Expert Guide to RS-232: Pinout, Connections, and Applications
Author:admin Date: 2025-10-17 02:44 Views:317
Introduction
This guide looks into how RS-232 works, its features, applications, and more. This ensures you can fully understand what the standard is all about and how it applies to modern electronics today.
What is RS-232?
An RS-232 is a type of serial communication standard used to define the electrical, mechanical, and
functional characteristics for connecting devices such as printers, modems, and embedded systems.

How RS-232 Works
RS-232 works by transmitting data serially. This means one bit at a time between two devices over a wire. The communication relies on voltage levels for representing binary data.
Serial Communication
In a serial communication, as suggested, the data is sent sequentially over a single wire. The data is transmitted from a pin on one device to the receiver pin on the other device and vice versa. A common ground wire is also available to provide a reference voltage for the signals in the communication.
Data Encoding
Encoding data is also part of the process. In this case, voltage levels are used to represent the data. A positive voltage represents binary 0, while a negative voltage represents binary 1. The start and stop bits are used at the beginning and end of each byte to help the receiving device synchronize.
Both the sender and receiver need the right transmission speed, which is known as the baud rate. It is measured in bits per second.
Flow Control
The RS 232 standard is asynchronous, meaning the start and stop bits are used for handling the timing for each byte since there is no separate clock signal for this part.
A handshake process is used to manage the data flow. It could be hardware or software-based.
Common Uses of RS-232
The RS-232 is commonly used in industrial automation, networking equipment, point-of-sale systems, and medical devices.
Industrial and Manufacturing
Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) use the standard to connect to other modules, Human-Machine Interfaces, robots, and more for data exchange and control.
The same also works with machinery for communication and automated control in industries. This includes CNC machines.
The same can also be used for data acquisition by connecting sensors and instruments to collect and monitor data in factories.
Networking and IT
Networking equipment comes with this type of connection for the setup, configuration, and troubleshooting of the routers, servers, and switches.
Connecting to older equipment is possible with such a port if the equipment lacks USB or Ethernet.
Point-of-Sale and Retail
If you need to connect peripheral devices such as barcode scanners, receipt printers, and cash drawers to a POS terminal, then this port or interface would work great.
Medical, Aviation, and Scientific
The RS 232 interface can find use in scientific and lab equipment. This includes data transfer and analysis. The same works great for medical devices for data transmission and integrating with other devices.
RS-232 Connector Types
You will come across two main RS-232 connectors in the market. They are categorized based on the number of pins. We have the DB-25 (25 pins) and the DB-9 (9 pins).

DB-25
This is what was specified in the original RS-232 standard. It worked quite well for a wide range of applications. Right now, it can only be seen in older equipment.
As you already know, it features 25 pins, but only a subset of these pins is used in standard signalling. The other pins are reserved for specific functions.
DB-9
It is smaller than the DB-25 type, considering it only has 9 pins. You will find such a port on modern computers and devices such as sensors, modems, and printers.
Even though it only has 9 pins, it still carries the same signaling information as the DB-25. This makes it compact while achieving the same functionality as the original standard.
RS-232 Pinout and Wiring
The RS-232 pinout table helps you understand what each pin can do in a connector or pin.
