Guide to Network Interface Cards (NIC) Performance
Author:admin Date: 2025-10-17 03:52 Views:208
- Introduction
- Components of a Network Interface Card
- How a Network Interface Card Works
- Network Interface Card Types
- NIC Performance and Speeds Explained
- Factors Affecting the NIC Speed
- How to Install and Configure NICs
- How to Troubleshoot Network Interface Cards
- Conclusion
- Video: What is NIC or Network Interface Card or Network Card?
Introduction
A network interface card (NIC) serves as a bridge between a device and a network, enabling the device to send and receive data. The NIC converts the data into electrical signals or radio waves for transmission, and reassembles the incoming data so the device can understand what is being transmitted.
Components of a Network Interface Card
The (NIC) network interface card is made up of several components. Each component has a function. Here is a list of the main components of the NIC.
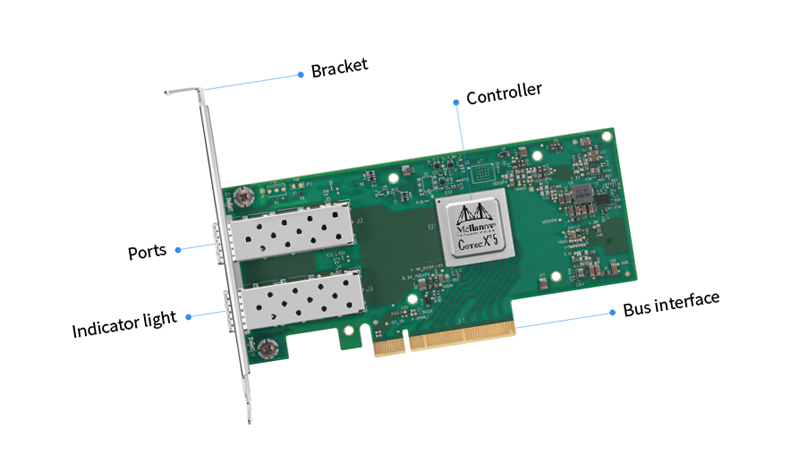
MAC Controller: The Media Access Control (MAC) is considered the brain of the NIC. Its role is to handle data-link layer functions, such as formatting data into packets and using the unique MAC address for network identification.
Physical-layer transceiver: This component converts data from the MAC controller into electrical signals for transmission over the network. It also converts incoming signals into understandable data for the device.
Buffer Memory: These are small amounts of onboard RAM used to store data packets during the receiving and transmitting processes temporarily.
Bus Interface: This component connects network interface cards to the computer’s motherboard. It is mainly via the PCIe slot, which allows it to communicate with the rest of the system.
Network Port: This is the physical port where the network cable is plugged into, thus allowing the device to connect to the network.
MAC Address: This is a unique 48-bit serial number assigned to a NIC. It is stored in the ROM and used to identify the device on a network.
How a Network Interface Card Works
Now that you know what is (NIC) Network Interface Card, we can further look at how it works. Well, it manages the data flow, translates data, and allows for physical network medium connection.
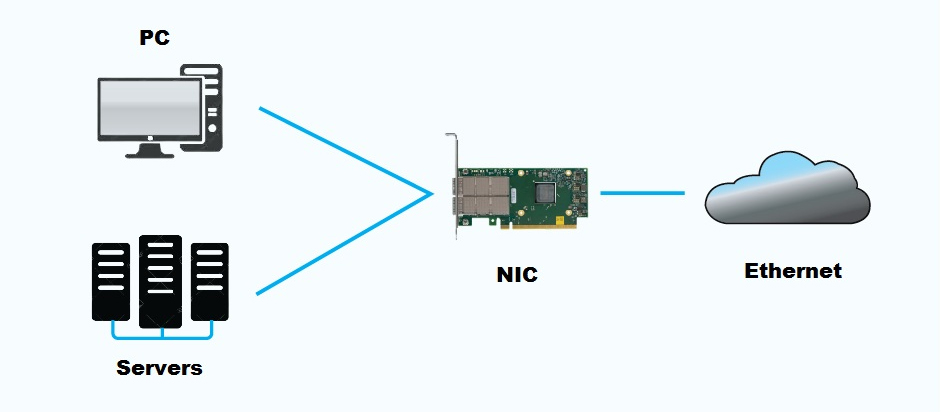
Data Transmission
The NIC receives data as packets from the computer’s operating system or network layer. It then encapsulates and formats the data correctly. This includes adding headers and trailers to the data. It follows network protocols such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi, converting the data into a stream of bits.
