What is Radio Frequency? Expert Explanation into RF, Its Uses, and Types
Author:admin Date: 2025-05-08 02:18 Views:967
Applications such as transmitting TV signals can sometimes make you wonder how it is possible. The same applies to wireless networks such as Wi-Fi. It all comes down to the technology used in the transmission. In this case, radio frequency plays a big part in how devices communicate, radar for detecting objects, and more. You can already see how radio frequency bands are crucial for the performance of many devices around us. Let us learn more about radio frequency below to see how best to use it.
What is Radio Frequency?
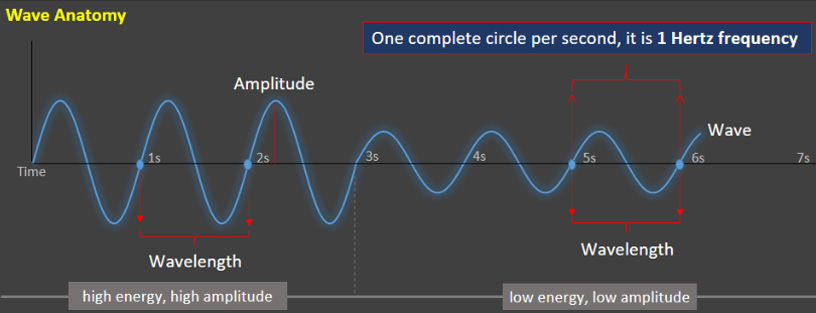
This type of electromagnetic wave frequency is used in radio communication and other uses. It typically has frequencies between 3KHz and 300GHz. Yes, radio frequencies are part of the electromagnetic spectrum, including microwaves, light, and infrared. The difference is the frequency range, which leads to this categorization.
Radio Frequency (RF) comes with many applications. This includes radio frequency identification, communication, wireless networks, radar, and more.
How Does Radio Frequency Work
Radio frequencies now have many applications, including radio frequency for skin tightening in addition to transmitting information from one device to another.
To understand how it works, we will consider using radio frequency to connect one device to the other.
1. Transmission
This includes the generation of the signal. This is done by a radio transmitter, which generates radio waves through oscillating electrical currents. They are then applied to the antenna for transmission.
The antenna radiates radio waves into space, allowing for transmission over a distance, depending on the type of antenna.
2. Reception
A receiver antenna captures these radio waves and then converts them into electrical signals.
The receiver features electronic circuits crucial for amplifying and filtering the signal. It is then demodulated so that the original information is extracted and displayed.
3. Modulation and Demodulation
These two are very important in radio frequency bands. Modulation means encoding information such as data or audio onto radio waves by changing their properties. For example, the amplitude of AM radio and the frequency of FM radio.
There is also demodulation. In this case, the receiver decodes the received radio waves by extracting the original information from the modulated signals.
Types of Radio Frequency Bands and Uses

Whether it is CB radio frequencies or radio frequency for facial, they all operate within a frequency band. This is what determines their classification. Below are the notable radio frequency bands and their applications.
Low Frequency
Frequency range: 30kHz to 300kHz
These are some of the most commonly used frequency bands. This is because the Earth’s ionosphere can reflect them. This property makes them good for long-distance communication.
You can use them for submarines in the military, RFID tags for access control, or low-frequency radio broadcasting.
Medium Frequency
Frequency range: 300kHz to 3MHz
Using a radio frequency detector shows how it operates in this frequency range, making the band quite versatile for many applications. It is popular mostly for wireless radio transmission, even though we have moved to higher frequencies now.
The adoption of this band was easier as it had a less complex antenna design but could still support many applications, including navigation systems, wireless communication, and other experimental uses.
High Frequency
Frequency range: 3MHz to 30MHz
This is also known as the short wave. The best part is that it can also be reflected by the Earth’s ionosphere, which means it is suitable for long-distance communication. This frequency band is mostly used in the aviation industry, government systems, weather broadcasting stations, and more.
Very High Frequency (VHF)
Frequency range: 30MHz to 300MHz
This frequency band has been used a lot in broadcasting. This includes TV and FM radio broadcasting.
Air traffic controllers and pilots also communicate using this band. Other uses include medical equipment such as MRI, military applications, and business radio stations.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF)
Frequency range: 300Mhz to 3GHz
This is probably the most critical band we use at the moment. It comes with a highly complicated design, but there are quite a few applications.
This technology is used in GPS navigation systems, pagers, Bluetooth, TV broadcasting, CDMA, LTE, 5G, and more.
