What is a Zener Diode? Working Principle, Specifications, and Applications
Author:admin Date: 2025-07-21 03:51 Views:660
Introduction
A Zener diode is a type of specialized semiconductor diode that can conduct current in the reverse direction so long as a specific reverse voltage is achieved. This is unlike regular diodes, which can fail during reverse breakdown. Zener diodes will still operate safely while in the breakdown region. For this reason, voltage regulators and voltage references in electronic circuits are the common applications for Zener diodes.
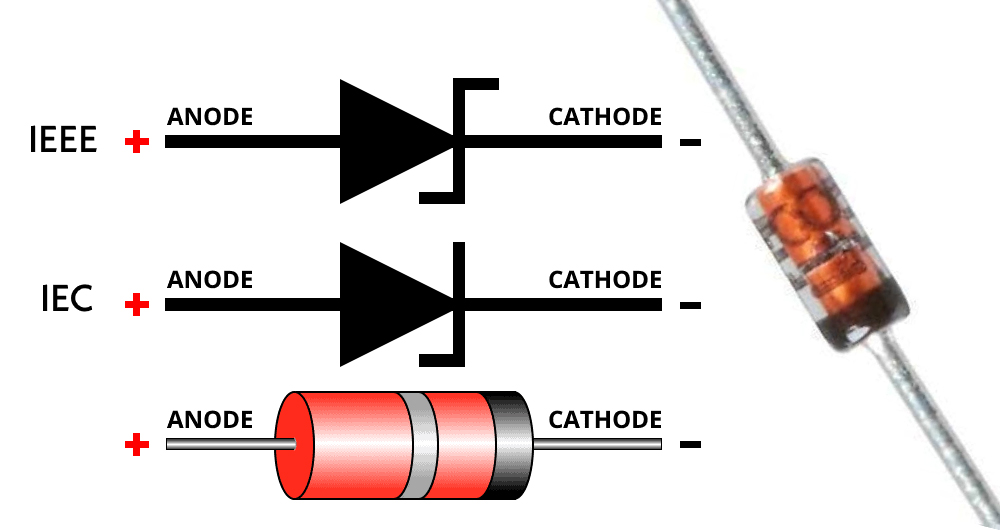
What Is A Zener Diode Made Of
Zener diodes are primarily made of silicon semiconductor. The Zener diode construction has a heavily doped P-N junction that has been designed to conduct current in the reverse direction whenever a specific voltage is achieved. The P-type and N-type regions are heavily doped with impurities so that you can have a very thin depletion region at the junction.
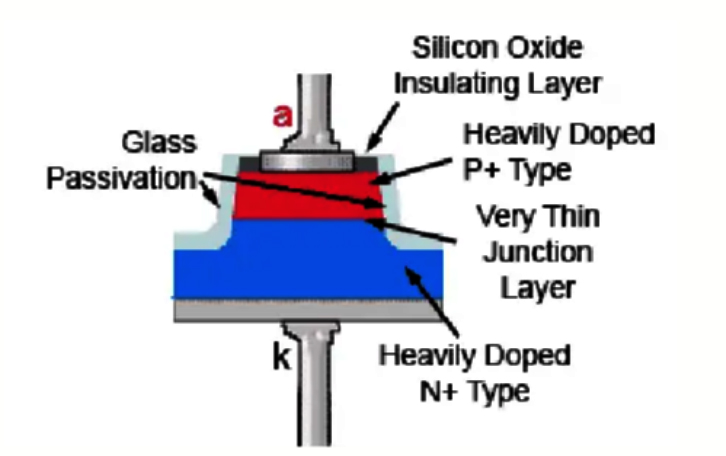
Construction of Zener Diode
Working Principle of a Zener Diode
By now, you already know what is a Zener diode. Next, we look at how the Zener diode works. A Zener diode works like a regular diode during the forward bias process. This is where a positive voltage is applied to the anode and a negative voltage to the cathode. It will conduct current once the forward voltage exceeds a certain threshold, which is usually around 0.7V.
Zener diodes also operate in reverse bias. In this case, the Zener diode behaves like a normal diode. This is where a small leakage current will flow through it until the reverse voltage reaches the Zener voltage. This leakage current is usually too small and will be ignored in most applications.
While still in reverse bias, the reverse voltage increases until it reaches the Zener voltage. This is when the diode enters the breakdown region. The diode allows more current to flow in the reverse direction while at the same time maintaining a constant voltage across the diode terminals.
The stable voltage is called the Zener voltage. It is determined by the diode’s doping concentration during the manufacturing process. You will also come across the Zener current in the breakdown region. This current in the Zener diode is limited by an external resistor. This is vital to prevent possible damage to the diode.
