The Ultimate Guide to USB Cables: Types, Speeds, Versions, and Applications
Author:admin Date: 2025-07-23 10:25 Views:676
- Introduction
- Anatomy of USB Cables
- How USB Cables Work
- Types of USB Cable Connectors
- USB Versions and Speeds
- Common Applications for USB Cables
- How to Choose the Right USB Cable
- Troubleshooting USB Cable Issues
- USB Cable Care and Maintenance Tips
- Conclusion
- Video: Understanding USB Cable Types and Which One to Use
Introduction
How many times have you used a USB cable without even understanding what it means? Or that it has many parts that make up the cable? Today, we want to explore more about the USB cable, its anatomy, how it works, the types, and so much more. We will make this guide as informative as possible about USB cables. Let us dive in.
A USB cable stands for Universal Serial Bus, and it is a common cable used for connecting different electronic devices for power delivery and data transfer.
That is why you can come across USB to USB cable, USB C to lightning cable, USB printer cable, and others. The applications are endless, so long as there is a USB port, you have a use for it.
We can see how it is possible to connect devices such as computers, smartphones, and accessories to share information or charge them.
Anatomy of USB Cables
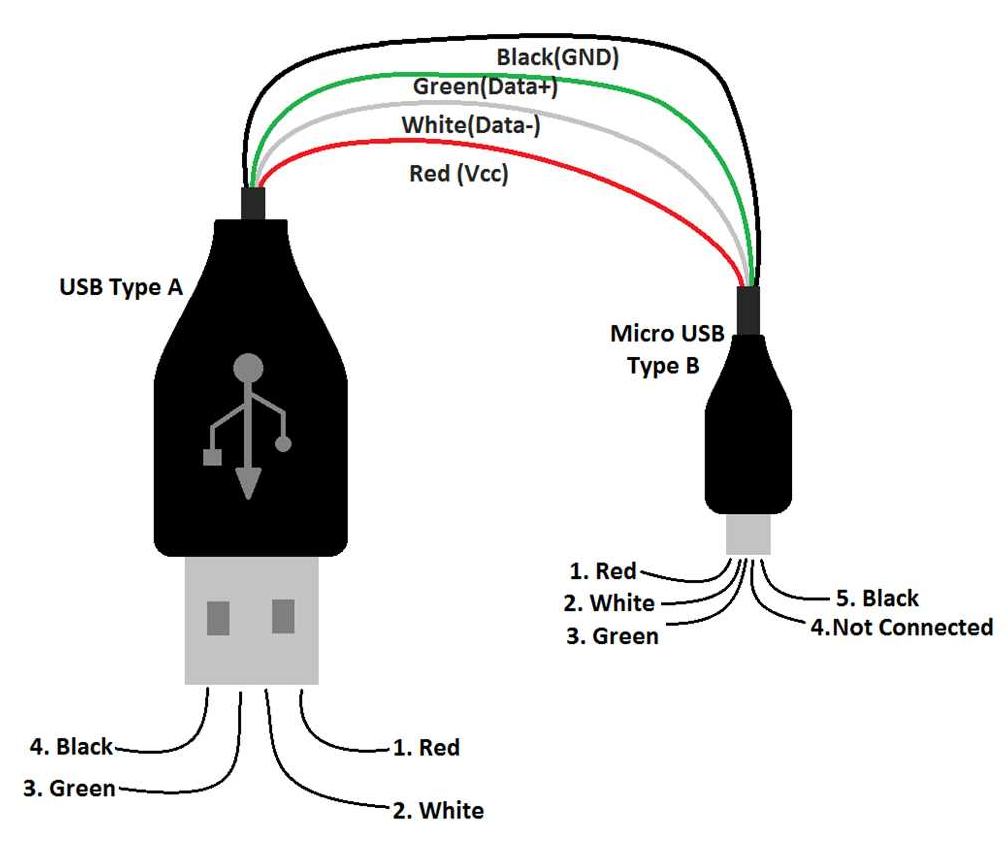
To better understand how USB cable types work, we have to look at the anatomy. A USB cable consists of connectors, conductors or wires, and an outer sheath.
Outer Sheath
Like most cables, the USB cable has a flexible layer made of durable rubber or plastic to protect the internal wires from bending, wear, and damage. Some premium cables have braided outer layers that offer additional strength and support.
