Loudspeaker: Components, Working Principle and Types
Author:admin Date: 2025-12-16 08:23 Views:175
Introduction
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer used for converting electrical audio signals into audible sound waves. The whole process relies on the principles of electromagnetism to generate the physical vibrations that move the surrounding air. This is what our ears perceive as sound.
You can think of the loudspeaker as the final link in the sound reproduction chain. It performs the opposite function of a microphone, which converts the sound waves into electrical signals.
Loudspeakers are essential in many applications. That is how you will come across them in home audio systems, professional audio systems, portable audio, and industrial or commercial audio.
Key Components of a Loudspeaker
The various components of a loudspeaker work together, using electromagnetism, to convert an electrical audio signal into sound waves. Here are the key elements of the loudspeaker.
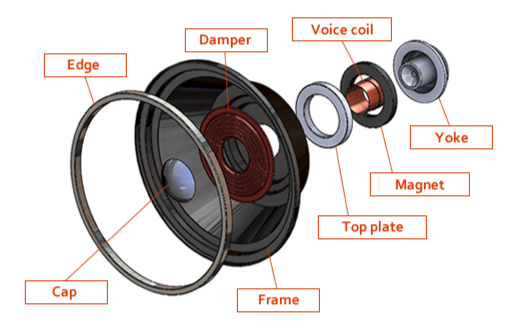
Cone (Diaphragm)
The cone is the primary vibrating surface. It is responsible for moving air, which results in sound waves.
The cone is made from lightweight and semi-rigid material. Examples of materials include paper, plastic, or metal. These materials move in and out with precision to give the right sound.
The size and material of the cone affect the speaker’s frequency response. For example, larger cones, such as those in wooders, handle low frequencies, or bass. The smaller cones, such as tweeters, handle high frequencies or treble.
Voice Coil
This is a coil of wire, which can be made of aluminum or copper, wound around a cylindrical former and attached to the narrow end of the cone.
Whenever an electrical audio signal from the amplifier is passed through it, the coil turns into a temporary electromagnet with a rapidly changing magnetic field.
Since the voice coil is what drives the mechanical motion, you can consider it as the speaker’s heart.
Magnet
This is a powerful permanent magnet surrounding the voice coil. Its job is to provide a constant, static magnetic field for the voice coil to interact with.
The magnet’s permanent magnetic field and that of the voice coil interact to produce a force that moves the voice coil back and forth rapidly.
Surround
The surround is a flexible ring of material that connects the cone’s outer edge to the frame of the speaker. It can be made of foam, rubber, or treated fabric.
The surround’s role is to make the cone’s back-and-forth movement easier. Also, it centers the cone to avoid any side-to-side movement.
It is also part of the suspension system, along with the spider, to ensure linear, controlled motion.
Cabinet or Enclosure
The cabinet is the box or the enclosure that houses the speaker driver. Its job is to hold all the components together.
Note that the cabinet’s design is crucial to the speaker’s overall performance. Its primary acoustic function is to manage the sound waves produced by the cone at its back. Without the cabinet, the backward waves would cancel out the desirable forward waves.
You can come across different designs of cabinets. For example, you have the sealed or bass-reflex design, which enhances specific frequencies and prevents distortion, improving sound quality and efficiency.
How Does The Loudspeaker Work
A loudspeaker converts electrical audio signals into physical air vibrations. That is how we end up hearing a sound. The whole process is based on the motor effect. Here is how the loudspeaker works, step by step:
- Electrical input
An amplifier sends a rapidly fluctuating alternating current (AC) electrical signal through the speaker wires to the voice coil.
- Magnetic field generation
When current flows through the voice coil, it makes the coil a temporary electromagnet. The polarity and strength of the magnetic field change constantly with the input audio signal.
- Interaction and force (motor effect)
The speaker’s voice coil is suspended in a strong, fixed magnetic field generated by the permanent magnet. When the voice coil’s fluctuating magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnet’s magnetic field, a force is generated, leading to rapid repulsion and attraction.
- Mechanical movement
This magnetic interaction forces the voice coil to move rapidly back and forth in a piston-like motion. There is a flexible suspension system that keeps the coil centered and ensures it moves smoothly along the magnet’s axis.
