Does a Resistor Lower Voltage or Limit Current? Complete Breakdown
Author:admin Date: 2025-11-05 08:19 Views:266
Introduction
We all know that a resistor opposes or limits the flow of electrical current in a circuit. This property causes the voltage drop and dissipates energy as heat.
We go a step further to understand in detail the matter of does a resistor lower voltage. We also consider whether a resistor is the best choice for regulating voltage, or whether better options are available.
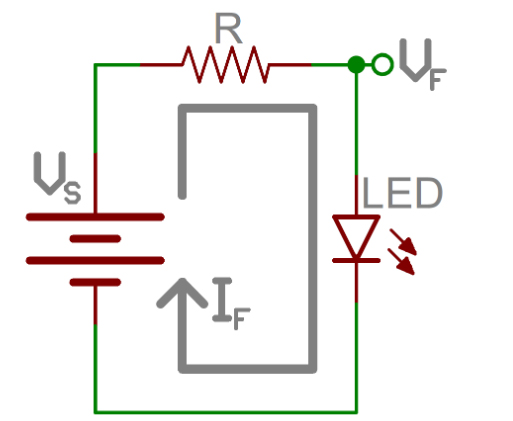
Ohm’s Law: How Resistance, Voltage, and Current Relate to Each Other
Ohm’s Law has three main components, including resistance, current, and voltage. It is key to understand how they relate to one another.
Voltage is the electrical pressure that pushes charged electrons through the circuit. Volts is the unit of measure for voltage.
Current is the flow of electrons through the circuit over time. Amperes is the unit of measure for current.
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current. Ohms is the unit of measure for resistance. You can compare resistance to friction. Having a higher resistance means more restriction to the flow of current.
According to Ohm’s Law, the electric current passing through a conductor increases with the applied voltage and decreases as the resistance rises.
The equation for Ohm’s law is V = IR
Where:
- V is the voltage (V)
- I is the current (A)
- R is the resistance (Ω)
You can rearrange the Ohm’s Law equation above to solve for current and resistance.
What Is Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop is the loss of electrical potential whenever current flows through a circuit’s wiring and components. All electrical conductors have some resistance, which causes voltage to drop or be consumed, leaving less voltage to reach the load.
Why Voltage Drop Occurs in a Circuit
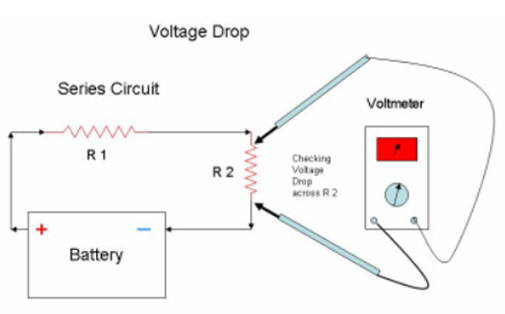
Still on does a resistor reduce voltage or current, we want to understand why voltage drop occurs.
Resistance is the primary reason you end up with voltage drops. It is unavoidable in a circuit since all conductors may have some form of resistance.
The resistance and voltage drops may be affected by a couple of things. Such include:
- Wire length: Having a longer wire may lead to higher total resistance and a larger voltage drop. This is quite noticeable for long cable runs.
- Wire gauge: Thinner wires tend to have higher resistance than thicker wires, even if they are made of the same material and length. So, always understand the application because sizing it with thin or thick wire.
- Wire material: Of course, some materials are better conductors than others. For example, copper comes with lower resistance than aluminum. It is why it is a better choice if you want to reduce voltage drop.
- Current load: Having a higher current flowing through the same resistance causes a larger voltage drop. A good example is when you drive a large load, such as a motor starting up, expect a brief voltage drop.
- Poor connections: Yes, having dirty or corroded connections introduces unwanted resistance in a circuit. This creates hot spots and may further lead to more voltage drop.