Wires or Conductors
These are the wires that carry the data and power when the cable is in use. Manufacturers use copper to make these conductors since the material offers high conductivity.
The number of conductors largely depends on the type and version of the USB cable.
Power conductors are usually black or white and red in color. They deliver an electrical current to the connected device. The amount of power they can handle varies depending on the USB standard. For example, USB 3.0 delivers 900mA while USB-C can deliver more than that.
Data conductors are labelled as D- and D+. These wires are used for transmitting data signals. They are usually made of a twisted pair to help reduce electromagnetic interference. As such, you end up with a reliable data transfer process.
Connectors
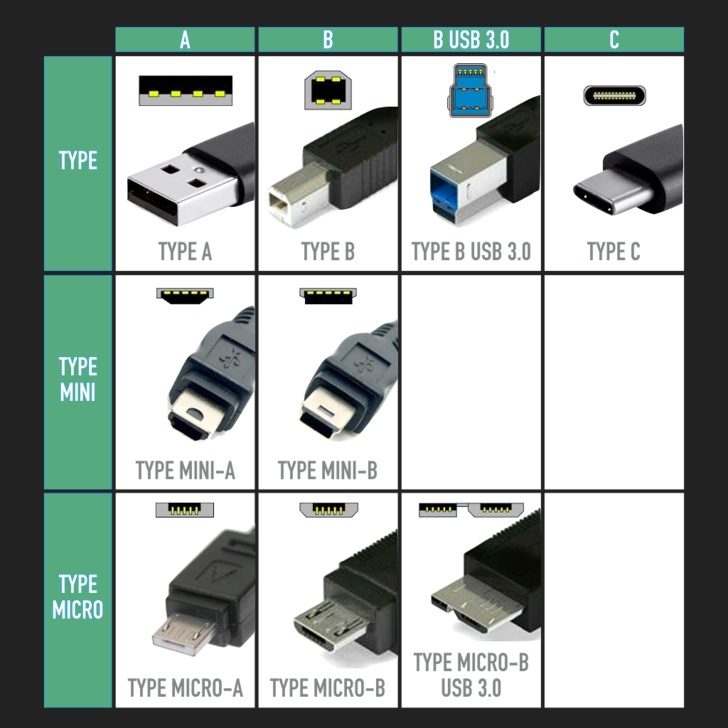
This is where you will come across USB-A, USB-B, and USB-C types of cables. The aim of the connector is to connect one device to the other. It also determines which devices can work with a cable.
The Type-A cable is an older connector commonly found on computers and chargers. We also have the Type-B connector, which is common in peripherals such as printers. Type-C is the latest standard that allows for supporting higher data transfer speeds and more power delivery.
How USB Cables Work
We have already established that USB cables are used for both data transfer and power delivery. We shall look at how this works.
Data Transfer
USB cables have two wires dedicated to data transfer. They can be green and white or sometimes a twisted pair for transmitting data bits.
The difference in voltage between the two wires represents binary bits and allows for digital data transmission.
The different USB versions have different data transfer speeds. The transfer speed is measured in Megabits per second.
Power Delivery
Yes, USB cable types are used for carrying power necessary for charging devices or powering peripherals. The red and black wires are used in this regard. The red is the positive wire carrying about 5 volts while the black wire serves as the negative or ground wire.
Modern USB stands can deliver much higher power compared to earlier generations. They can deliver high power of up to 100W for fast charging of laptops, smartphones, and other related devices.

Types of USB Cable Connectors
The USB connectors are important for determining which devices can work with a USB cable. Here are the main types you can expect to come across.
USB Type-A
This is probably the most recognizable USB connector. It is found on computers, hubs, and power adapters. This connector is characterized by having a flat and rectangular shape. Its design allows for only one orientation. Another thing to note is that this connector is backward compatible. This means older USB versions can work with the newer USB-A receptacles.
USB Type-B
These USB cable connectors have a slightly different design. It comes with slightly beveled corners and would be found on larger devices such as scanners, printers, and external hard drives. The design of this connector type is meant to offer a more secure connection compared to USB-A.
