnel who will be working on the project.
Conclusion
A current transformer can be suitable for various uses in power systems. We find it essential in metering applications. That is why you must get the current transformer sizing right to work well with your application. There are also various types of CTs, so pick the correct one for the application. If you ever have issues with your transformer, make sure to have a professional look at it to avoid further problems. Keep taking care of it as the manufacturer recommends, and you should always have a good working unit.
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can current transformers work with DC current?
No. CTs are built to work only with alternating current. They rely on AC’s process of electromagnetic induction to produce current in the secondary winding.
What does a current transformer ratio mean?
This is the relationship between the primary and secondary current. It determines how much current will be in both the primacy and secondary windings.
Why is it important not to have a non-open circuit for the secondary windings while energized?
Having an open secondary leads to very high voltage, which may damage the current transformer or be a safety hazard for the user. It is important to connect the secondary windings to a load or burden.


