Electrical Panelboard Basics: Types, Functions, and Buying Guide
Author:admin Date: 2025-06-18 07:40 Views:706
How Do Electrical Panels Work – An Explanation of All the Parts!
- Introduction
- Key Components of an Electrical Panelboard
- Importance of an Electrical Panelboard
- Types of Electrical Panelboards
- Applications of Electrical Panelboards
- How to Choose the Right Panelboard: Buying Tips
- Steps for Installing Electrical Panelboards
- Signs it is Time to Upgrade the Electrical Panelboard
- Conclusion
Introduction
An electrical panelboard is an important part of any electrical system. It is also called the distribution board or panel, and its job is to distribute electrical power to different circuits connected to it.
As part of its operation, it houses many things. Depending on the type and application, this includes fuses, circuit breakers, lugs, and more. You are likely to come across the panelboards in commercial and industrial setups. However, they can also be used in larger residential buildings.
Key Components of an Electrical Panelboard
Since it is a distribution center for different types of circuits, the general electric panelboards will likely have many components to make their operation possible. Here are some of the components to keep in mind.
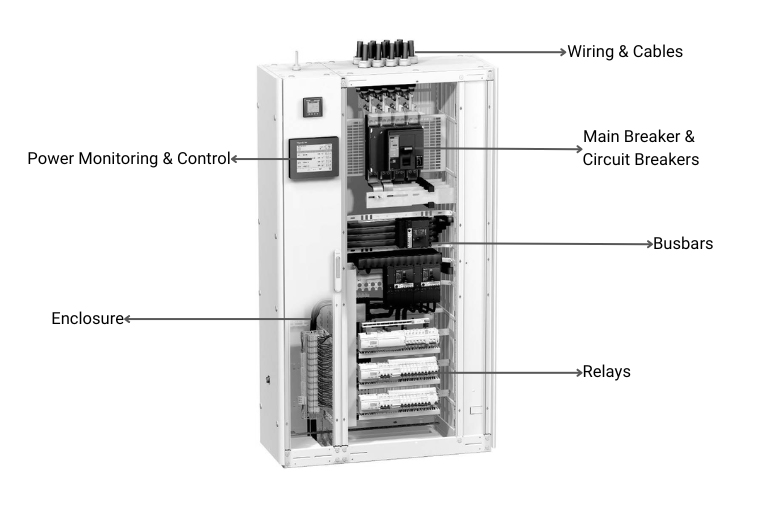
Main Breaker or Lugs
The main breaker of electrical panelboards works as an entry point for electricity into a panel. It controls the overall power flow to the panelboard and can be used to disconnect power during maintenance or if there is an overload.
Busbars
These are metal bars that distribute electricity to the other individual circuit breakers in the panel. Their job is to ensure a reliable and efficient path for current to reach the different circuits.
Circuit Breakers
The electrical panelboard will also have circuit breakers. They protect each individual circuit from cases of short circuits or overloads. In case there is too much current in the circuit, the breaker simply trips, disrupting current flow. This prevents potential device damage.
Neutral and Ground Bars
Any circuit needs a neutral and ground point to complete it. These points provide a common connection for the neutral and ground wires, ensuring safe electrical system operation and protection against electrical shock.
The other components worth mentioning include:
- An enclosure which is important for housing all the components and protecting them from the environment
- Surge protectors are also vital for protecting the electrical panelboard and the connected appliances from issues such as voltage spikes due to power surges or lighting.
- Voltage meters can also be included to show the voltage amount by the supply line
- DIN rails can be added to help with mounting different types of components, including circuit breakers.
Importance of an Electrical Panelboard
By now, you have an idea of what is a panelboard in electrical systems. Next is to look at its importance in detail so that when you are choosing one, you know how best it can be used.
Safety
This is the primary use of an electrical panelboard. It will help protect the electrical system from overloads and short circuits. If a fault is detected, you will have fuses and circuit breakers as part of the electrical panels so that they can blow or trip respectively.
This is important for protecting the appliances connected to the panelboard. Also, it helps prevent potential fire outbreaks because of overloads or short-circuiting of the wiring.
Distribution
The Schneider electric i-line panelboards are handy for distributing the power to the different circuits connected to the main panel. This ensures a controlled area for all the circuits and helps organize the electrical wiring for the whole building.
Since there will be many circuits in a panelboard, it is best suited for commercial and industrial applications.
Control and Monitoring
When you look at the electrical panelboard diagram, you will see how it comes in handy for controlling and monitoring the whole electrical system. This is important for times when you need to do maintenance or troubleshoot the circuits.