USB Type-C
This is the latest USB cable connector type. It is the most versatile thanks to its reversible design. This is where you can plug in the connector in either way. That is not the only advantage, as it also allows for high-speed data transfers and fast charging. The connector even allows for video signals. This connector is quickly becoming a standard for many devices. They are readily available on devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
Mini-USB
These are smaller versions of USB-A and USB-B connectors. They work based on the USB 2.0 standard. The aim was to have them on smaller devices such as MP3 players and digital cameras. They are still used for data transfer and charging devices as well.
Micro-USB
These USB cable connectors are smaller than the Mini-USB connectors. They are common in tablets, smartphones, and related portable devices. They are also able to support the USB 2.0 standard.
USB Versions and Speeds
USB technology has evolved a lot over the years ever since its introduction in the late 90s. Below are the USB versions and their speeds.
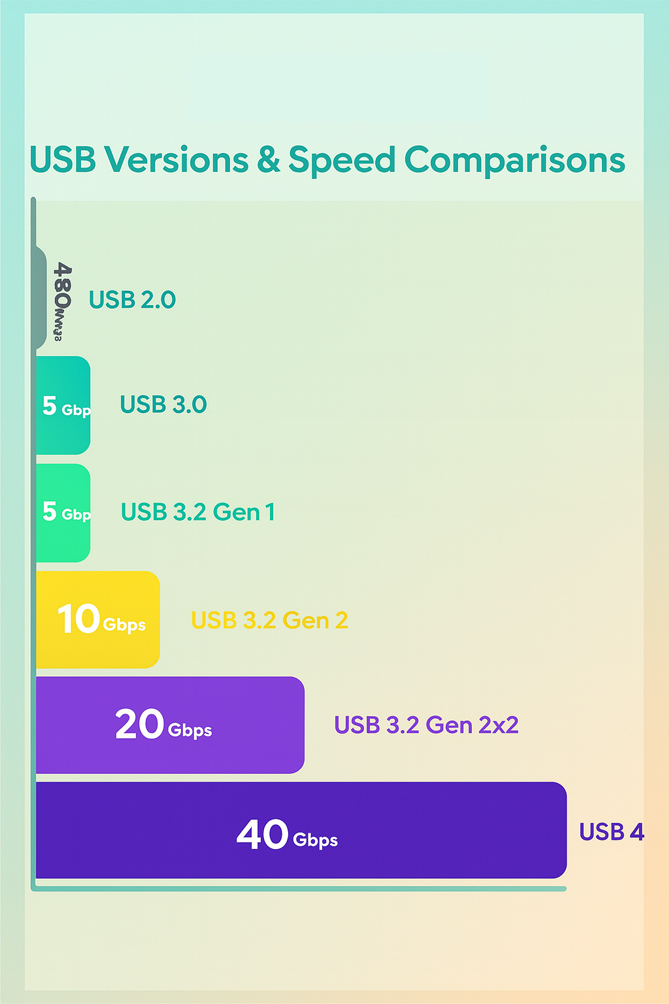
- USB 1.0/1.1—This was the first version, and as expected, the speeds were not the best compared to modern standards. They have a transfer speed of 1.5Mbps for low-speed devices and 12Mbps for high-speed devices.
- USB 2.0 – This was introduced to replace the first generation with impressive speeds for the time. It could do up to 480 Mbps.
- USB 3.0/3.1 / 3.2—This is the third version that led to impressive improvements in data transfer speeds. The first generation could do up to 5Gbps, while the second and third generations could do 10Gbps and 20Gbps, respectively.
- USB 4- This is the latest USB cable version with very high speeds reaching 40Gbps. The best part is that it also supports other features such as protocol tunneling for USB, PCI Express, and DisplayPort. It also supports backward compatibility with USB 3.2 and USB 2.0 versions.
Common Applications for USB Cables
Cables such as USB-C to Lightning cable or printer USB cables are all important for various applications. Below, we look at more ways you would use a USB cable in everyday applications.
Data Transfer
USB cables can link computers to peripherals such as printers, external hard drives, scanners, and mice. This enables data exchange for applications such as printing, storage, and control.
Smartphones, cameras, and tablets also need USB cables to transfer photos, videos, and other files to computers or storage devices.
USB cables are also useful for connecting other devices, such as game controllers, digital cameras, and audio interfaces, to computers and related hosts for data transfer.
Charging
Just as the USB cable is useful for data transfer, it can also be used for charging devices. This applies to mobile devices such as tablets, laptops, and smartphones. We can also use the USB C charging cable for portable speakers, flashlights, and other battery-powered gadgets.
