What is an Open Circuit? Definition, How It Works, and How to Test It
Author:admin Date: 2025-07-26 03:40 Views:825
- Introduction
- Role of Continuity in a Circuit
- Causes of Open Circuit
- Behavior Of Voltage And Current In An Open Circuit
- Importance of Intentional Open Circuits
- How to Detect and Test for Open Circuits
- Applications of Open Circuits
- Open Circuit vs Short Circuit: The Differences
- How to Prevent Unintended Open Circuits
- Conclusion
- Video: The Concept of Open Circuit
Introduction
An open circuit is a type of electrical circuit in which the path for electricity or current flow is broken. The path can be broken intentionally by using a switch or unintentionally because of a damaged wire or loose connection. Basically, an open circuit breaks the circuit’s continuity, which results in zero current flow.
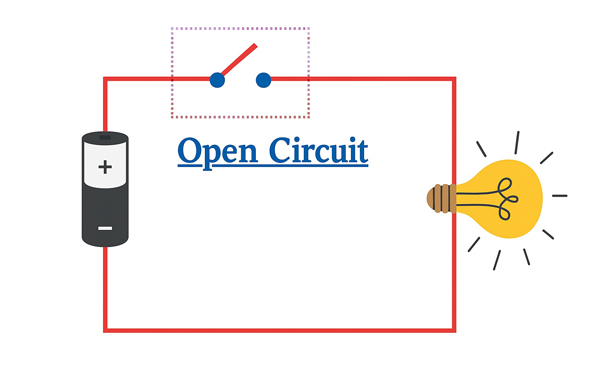
Is this something you would want? We look at more details about what is an open circuit, where you would use one, and how to test and detect unintentional open circuits.
Role of Continuity in a Circuit
Now that you know what is an open electrical circuit, next is to understand why continuity is important in circuits.
You have to understand that continuity means a complete path for the current flow. There are no gaps, interruptions, or breaks that inhibit the circuit’s conductive path. The path can be made of a PCB board with traces, wires, or components such as diodes or resistors.
The current flow in such a circuit is unimpeded. When the current flows, it will ensure that the electrical devices and circuits are operating as expected.
How do you know there is continuity in a circuit? Other than the device connected to the circuit not working, doing a continuity test is a better way of determining if the circuit is closed or open.
We do a continuity test by using a multimeter. If the multimeter beeps or shows low resistance, it means there is continuity. However, if there is no current, the multimeter will not beep, meaning it is an open circuit.
Causes of Open Circuit
Troubleshooting your circuit can be easier if you understand what is an open circuit fault reason. Below are some of the reasons you end up with an open circuit.
Component Failure
Broken wires, caused by age, physical stress, accidents, or wear and tear, can lead to open circuits. The same applies to blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers. These are safety devices that help prevent overcurrent by creating an open circuit.
Faulty switches that do not function as expected may lead to such issues as well.
Component damage, such as damaged resistors, transistors, and other electronic components, can fail, leading to an open circuit.
Physical Disconnections
Loose connections at the terminals, solder joints, or wire splices can lead to open circuits. This could be due to vibration or other reasons, making the connections not hold strongly.
Wire breaks can easily lead to an open circuit because of physical stress or damage.
Sometimes it can be an intentional interruption. For example, when you open a switch or circuit breaker as a deliberate way of creating an open circuit.
Manufacturing Defects
Manufacturing defects can occur depending on how the device is made. For example, etching issues in PCBs may lead to open circuits on the PCB board.
Some manufacturers also use substandard materials, which easily lead to open circuits. You would want to ensure the devices you buy are from top brands that assure you of the use of high-quality materials to prevent open circuits.
Behavior Of Voltage And Current In An Open Circuit
You might be wondering, what is the current in an open circuit? When there is an open circuit, the voltage source does not stop producing voltage. For example, a battery will still have voltage across its terminals, only that it is not connected to a load. This type of voltage is referred to as the open circuit voltage.
However, what about the current? Since there is a break in the circuit, electrons do not flow. As a result, there is no current in an open circuit. An open circuit is a state where there is a presence of voltage, but no electricity flow.
Importance of Intentional Open Circuits
Circuit breakers and fuses are some of the intentional open circuits we have. Having the ability to create open circuits when needed is core for these protective devices. Each time the current is past the safe limit, the circuit breaker trips or the fuse blows to ensure the excess current does not reach the sensitive device which might otherwise damage it.
Switches are practical ways of creating an open circuit when placed in the off position. It is intentional, as you may want to turn off lights if you are no longer using them.
How to Detect and Test for Open Circuits
When it comes to detecting and testing for open circuits, we can use a multimeter to help us understand what is happening in the circuit. This part answers the question what is the resistance in an open circuit, and how it can be measured. This is because we test for resistance in the circuit to find out if there is continuity or not.
Here is the process to follow:
- Power off the circuit and make sure it is de-energized before testing it.
- Set up the multimeter in continuity mode or resistance mode before you start testing.
- Connect the multimeter test leads to the appropriate terminals. Red goes to the positive and black to the negative or common jacks.
- In the case of continuity resting, place the probes on either side of the area where you suspect the break. It is the same process when testing for resistance.
- Interpreting the results is just as important. If there is continuity, there is a beep or low resistance reading, which indicates a good connection or closed circuit. If there is no beep or a very high resistance is recorded, it indicates an open circuit.