DB9 Pinout
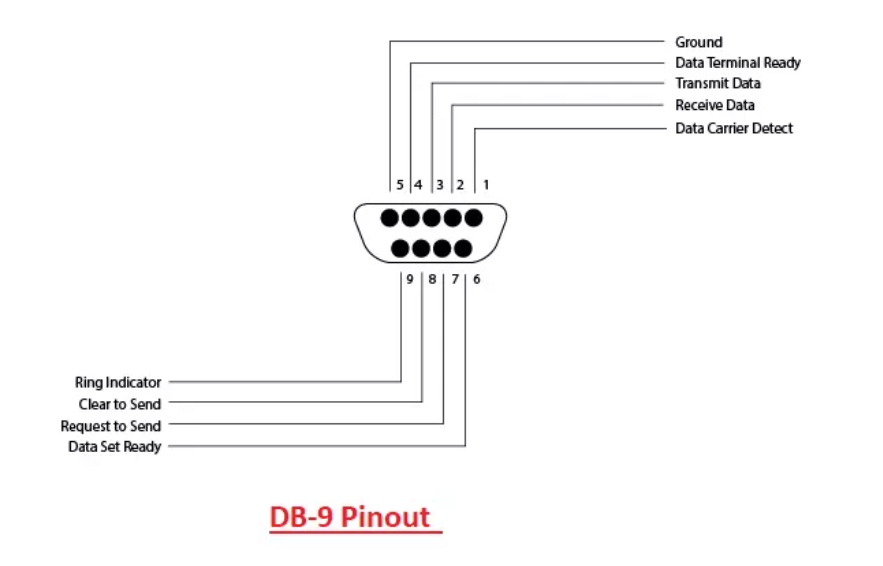
| Pin Number | Signal Name | Description |
| 1 | DCD | Data Carrier Detect |
| 2 | RXD | Receive Data |
| 3 | TXD | Transmit Data |
| 4 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | DSR | Data Set Ready |
| 7 | RTS | Request to Send |
| 8 | CTS | Clear to Send |
| 9 | RI | Ring Indicator |
DB25 Pinout
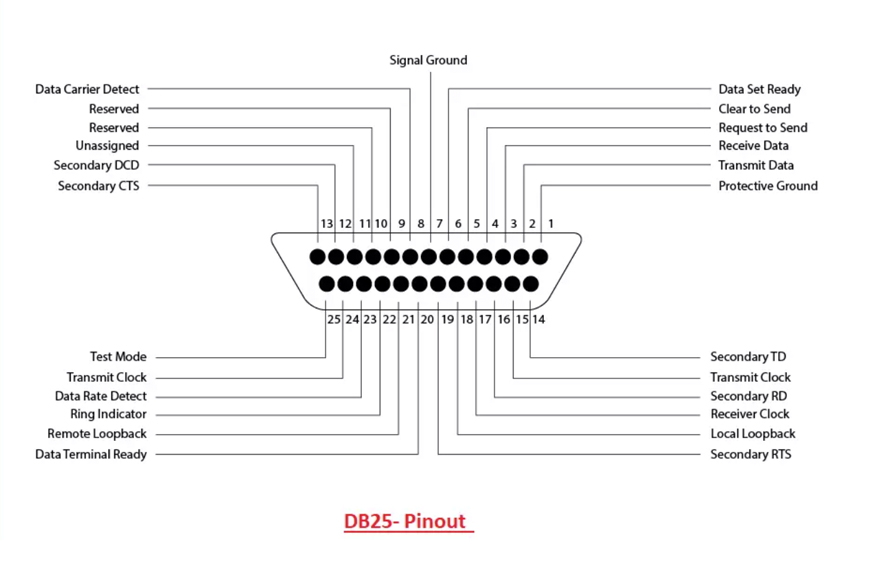
| Pin | Signal Name | Description |
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | TXD | Data Transmission |
| 3 | RXD | Receive Data |
| 4 | RTS | Request to Send |
| 5 | CTS | Clear to Send |
| 6 | DSR | Data Set Ready |
| 7 | GND | System Ground |
| 8 | DCD | Carrier Detect |
| 20 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready |
RS-232 Cable Length and Signal Integrity
The recommended maximum length for a RS 232 cable is 50 feet or 15 meters. Shorter cables support higher data rates. Signal integrity may be compromised over long distances because of several factors.
Here are the factors that affect signal integrity:
- Cable capacitance: The total capacitance of the cable, including the connectors. This value should not exceed 2500 pF for reliable communication. A longer cable often results in higher capacitance.
- Data rate: The data speed and cable length are inversely proportional. The standard speed for a 15-meter cable is around 9600bps, but at higher speeds, the length needs to decrease significantly.
- External noise: RS-232 is a non-balanced, single-ended signal. This makes it susceptible to electrical noise, especially over long distances. Shielded cables help a lot in mitigating this problem.
- Cable Quality: Using a low-capacitance cable is only one factor; overall cable quality also affects performance. So make sure you always use your cables from top brands known for making the best cables. Being shielded even makes it better.
RS-232 Converters and Interfaces
RS-232 converters and interfaces are vital for enabling communication between devices with different RS-232 interfaces.
Common types of RS-232 interfaces include:
RS-232 to USB Adapter: This is a simple cable adapter that allows modern computers with USB to communicate with older devices that use the RS-232 serial interface. This is mostly a plug-and-play solution that works on various operating systems.