Some modern panel boards come with performance monitoring features as well. This means you can identify potential electrical system issues and resolve them before they become big issues later on.
Regulatory Compliance
In some states, panelboards are required as part of the electrical system to comply with the building code. This ensures proper safety and management of the electrical systems.
Types of Electrical Panelboards

You can invest in Schneider electric panelboards simply because the brand is known for making high-quality panels. It is worth looking at the main types of electric panelboards to know which one to get for your application. Here are the top types of panels to consider.
Main Breaker Panels
These panels are also called the mother panels, and their job is to act as the primary panel in a building’s electrical system.
It receives the main power supply from the grid and distributes it to the other panels or circuits connected to it.
It will have a main breaker that can disconnect the entire panel so that you can cut off power easily to the whole building in case of emergencies or maintenance operations.
The amperage ratings for this panel can vary depending on the use. Expect the range to vary from 100 to 400 amps. Look at the electrical load before deciding which amperage rating will work for you.
Sub-panel
You will also come across a sub-panel as a type of electrical panelboard assembly. As the name suggests, this one receives power from the main panel and distributes it to other circuits in a specific area.
They are useful for controlling the power in specific sections of the building, such as the garage.
You get a sub-panel because you need to manage the electrical load better and simplify the building’s wiring.
Main Lug Panel
Such a panel type does not come with the main breaker as part of construction but relies on the main panel’s breaker for power shutoff.
You would use such panels as sub-panels or in applications where the disconnect is located in a different location.
Transfer Switch Panel
The transfer switch panel will be used in conjunction with the backup power systems, such as the generators. This allows for a seamless transition from the main power supply to the backup power supply.
The transfer switch panel automatically switches the electrical load to a generator in case of a blackout, ensuring a continuous power supply.
Motor Control Center (MCC) Panels
This is another panel you can use in your building setup. It is mostly designed to control and protect electric motors. These panels include starters, overloads, and several other protective motor control features.
You should encounter them in industrial and commercial settings, where you are expected to use the motors more often.
Power Control Center (PCC) Panels
These panels are key for controlling and distributing power to different types of electrical loads. Such include motors, transformers, and other electrical equipment.
They come with parts such as protective relays, busbars, circuit breakers, and others that are vital for power management.
Applications of Electrical Panelboards
Siemens electrical panelboards are quite popular because of their overall performance. Here is how you are likely to use them.
Residential
The panels will be good for power distribution in homes to appliances, HVAC systems, lighting, and other types of electrical loads.
Since the panels come with circuit breakers and fuses, they can trip or blow during cases of overloads and short circuits. This prevents fires and further protects the appliances.
Modern homes with solar panels or backup generators also need panelboards, which provide a centralized point for managing the power source.
Commercial
You are likely to encounter a panel more often in a commercial setup. They are still important for managing the power distribution to the lighting systems and HVAC units.
If you decide to automate the building’s operation, such a panel is important. It allows you to control individual circuits from one place.
Submetering can also be done from the panelboard. This ensures there is separate billing for each person. For example, we can use this panel for apartments where each unit needs a different metering system.
Industrial
These panels are also standard in industrial settings. They will be used to control motors in various applications. For example, they can protect the pumps, machinery, and conveyors.
They can also be customized depending on the application. That is why they can also come with additional components such as programmable logic controllers, relays, and contactors. This makes them tailored for a specific industrial automation need.
Process control is another reason for the use of units in industrial applications. This is where you can find panelboards controlling circuits for manufacturing, production lines, and other key industrial processes.
How to Choose the Right Panelboard: Buying Tips
With the basics of electrical panelboards in mind, it is best to see how you would choose one for your application.
Determine Your Electrical Load
Calculating the total power that the electrical system will need, including current and future needs, is important to avoid overloading.
For example, you can estimate what each home is likely to use for an apartment building. Do not forget to factor in heaters, dryers, HVAC systems, and other appliances that draw a lot of electricity at any given time.
When you have the total load in mind, you can choose better, knowing that the panelboard’s rating can handle the load.
Consider the Right Amperage and Voltage
The amperage range for residential panels ranges from 100 to 200 amperes. Modern homes right now use the 200-amp panels since they can handle their needs better.
You also have to consider whether it is a single-phase or three-phase connection. Single-phase power is recommended for residential settings, while a three-phase power supply is recommended for industrial settings.
Circuit Count and Space Available
The circuit capacity of the antique electrical panelboard will determine how many circuits can be connected to it. If you have many circuits to set up, consider matching that to a panel with the right capacity.