How a Resistor Reduces Voltage
A resistor will cause a voltage drop when current flows through it. The resistance is expected to be as per Ohm’s Law. It also depends on how the resistor is arranged in the circuit. That is why the voltage drop in series and parallel circuits will be different.
A resistor can cause a voltage drop due to its resistance and energy conversion. The primary function of the resistor is to oppose the current flow. It does this by converting the electrons’ electrical energy into heat. This energy loss across the resistor is called the voltage drop.
The most common way for resistors to reduce voltage is by being used in a voltage divider circuit. In this case, two or more resistors are connected in series to a voltage source. The voltage from the source is divided among the resistors according to their resistance values. The voltage at any point between these resistors is a fraction of the input voltage.
Using Resistors to Reduce Voltage in Applications
Resistors can be used to reduce voltage in many applications. This is mostly where they are used to cause a controlled voltage drop, whether it is in a series resistor or a voltage divider circuit.
Here are some of the common applications:
- Using resistors for current limiting for LEDs
You can use a resistor in LEDs to protect the sensitive components from excessive current. In this application, the resistor limits the current that the LEDs draw from the power source to prevent them from burning out.
- Signal level shifting for microcontrollers
Resistor voltage dividers are also used in digital electronics as an interface between two circuits operating at different voltage levels. A voltage divider helps step down a higher-voltage signal to the level required by the low-voltage circuit.
- Sensor measurement interface
Many passive sensors in the market, such as thermistors and photoresistors, work as variable resistors. Their job is to produce a variable-voltage output that a microcontroller can read.
- Creating voltage references
Voltage dividers can also come in handy as stable reference voltages for comparison circuits. Examples include comparators and operational amplifiers. For instance, in a 555 timer chip, the internal resistors form a voltage divider for creating reference voltages at ⅓ and ⅔ of the supply voltage. The circuit’s behavior depends on these stable internal references.
- High-voltage measurement
For safety, it is key to scale down very high voltages before measuring them with a standard voltmeter. A specialized voltage divider is used in such applications to ensure high precision and safety as well. It does this by producing a much lower, proportional output voltage that is safe for standard measuring devices.
Why a Resistor Isn’t Always the Best Tool for Reducing Voltage
Resistors are generally useful for simple and fixed voltage reduction applications, but they are not the best tool for many other applications. The limitations of resistors for voltage regulation include:
- They have inconsistent output voltage when used with variable loads. If they are used with a simple series resistor or as a voltage divider, the output voltage will be correct only if the load current is constant.
- Issues of poor energy efficiency and heat generation may arise. Resistors reduce voltage by converting electrical energy into heat. This is mainly for high current loads. In such applications, you will end up wasting a lot of power as heat.
- The stability of such a system depends on the stability of the power source. If the input voltage changes, the output voltage will change even with a fixed resistance.
- Whenever the load is attached to the voltage divider, it adds a parallel resistance to the circuit. This changes both the total resistance and the output voltage. So, it is crucial to choose a voltage divider setup with low impedance relative to the load.
Conclusion
We have seen that a resistor can reduce the voltage by limiting the current going through the load. This passive approach is the best for simple and predictable applications. For example, you can use it to limit LED current or to create a stable voltage reference. You can always opt for a voltage regulator, as it provides a more stable voltage output than resistors. So, it comes down to the application you are handling.
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Resistors vs Voltage Regulators: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between a resistor and a voltage regulator is how they function. A resistor works by passively resisting current, creating a variable voltage drop. As for the voltage regulator, it actively maintains a stable output voltage.
Can you use a resistor to step down the voltage for LEDs or sensors?
Yes. Resistors are a good pick for limiting current and reducing voltage for low-powered components such as LEDs, logic circuits, and sensors. However, it is important to calculate the correct resistor value depending on the input voltage, the device’s current rating, and the desired output voltage.
What happens to the “lost” voltage in a resistor?
The lost voltage is mainly converted into heat energy. That is why the resistors get warm as you keep using them in a circuit. This happens as they continue to oppose the current flow, transforming the electrical energy into heat, which is then dissipated into the environment.