- If you are using resistance mode, a low resistance reading means a good connection, while a high resistance reading indicates an open circuit.
- If you are working with more complex circuits, it is best to use a logic analyzer or an oscilloscope to understand trace signals and identify breaks.
Applications of Open Circuits
Open circuits are important in many ways. Here is a quick list to help you understand situations where open circuits might be necessary.
1. Turning off devices
Open circuits can be useful in applications such as turning off devices. You would want that circuit open, for example, when you need to turn off the light.
Open circuits can also be used to control circuits as part of switching applications. You can now enable or disable parts of a larger circuit depending on which part you need powered.
2. Safety
You are likely to encounter fuses as safety devices that help protect devices in a circuit by opening the circuit. In this case, the fuse blows if the current exceeds a certain limit, leading to an open circuit vital for protecting the devices.
You can also have deliberate short circuits, which trigger an open circuit. For example, the crowbar circuits use this mechanism so that a circuit breaker comes in to open the circuit.
3. Troubleshooting and Maintenance
An open circuit can also indicate fault detection. It could be a broken wire or disconnected components. Once you identify the location of the open circuit, you can determine which repairs to make.
Open circuits can be used to isolate sections of the circuits for general repairs and maintenance.
Open Circuit vs Short Circuit: The Differences
An open circuit happens when there is a break in the electrical circuit path. It could be a broken wire, disconnected component, or the switch being in the off position. In this case, the current cannot flow because there is no path for it. The resistance, on the other hand, is extremely high.
Short circuits happen when a low-resistance path is created and bypasses the intended component in the circuit. The difference from open circuits is that in short circuits, a large amount of current flows through this unintended path since there is low resistance. For example, when you touch both terminals of a battery, it leads to a low-resistance path, thus short-circuiting it.
Looking at the two, you will see that an open circuit may not always be dangerous. It simply prevents a device from working correctly. However, short circuits are dangerous as they may lead to overheating, fires, or even damage to components.
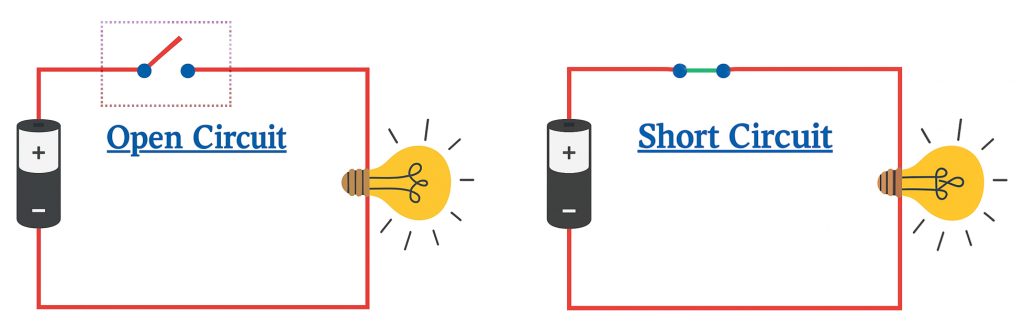
Here is a table comparing the two.
| Feature | Open Circuit | Short Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Infinite | Near zero |
| Current | Zero | Very high |
| Voltage | Supply voltage available | Near zero |
| Effect | No current flow | Has excessive current flow |
| Common Causes | A switch is open, broken wire | Faulty installation or component failure |
| Impact | No power for the load | Overheating and component damage |
How to Prevent Unintended Open Circuits
Now that you know what happens if there is an open circuit, we can examine steps to take to prevent unintended open circuits. Here is what to do.
- Make sure that all your wires and connectors are tightened correctly. Any loose connections can create resistance and lead to open circuits eventually
- You should also install circuit protection devices such as circuit breakers and fuses that prevent damage from short circuits and overloads
- Regular inspection of your wiring and components helps to identify signs of damage, such as burnt spots or fraying
- Proper handling and storage of PCBs is important to avoid scratching and damage to the components.
- If you are going to solder components, using a proper technique is important to ensure the best performance.
- Component testing might be necessary if you are unsure there is an open circuit. Use a multimeter to test for continuity.
Conclusion
Depending on the situation, an open circuit can be a good thing or an inconvenience. It is a good thing if you want to turn off the lights in a room. However, when the device suddenly stops working because of a broken wire, which leads to an open circuit, then it becomes an inconvenience. For that reason, you have to understand why you need an open circuit and when it is an issue that needs repairs before the device can start working again. We have discussed some tips to keep in mind above so that you can prevent unintended open circuits and keep using your devices.
Video: The Concept of Open Circuit
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is an open circuit different from a closed circuit?
In a closed circuit, the electrical path is complete. This means electricity can flow. However, in an open circuit, there is a break in that path resulting no current flowing in the circuit.
Is an open circuit dangerous?
An open circuit is not as dangerous as a short circuit. However, when it happens unexpectedly in essential systems, it can lead to other problems and may cause a bigger issue in your system. You
have to understand what is causing the open circuit to deal with it.
How can you test for an open circuit?
Using a multimeter in continuity mode can help with testing an open circuit. If there is an open circuit, the multimeter will not beep. However, the multimeter beeps if there is continuity.