- Air vibration
The voice coil is attached to the cone or diaphragm. As the voice coil moves, the cone also moves with it. This pushes and pulls the surrounding air molecules. So, you end up with areas with high pressure and low pressure, which propagate outward as sound waves.
- Audible sound
These pressure waves travel through the air to someone’s ears. They vibrate the eardrum, which converts them into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound.
Types of Loudspeakers
Loudspeakers are quite diverse in terms of the types available. Below, we look at the various categories of the loudspeaker to find the right one for your application.

Based on Technology
Different technologies offer unique advantages in fidelity, frequency response, and efficiency. Here are the common types.
Dynamic Loudspeakers
This is the most common type in the market. The loudspeakers use a voice coil suspended in a magnetic field attached to a cone. When current flows through the coil, a magnetic force acts on the cone, making it move back and forth. This produces the sound waves.
Electrostatic Speakers
These come with a thin, charged plastic diaphragm suspended between two metal grids. When the audio signal is applied to the grids, a varying electrostatic field is formed. This field pushes and pulls the diaphragm to generate sound. These speakers have exceptional clarity and detail, but they can be expensive, large, and may not deliver the best bass response.
Planar Magnetic Speakers
These speakers have a thin, flat diaphragm with a conductor embedded or attached to it. The diaphragm is suspended within the magnetic field that is created by the permanent bar magnets.
These speakers offer excellent transient response and clarity. They often serve as a middle ground between the dynamic and electrostatic speakers.
Horn Loudspeakers
These couple a driver to a flared horn. The horn’s purpose is to amplify the sound the driver mechanically produces. This is done by coupling the driver’s output to the air, which significantly increases efficiency and directionality.
Expect to come across these speakers in public address systems and stadiums as they can project sound over large distances.
Ribbon Speakers
These come with an extremely thin strip of metallic ribbon suspended between powerful magnets. The ribbon acts as both the diaphragm and the conductor. This keeps it moving directly in the magnetic field.
Ribbon speakers are known for their incredibly fast response times and extended frequency response, making them ideal tweeters in high-end audio systems.
Based on Usage
These loudspeakers are designed to suit a specific consumer need and environment.
Bookshelf speakers
These are compact speakers designed to be placed on a shelf, table, or stand. They are quite popular for small rooms or for secondary listening areas. They often require a separate amplifier.
Tower/Floorstanding loudspeakers
Large, tall speakers designed to stand on the floor. They will often have multiple drivers in one cabinet. This provides full frequency range and will offer more powerful and room-filling sound. They are the best for large home theaters.
Soundbars
These come with a long spender enclosure that combines multiple speakers into a single unit. They are designed to sit beneath the TV. You can take them as an easy and effective upgrade to TV audio quality and also simulate surround sound.
Subwoofers
Subwoofers are specialized speakers that reproduce the very low frequencies or bass. They are mostly large drivers within a dedicated enclosure. They are used in conjunction with other spears for adding depth and impact to music and movies.
Portable Bluetooth speakers
These are compact, battery-powered, wireless speakers which connect to devices via Bluetooth for on-the-go music.
Outdoor loudspeakers
These speakers are built with weatherproof materials to withstand the elements such as rain. UV rays, and temperature changes. You can use them for providing sound for patios, pool areas, and gardens.
Active vs Passive Loudspeakers
The main difference between the active and passive loudspeakers is the location of the power amplifier. In active speakers, the amplifier is built into the speaker cabinet, making it be an all-in-one solution. As for passive speakers, they require a separate, external amplifier or AV receiver to operate.
Active Loudspeakers
The active speakers are also known as powered speakers as they incorporate the amplifier and other key electronics such as active crossover and a digital signal processing unit in the speaker enclosure.
Pros
- Offer great simplicity
- Have optimized performance
- Many come with additional inputs and connectivity options
- Expect a more compact unit due to build-in electronics
Cons
- Since it is a closed system, there is limited upgradeability
- Repairing is not easy as you may need to open the whole cabinet for single component
Passive Loudspeakers
The passive speakers are the traditional speaker system when it only has the drivers and a passive crossover network in the cabinet. They rely on the external amplifier to boost the audio signal.