Also, consider the available installation space to choose the right panel. It should be possible to fit it into the space without any issues.
Safety Features Available
Different panels might have different protective and safety features. The most important is surge protection. You need a panel that can protect your appliances and electronics from voltage spikes.
You can also get panels with tamper-resistant breakers. This helps prevent unauthorized access and tampering of the panelboard.
Other safety measures can include GFCI and AFCI breakers. These addons are key in enhancing safety as the panels can now detect and interrupt power supply to prevent potential hazards.
Panelboard Type
The type can determine where best to use it. For example, reading through the General Electric panelboard description helps determine the best-recommended application for such a panel. As a result, you can know when to use the panel for commercial or residential applications.
Brand and Warranty
The brand you choose to supply the electrical panelboard can determine how well the panel will deliver on the applications. We recommend brands such as Schneider Electric, Eaton, Siemens, ABB, General Electric, Paneltronics, and Mitsubishi Electric. All these brands have the high-quality panels you need for your application.
Also, the warranty should be good to ensure that you can always get a replacement in case the current panelboard has an issue.
Steps for Installing Electrical Panelboards
The installation process is critical to ensure you have a good working panelboard. There are a couple of steps you should take to do the right installation. However, if you are unsure, a professional electrician can help you. Here is how it can be done.
Planning and Preparations
Assess your electrical needs to choose the right panel and select the panel based on the capacity and application.
Figure out the right location for the installation. It should comply with the electrical codes, which ensures safety and maintenance can be done if needed.
Get yourself tools such as a wire stripper, screwdrivers, fasteners, drills, and many others. Also, remember to have safety gear such as insulated gloves and eye protection.
Panelboard Mounting
Make sure the panel is level and securely mounted onto the wall. Using a level ensures that the panel is well-aligned.
Next, start connecting the conduits to the panelboard. You should have chosen the right sizing for the specific conduits so they can be secured easily.
Wiring and Connections
Pull the feeder wires through the conduits and straight into the panel. Leave enough slack necessary for connections later.
Install the circuit breakers based on the panelboard design and the electrical plan. Remember to ground the necessary circuits for safety. The same applies to ensuring the neutral connection is also done right.
Testing and Inspection
Ensure that the wire connections are tight and secure. Then, test the circuit breaker’s functionality. You need to be assured that the breaker will work when the time comes.
Clear labeling of the circuits and breakers helps with future identification so that you can easily do maintenance.
Once you have completed the final inspection, turn on the panelboard to power the individual circuits.
Signs it is Time to Upgrade the Electrical Panelboard
Sometimes, the electrical panelboard might not work as expected, and it is time to replace it. Here are signs that help you know it is time to upgrade the panel.
- Frequent breaker tripping can occur, even when the system has no faults of overloading or short circuits. This means the panel is struggling to handle the system’s electrical demand. It could be that the panel is undersized, faulty, or outdated wiring.
- Flickering or dimming lights when using other appliances means the panel cannot provide consistent and reliable power. Have it checked to see what could be the issue, or have it replaced.
- An outdated panel, which you may have been using for more than 20 years, also needs replacing. Upgrading leaves you with a panel that can better handle modern electronics and has more safety features.
- If your electrical demand has increased, it is time to upgrade the panel. For example, if you want to start charging your electric vehicle at home, it is important to have a panel that matches the new electrical demands.
Conclusion
Electrical panelboards are key to ensuring safety while distributing power to different circuits, depending on the application. They are common in apartments, commercial spaces, and industrial applications. There are several types available, so make sure you only pick based on your needs. As for the installation, it is best to work with a professional to ensure everything is set up correctly. Practice regular checks and maintenance to ensure the unit is working as expected.
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a difference between a panelboard, switchboard, and load center?
A panelboard is designed mostly for commercial and residential settings. As for a load center, you can expect it in residential applications most of the time. The switchboard is larger and more robust. This makes it more suitable for industrial and large commercial applications to distribute higher voltage.
How do residential and commercial panelboards differ?
The residential panelboards are generally smaller and have lower voltage and amperage ratings. The commercial panelboards will be built for higher power loads, larger breaker capacity, and may also have more advanced safety features.
How often should a panelboard be inspected or maintained?
Have a licensed electrician inspect the panelboard every 3 to 5 years. Still, you can have it checked in case there are electrical issues. Maintenance involves tightening connections, checking for heat buildup, and ensuring the breakers are functioning properly.