RS-232 to RS-485: This converter translates the RS-232 signals to and from RS-485 signals. This makes it possible to work with long-distance applications. Also, multi-drop communication is enabled, unlike the point-to-point nature of the RS-232 interface.
RS-232 to Ethernet: These RS-232 connectors connect the RS-232 serial interface to a local area network. The adapter converts the RS-232 data into Ethernet packets. A good use for such adapters includes working with sensors, industrial equipment, and other serial devices.
RS-232 to TTL: This is another key interface for devices such as microcontrollers and other digital circuits. The converter converts the RS-232 voltage signals to Transistor-Transistor Logic levels. This is essential for devices that use lower-voltage logic than the RS-232 standard.
RS-232 vs. Other Standards
The RS-232 interface does its job well, but how does it compare to other options on the market? We will look at such comparisons below to help you learn more.
RS-232 vs RS-485
| Feature | RS-232 | RS-485 |
| Communication Method | Single-ended. Has a single wire for data and a common ground wire. | Uses two wires for data. Logic gates are determined by the voltage difference between these two wires |
| Distance | Up to 50 feet | Up to 4000 feet |
| Noise immunity | Poor | High |
| Topoloty | Point-to-point | Multi-point |
| Duplex | Full duplex | Half-duplex |
| Speed | Up to 1mb/s (decreases with distance) | Up to 10 mb/s ( over short distances) |
RS-232 Vs USB, Ethernet, and Bluetooth
| Feature | RS-232 | USB | Ethernet | Bluetooth |
| Communication type | Wired serial data | Wired serial data | Wired network | Wireless network |
| Speed | Low | High to very high | High to very high | medium |
| Range | Short | Very short | Long | Short |
| Topology | Point to point | Point to point | Networked | Networked |
| Power delivery | No native power delivery | Yes, provides power to devices | No | No |
| Interference | Prone to electrical noise | Susceptible to noise, but better than RS-232 | Robust, but depends on cable quality and shielding | Prone to radio frequency interference |
| Applications | Legacy industrial equipment | Modern peripherals such as keyboards, printers, and mic | Local area networks, internet access | Wireless headsets, speakers, and short-range devices |
RS-232 Troubleshooting
You may experience a few issues with the RS-232 interface. Below are possible solutions you can consider:
- Check the physical connections and cables
Ensure all cables are securely connected. Check both ends where the cables are plugged in.
Check the pin connections as well. The connector allows you to connect the device correctly, ensuring it works properly.
Check for shorts or damage. Sometimes, broken wires, damaged connectors, and other physical defects in the cable can cause shorts.
- Verify the communication settings
You are advised to match the baud rate, data bits, stop bits, and parity bits. These settings should be identical on both the receiving and transmitting devices. Most common settings include 9600 baud, 1 stop bit, no parity, and 8 data bits.
Some devices may come with default settings that should be changed before they work correctly. Consult the device manual to confirm the settings are done right.
- Perform advanced tests
Perform a loopback test to evaluate the device’s performance. This test checks if the port is receiving and transmitting correctly.
Sometimes you can swap the TX/RX pins to see if it resolves the issue.
- Troubleshoot power and software issues
Check that both devices are powered and are using a stable power supply. Sometimes devices may disable the RS-232 port if they are in a power-saving mode.
Restart the system to fix potential software glitches. Also, make sure you are using the appropriate software that is compatible with the device and the communication protocol.
Conclusion
The RS-232 is one interesting interface right now. It is common on legacy equipment, but still remains key for some equipment. That is why you can come across converters and adapters that allow such devices to communicate and send data to modern equipment. If you ever come across an RS-232 port that needs troubleshooting, we have given you tips to consider above. Always make sure the cables are well secured for a reliable performance.
Video: What is RS232 and What is it Used for?
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is RS-232 still relevant today?
The RS-232 port may still be relevant today. The interface is primarily used in industrial and commercial applications where you need simplicity, reliability, and compatibility with other legacy equipment.
What is the RS-232 pinout?
The pinout diagram shows the arrangement of the pins in the connectors and their functionality in any setup.
Is there a difference between the RS-232 and RS-422?
Yes, the RS-232 uses single-ended signaling and works with short cables. The RS-422 uses differential signaling, which is better for long-distance transmissions and higher speeds. The RS-422 interface can communicate up to 1200 meters and can support one transmitter and multiple receivers.