The stream of bits is further converted into the appropriate electrical signals for transmission over a wired connection or radio waves for a wireless connection.
Once the conversion is done, the NIC sends the signals out onto the physical network medium.
Data Reception
The NIC also receives signals from the network through its port or antenna. Once the data is received, it is converted into a digital stream of bits. The NIC further formats the bits into frames and then checks if the frame’s MAC address matches its unique MAC address.
The network interface card still performs a Cyclic Redundancy Check or CRC to verify the frame’s integrity and discards it in case there are errors.
If a frame is valid and its MAC address matches, its header and trailer are removed. It then sends the remaining data packet to the computer’s network layer for further processing.
Network Interface Card Types
Network interface cards can be categorized in different ways. Below are a few types for you to have a good understanding.
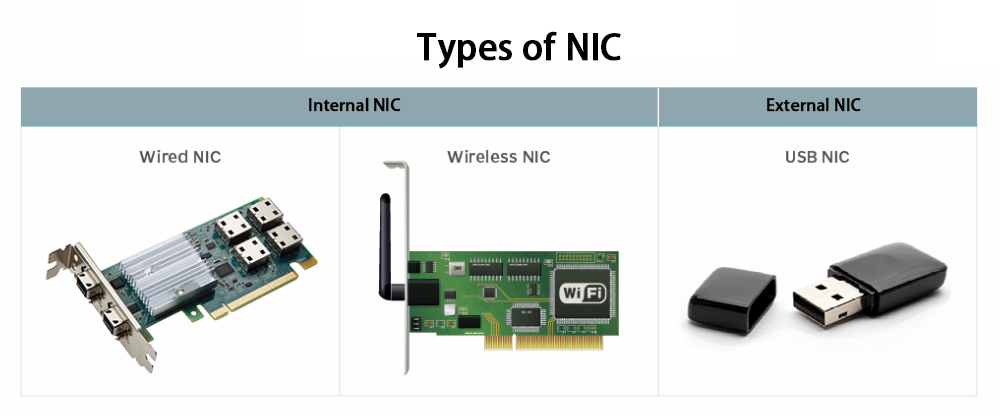
Wired NICs vs. Wireless NICs
| Feature | Wired NICs | Wireless NICs |
| Connectivity | Uses physical Ethernet cables for connecting to the network | Uses antennas and radio frequencies for connecting to a wireless access point |
| Speed and stability | It is generally faster and more stable with low latency. Less prone to interference | It is slower and more susceptible to interference |
| Secuirty | It is considered more secure as you must be physically connected to the network | More vulnerable to unauthorized access as it relies on radio waves |
| Common uses | Desktops, servers, or where high speed and stability are needed | Laptops, smartphones, and many portable devices |
Integrated Vs. Dedicated NICs
| Feature | Integrated NICs | Dedicated NICs |
| What it is | An NIC built directly onto the computer’s motherboard | A separate NIC that is inserted into the motherboard via an expansion slot or external port |
| Benefits | Convenient and cost-effective Sufficient for basic use | Good for making upgrades Can provide higher performance or specialized functionality |
| Limitations | Limited upgrade options | Requires physical installation and an expensive purchase upfront |
PCIe vs USB NICs
| Feature | PCIe NICs | USB NICs |
| Connection Type | Plugs into the Peripheral Component Express (PCIe) slot on the computer motherboard | Plugs into the USB port on the exterior of a device |
| Performance | Expect a higher performance and bandwidth. Ideally suitable for desktops and servers. | The USB standard limits performance. |
| Ideal applications | Desktops or servers | For portable devices or a desktop that lacks a NIC. |
Server NICs vs. Desktop NICs
| Feature | Server NICs | Desktop NICs |
| Port count | Comes with multiple ports useful for redundancy, load balancing, or connecting to various networks. | Typically comes with a single port |
| Speed | Frequently supports higher speeds such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet and more to handle a large traffic need. | Can handle mostly standard speeds, such as 1Gbps, but you can get faster options available |
| Reliability | It offers high reliability and has proper hardware important for offloading to free the CPU to handle other tasks. | It is still reliable, but will have fewer features compared to server NICs. |
NIC Performance and Speeds Explained
The NIC speed standards largely depend on the type. You can get some older standards with a maximum of 100 Mbps, but now speeds are better with newer NICs. You can get options such as Gigabit Ethernet with speeds of up to 1Gbps, which is 10 times faster than the earlier models.