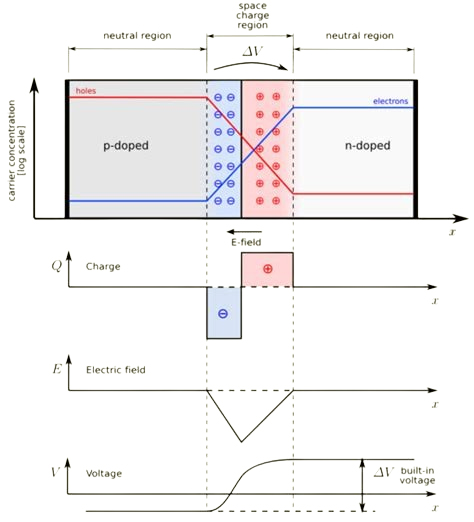
Key Characteristics of a Zener Diode
Before we look at what is a Zener diode used for, here are a few characteristics that guide its applications.
Zener Breakdown Voltage
The Zener diode will start to conduct more significantly at this voltage level. In case you were wondering what is breakdown voltage for Zener diode, this is it. Such a parameter is important to determine how the diode can be used for voltage regulation.
Reverse Breakdown Region
Still on what is a Zener diode and how does it work, we have the reverse breakdown region. In this case, it is a region where the Zener diodes operate well compared to regular diodes, which may fail. The Zener diode operates effectively in the reverse breakdown region so long as the reverse voltage is more than the Zener voltage.
Voltage Regulation
Voltage regulation is a core function of the Zener diode. We can consider it as the ability to maintain a stable voltage level when it is in the breakdown region. This is why the diode will be used in applications that require a stable voltage reference or for protecting circuits from voltage spikes.
Forward Bias Behavior
During forward bias operation, the Zener diode behaves like a standard diode, conducting current as long as the forward voltage exceeds a specific threshold.
Current Handling Capacity
Just like any other diode, it will have a maximum current rating. When you expose it to current more than this rating, then it could lead to damage to the diode.
Temperature Coefficient
A change in the Zener voltage can also change the temperature. Expect to find Zener diode manufacturers indicating the temperature coefficient of the diodes to indicate their sensitivity.
Zener Resistance
After learning about what is breakdown voltage of a Zener diode, another important parameter is the Zener resistance. Zener diodes have resistance or impedance in the breakdown region. This resistance affects how the diode performs in terms of voltage regulation, especially with varying currents.
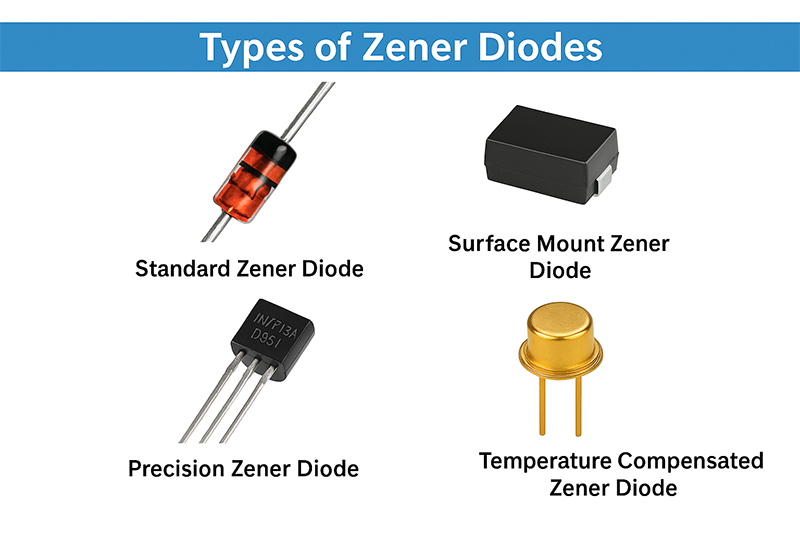
Types of Zener Diodes
Picking the best Zener diodes just got easier as we discuss the main types of Zener diodes. Here are examples.
Standard Zener Diodes – The standard Zener diodes are the most common on the market. We commend them for general-purpose voltage regulation. Expect them to be available for a wide range of voltage and power ratings. Many device manufacturers are likely to use such diodes in circuits where a stable reference voltage is necessary.
Surface Mount Zener Diodes (SMD) – These Zener diodes are the best for limited space applications. Examples include portable devices. Expect SMD diodes to be smaller than the regular Zener diodes.
Precision Zener Diodes – Are you looking for higher precision in Zener diodes? Then pick the precision Zener diodes. Their design allows for a high degree of accuracy and stability. Such features make them good for voltage regulation. Also, they are recommended for applications where tight voltage tolerances are necessary.
Temperature Compensated Zener Diodes – These diodes are designed to help minimize the effects of temperature changes based on the Zener voltage. As such, they can work quite well where temperature stability is important.