Peripheral Connectivity
You can also use USB cables to establish connections between computers and other devices, such as keyboards, webcams, and mice. Most of these devices have plug-and-play functionality.
USB cables can also connect audio interfaces such as MIDI controllers, video devices, and others. This is for facilitating both data transfers and charging.
How to Choose the Right USB Cable
You might be considering a USB to HDMI cable or any other type of USB, but you are not sure how to buy one. Below are tips to help you choose correctly.
Device Compatibility
Look at the connector type so that you can choose accordingly. You want to make sure that the connector type matches the device’s ports. This will allow for ease of connecting of the devices.
Data Transfer Speeds
Different versions of USB cables will have different data transfer speeds. Make sure that you choose based on the one that offers the best data transfer speeds. For example, USB 3.0 is preferred for faster data transfer speed. If your device can support the USB 4.0 standard, the better the speeds.
Charging Needs
Different versions of USB cables offer different charging capabilities. Some come with high power delivery, meaning they can charge devices faster. So, what kind of charging needs do you have? Also, just buying a fast charger does not mean your device will work with it. Make sure that it is able to support fast charging.
Durability
Make sure that you also consider the durability of a cable. The overall construction helps with understanding durability. In addition to the normal construction, some models come with reinforced connectors, sturdy materials, and braided exteriors. This is vital so that the cable can withstand frequent use and bending.
Cable Length
Choosing the right cable length is essential for ease of connectivity and functionality. This might make you feel like choosing excessively long cables. A standard length of up to 5m is recommended. Anything longer than that will lead to signal degradation and cause clutter as well.
Price vs Quality
It is important to balance price and quality. Sometimes, you might be looking to save so much that you end up with a poor-quality cable. We recommend looking at the cable type and comparing it to the value it offers. Reading reviews and brand reputation can help a lot in determining if the cable is good for your application or not.
Troubleshooting USB Cable Issues

Are you having issues with your USB cable? Here’s how to troubleshoot it and ensure it is in good condition or needs replacing.
Check the USB Cable and Ports
Examine the USB cable and ports for signs of damage such as bent pins, loose connections, or frayed wires.
Test the cable with different USB ports on the computer to see if it works. If it works, there could be an issue with the other port. If not, the cable might be faulty and needs replacing.
Trying different USB cables can help rule out if one is faulty or not.
Check the Connected Device
You may also want to check the connected device to ensure it is working correctly. For example, you can restart the device to see if it resolves the issue.
If you are using a computer, check with the device manager option to see if there are any errors with the device. Sometimes you need to update or reinstall drivers for the device to work with your computer.
USB Cable Care and Maintenance Tips
Caring for your USB cable is what will make it last longer. For example, gentle insertion and removal are highly recommended. This keeps the connectors in good condition and prevents bending.
When not in use, store the cables correctly as well. Keep them away from moisture and direct sunlight. We do not recommend wrapping them tightly. A cable organizer can help in storing them correctly.
Avoid sharp bends and kinks in the cable. This may damage the internal wiring and lead to potential cable failure.
As for cleaning, using a soft dry cloth to wipe the cable should do it. Avoid using harsh cleaning methods. Still, handle with care when cleaning.
Conclusion
USB cables are very common today and are used for important applications. We use them for transferring data and power delivery. As the USB versions continue to evolve, you can expect to find many other applications. One thing is for sure: if you invest in high-quality cables, they will give the best performance. Start by researching USB cables to find the right one for your applications. Regular inspections of the cable should help determine which one needs replacing where necessary.
Video: Understanding USB Cable Types and Which One to Use
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you use any USB cable for transferring data between devices?
No. It depends on the type of cable. Some USB cables are used for charging devices only and do not support data transfer. So, it is important to understand what the cable is designed to do before buying.
How do I know which USB cable works for my device?
Start by checking the device’s port as it will guide you on picking the right USB connector and version. Choosing the right version is important to ensure the cable performs as expected. For example, USB-C will do a better job for the best charging and data transfer speeds.
Why is my USB cable not working?
The USB cable may not be working for a number of reasons, such as a damaged cable, poor-quality connectors, internal wire breakage, or an incompatible version. Try using the cable on a different device or port to test if it works as expected. If the issue persists, you can replace the cable.