Pros
- Having separate component allows for flexibility and customization
- These speakers are lighter and easier to install in walls or ceilings
- Having fewer complex electronics also means they can last for longer
- Expect to gte a wider selection for such speakers in the market
Cons
- Setting up a passive system is complex as it needs matching between the speakers and amplifiers
- The system would need more components and cables taking up more space
How to Buy a Loudspeaker
Buying loudspeakers requires a proper balance of understanding the specific use of the speaker, the room acoustics, budget, and other key technical specifications. Here is how to choose the right loudspeaker.
Intended Use
Make sure you decide based on the speaker’s primary function. A portable Bluetooth speaker is for outdoor use will have different requirements compared to the floorstanding speaker meant for a home theater.
Room Size and Acoustics
A large room will need more powerful speakers to fill the space effectively. As for a small room, using the compact bookshelf speakers is better to avoid overwhelming the space with sound.
Also, the room surfaces and available spaces available for placement.
Budget
Set a realistic budget, however, you can still be flexible in case there is a higher-priced model offering all the features you are looking for. Always budget for potential additional components such as quality cables, amplifier, or receiver.
Match Components
Decide whether you want active speakers or passive speakers. Also look at the power handling capabilities. This indicates how much continuous power the speaker can handle without damage. Match it with your amplifier’s power output.
Listen with Familiar Music
It is important to trust your ears by listening to music you know well so that you can judge it better. Look into the clarity, soundstage, and balance.
Read reviews as well. Check out professional and user reviews about the loudspeaker so that you can choose the highly rated options in the market.
How to Maintain, Troubleshoot, and Repair Loudspeakers
Maintaining, troubleshooting, and repairing loudspeakers help ensure the speakers last long and offer optimal performance.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance focuses on preventing common environmental and electrical issues which may damage the loudspeakers. Here is what you can do:
- Regular cleaning is important. Dust is a major energy. Make sure to use a soft, dry cloth or a soft brush to clean the cabinets and speaker cones. Avoid using harsh chemicals which can damage the wood finishes or speaker surrounds.
- Environmental control is also important. Keep the speakers away from direct sunlight, heaters, and fire sources. This is to prevent overheating, which damage the voice coils.
- Humidity is also a big enemy to speaker durability. Make sure to store or place speakers in a dry, climated-controlled environment. Too much moisture leads to corrosion and deterioration of the foam surrounds.
- Plug the active speakers or amplifier into high quality surge protectors. This is to protect them against power surges. For the passive speakers, ensure the amplifier’s power and impedance ratings match with the speaker’s specifications.
- Inspect the wire connections to ensure they are secure. The last thing you want is loose connections which cause intermittent sound, short circuits, and crackling.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Symptom | Causes | Troubleshooting |
| No sound | Muted settings Loose cablesWrong input sourcePower off | Check the volume controls Confirm that the power cords are plugged in and secureMake sure you are using the corrent input source |
| Distorted or funny noise | Loose connections Physical damage to voice coil or coneAmplifier clippingElectrical interference | Check if the speaker cone has tears or loose partsPush the cone in gently A scraping sound indicates the voice coil needs requireCheck for loose cables |
| Low volume | Incorrect audio settingsInefficient speakerPlacement issues | Ensure all the volume levels are turned up moderatelyCheck equalizer settings for the right balanceVerfiy the speaker placement is not muffling sound. |
| Humming or Buzzing | Ground loop issuesFaulty cables Electrical interference | Ensure all the components are protected via a surge protector Use different cables or audio isolation transformer to help reduce interference |
Conclusion
Loudspeakers remain critical components in our lives as we continue to listen to music and other types of sound. You can expect tiny speakers to massive stadium loudspeakers. What is important is that they operate using the same principle. If you are going to buy one, make sure to keep in mind the factors mentioned above. This is to ensure you always get high quality loudspeakers in the market.
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main parts of a loudspeaker?
A loudspeaker contains parts such as the cone, voice coil, magnet, surround, spider, basket, crossover, and enclosure.
What does speaker impedance mean?
Impedance indicates the electrical resistance a speaker presents to the amplifier. It is measured in ohms. It is important to do impedance matchings to prevent amplifier overload and ensure there is optimal performance.
What is loudspeaker sensitivity?
Sensitivity is the measure of how loud a speaker gets with 1 watt of power at 1 meter. It is measured in decibels. Having higher sensitivity speakers means more efficiency and needs less power to achieve the high volume levels.