Applications of Zener Diodes
We have looked at what is a Zener diode and it is time to focus on what is the use of a Zener diode. Below are some of the applications you can expect to come across.
Voltage Regulation
How the Zener diodes work makes them the best choice for voltage regulation. These diodes can effectively maintain a stable output voltage in different types of power supply applications.
Zener diodes can deliver on the best voltage regulation as they conduct the excess current to ground. This is done so long as there is more voltage than the breakdown voltage.
Voltage Reference
Voltage reference is another reason for using Zener diodes. This is because they are able to provide the user with stable voltage and an accurate reference for several circuits. This includes analog-to-digital converters and operational amplifiers.
Overvoltage Protection
A Zener diode can be used as a safety mechanism for applications where overvoltage protection is needed. How is this done? The diode will clamp the voltage to a safe level depending on how you have set it up.
This type of working mechanism is vital for protecting sensitive components in the circuit from damage, especially from voltage spikes and surges.
Clipping Circuits
Still on what is a Zener diode and where is it used, we have clipping circuits. This is where the diode is used for limiting the amplitude of AC signals so as to prevent them from exceeding a certain voltage level or causing distortion.
Noise Reduction
Zener diodes can also be used in noise reduction. This is where they can help in suppressing high-frequency noise in various electronic circuits. This is possible as they can shunt the noise to ground.
How to Choose a Zener Diode for a Project
Let us say you want to work on a project using Zener diodes, then how would you choose one? Here are a few considerations to keep in mind.
Determine the Required Zener Voltage
This is important to identify so that you know its limitations and applications. The Zener voltage is key in determining the overall voltage a Zener diode can maintain or regulate in a circuit.
Calculate the Power Dissipation
Determine the maximum current that the Zener diode can handle under the worst-case scenarios. From the maximum current, it is possible to calculate power dissipation since you already know the Zener voltage.
Appropriate Power Rating
You are also supposed to select a diode with the right power rating that is higher than your calculated power dissipation above. This ensures you can prevent overheating and potential damage.
Consider Tolerance
Zener diodes also come with Zener voltage tolerance. It can be +/- 5%, which affects how the diode is used in the circuit. So, if the application requires precise voltage, it is recommended to get a Zener diode with a tighter tolerance.
Zener Diode Type
Consider the various types available to select the one that best suits your application’s needs, taking into account compatibility and performance. Additionally, the available mounting space can determine which type works best for you.
Temperature Effects
Zener diode performance can change based on the temperature. Look at the temperature coefficient of the Zener diode so that it can help determine the temperature range of the application.
Evaluate the Cost
Zener diodes are generally available at different price points. The one you choose should be able to work, but still within budget. Sometimes, it may be necessary to have a flexible budget to obtain the correct Zener diode for the application.
How to Troubleshoot Zener Diodes
The are a couple of ways you can troubleshoot Zener diodes to ensure they are working as expected. Here is what to do.
Visual Inspection
Start by looking for any physical damage to the Zener diode. Look for burns, cracks, or discoloration. If you come across visible damage, then the diode might be faulty and needs replacement.
Multimeter Testing
A multimeter can be used to test the Zener diode. Start by setting it in the resistance or ohm mode to test the diode’s performance in both reverse and forward bias modes. During the forward bias process, a good diode will show a low resistance reading. However, for reverse bias, we expect it to have very high resistance. If these two results do not match, it is best to replace the Zener diode.
Voltage Regulation Test
A Zener diode is designed to maintain a stable output voltage wherever it is used in a voltage regulator circuit. This remains true even with changes in input voltage or load current. Consider applying a varying input voltage or changing the load current and watching the output voltage.
If the output voltage fluctuates significantly, then the Zener diode may be faulty.
Conclusion
A Zener diode offers better performance while in reverse bias configuration than regular diodes. This makes it good for applications such as voltage regulation and many others. With that in mind, expect to come across it in many consumer electronics and industrial applications as well. If you plan to use it in a circuit design, we have highlighted key considerations. This ensures optimal performance, allowing the diode to function as expected. With troubleshooting steps also included, you will have an easier time working with Zener diodes.
Video: Zener Diodes
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the clamping voltage of a Zener diode?
The clamping voltage of a Zener diode is the voltage at which the diode starts to conduct current in the reverse direction while limiting the voltage across it to a specific value. Basically, when the voltage reaches the Zener voltage, it enters the breakdown region and starts to conduct, which prevents the voltage from rising further.
What is the impedance of a Zener diode?
This is also called the slope resistance or dynamic impedance. It is the resistance that the Zener diode offers in case there is a change in current flow when it is operating in the reverse breakdown region.
What happens when a Zener diode is shorted?
A shorted Zener diode works as a piece of wire. This means it can conduct in both directions with little resistance. The result is that it can lead to increased current flow in a circuit, which may damage other sensitive components or cause a fuse to blow.