In case it is a data center or enterprise kind of setup, you will come across other standards. We are talking about standards such as 100 Gbps, which is 10 times faster and can handle rapid file transfers and large data volumes.
Factors Affecting the NIC Speed
A few things may affect how well the NIC performs. Below are some of the key factors to keep in mind.
- The network bandwidth and cable quality. A high-speed NIC can be limited to the performance of a slow component in the chain. It could be the network bandwidth and the cable connecting the device. So, choose these things correctly to match your needs.
- Duplex settings: This is the direction of data flow. Half-duplex generally sends data in a single direction while full-duplex sends and receives data simultaneously, which is important in achieving higher speeds.
- Buffer size and interrupts: The buffer size of an NIC is crucial, as it determines the amount of data the NIC can store. If the buffer is too small, data loss can occur. If the buffer is too big, then it can lead to latency. Still, the frequency of interrupts sent to the CPU can affect overall NIC performance.
- System hardware compatibility: The system’s CPU, PCIe, or motherboard must match the NIC speed performance to avoid having performance bottlenecks.
How to Install and Configure NICs
Right now, we know what does a network interface card (NIC) do, let us get to installing and configuring it.
It is important to always check for compatibility. Ensure that the NIC is compatible with the existing motherboard expansion slots.
Physical Installation of the NIC
- Shut down the computer and disconnect the power
- Remove the computer case cover
- Identify the available expansion slot
- Remove the slot cover from the back of the case
- Align the NIC with the slot and press it down firmly so that it is seated properly in the slot
- Secure the card using a screw
- Replace the computer case cover
Installing Drivers
- Boot the computer
- In case the operating system does not automatically detect the new NIC and install drivers, then you need to install them yourself.
- Insert the driver CD that came with the NIC to install the drivers, or download the latest drivers from the NIC manufacturer’s website
- Follow the instructions from the driver software to complete the installation.
By now, your NIC should be ready for use.
How to Troubleshoot Network Interface Cards
Some of the common NIC problems include:
- Slow network speeds: This may be caused by network congestion, faulty cables, and outdated drivers.
- No network connection: This is mostly due to incorrect settings, a hardware problem with the NIC, or a disabled adapter.
- No Internet Access or Unidentified Network: This means the device is connected to the router but has no internet access. It could be issues with the IP address or DNS settings.
There are various ways to diagnose these NIC problems. First, check the network settings to see if it is a software or hardware issue. If the network adapter is disabled, enable it to see if there are any changes.
Test the network cables and ports to see if they are working correctly. Try a different network cable to eliminate a faulty cable.
Once you update the drivers, most of the time, the network problems are resolved. Go to the manufacturer’s website to find and download the latest NIC drivers to improve its performance.
Conclusion
Network interface cards are vital to a device’s network performance. We have seen the various types above. So, it is easier to pick the right NIC for your device. Also, we have shared tips on identifying NIC problems and resolving them to ensure optimal performance at all times.
Video: What is NIC or Network Interface Card or Network Card?
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you know if a computer has a NIC?
Most computers now come with a built-in NIC on the motherboard. Simply check via the computer’s Device Manager, looking for Network Adapters. Also, if a Desktop or laptop has an Ethernet port, it indicates the presence of an NIC.
Can you have multiple NICs on a single computer?
Yes. Having multiple NICs increases redundancy, improves performance, and helps with separating traffic for different networks. More NICs on a single device also offer load balancing and failover protection.
What is a Smart NIC?
This is a NIC designed with offloading capabilities such as encryption, traffic management, and packet filtering. This takes the load away from the CPU so that it can handle other tasks more efficiently. You will come across them in data centers or environments where network performance is vital.