Super High Frequency (SHF)
Frequency Range: 3GHz to 30GHz
This type of radio frequency band operates in a line-of-sight path. Suppose there are any obstructions, communication breaks. Expect to encounter it in 5G networks, satellite systems, and digital TV broadcasting.
System design is usually difficult for this type of frequency, and having a smaller wavelength does not help.
The frequency bands mentioned above are what you will come across most of the time. However, there are more bands that offer more applications for various devices we use in our lives.
Applications of Radio Frequency
– Everyday Applications
Communication is the biggest use of radio frequencies in everyday life. It is the foundation of telecommunication, which enables phones to work, Wi-Fi, radio and television broadcasting, and more.
– In Industrial and Consumer Devices
Consumer electronics such as wireless keyboards, mice, and remote controls all rely on radio frequency to function.
As for industrial applications, you can get radio frequency ID cards that are used to track inventory or offer access control.
RFID tags can also help collect data from industrial processes to optimize the industry’s production processes.
– In medical and Aesthetic fields
We have seen cases of radio frequency microneedling as one of the ways radio frequency is used in medical and aesthetic fields. Skin tightening and fat reduction are also some of the additional benefits of this technology.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is another application that utilizes radio waves to create a detailed image of the body.
RF ablation also uses radio frequency to treat various conditions, including pain, tumors, and heart arrhythmias.
– In Military and Aerospace
Radar systems can be used to detect objects, measure distances, and track objects. This is possible as these systems rely on RF waves.
You also get RF communication applications in the military. The difference is that this communication would be made as secure as possible.
Radio Frequency Safety: What You Should Know
Picture placeholder
Include an image showing the radio frequency safety
You may have head scenarios where someone complains about how radio frequency ruined my face. Well, it depends on the application and exposure that the person had to face before it led to such issues. Below are some notable radio frequency safety considerations.
- High radiation from radio frequency energycan lead to heat issues. This could damage tissue, cause burns, and sometimes affect the reproductive system.
- It is worth noting that there are limits to how much of these waves you can be exposed to. Regulatory bodies such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) have guidelines on the exposure levels to radio waves.
- High-power antennas often have signage and barriers that restrict access. These will have information to warn individuals about the risks of RF exposure and keep them away.
- Proper training is usually offered to those working regularly near the RF sources. There will also be equipment for monitoring the exposure levels. RF meters are good examples of devices for monitoring exposure levels.
- It is also advisable to increase the distance from RF sources to reduce the exposure and use proper shielding materials to block and minimize RF energy transmission.
Common RF Myths: Know the Truth
Whether it is radio frequency treatment or any other application, you may have come across many myths. Here are a few of them as we try to dispel them.
- High radio frequencies do not travel as far as lower frequencies
High frequencies may be affected by objects and environmental factors, but they can still travel long distances as well in free space. The range of the frequencies is determined by the environmental conditions, terrain, atmosphere, and signal strength.
- Encryption is what makes the RF signals invincible
That is not the work of encryption. The process of encrypting data simply protects it from unauthorized access. RF carriers will still intercept and transmit the signal to the necessary receiver.
- RF treatments are only for the face
A radio frequency machine can treat various conditions in different parts of the body. While facials are more common, the machine can also be used for other applications.
- 5G is a new technology that people do not fully understand
5G is built upon the principles of previous technologies such as 4G, 3G, and more. They all use the same type of electromagnetic radiation key to enable communication.
- Having more antennas makes a device better in performance
The number of antennas on a device is just one performance factor. You also need to consider the antenna quality, the design of the device, and environmental factors, which can determine the overall performance.
Challenges and Limitations of Radio Frequency
Radio frequency may also have limitations depending on the application. Below is what you can expect:
Interference
Radio frequency signals are vulnerable to different types of interference, including electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference. All these lead to the degradation of signal quality and reliability.
Propagation Issues
Conditions such as lightning and static can also interfere with the RF signals. This leads to propagation effects such as frequency shifting and fading. It may also affect the signal strength and availability.
Security
Without proper encryption, RF transmissions can be intercepted, thus making them vulnerable to eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
Design Complexity
Designing the RF ICs and other supporting systems can be complex, especially when dealing with high frequencies and integration. This may lead to longer development times and costs as well.
Thermal Management
High-frequency operations and high integration levels can lead to significant heat generation. You need the right thermal management processes to ensure performance and reliability.
Bandwidth Constraints
RF modules can offer good wireless communication, but they also tend to have bandwidth limitations. These can restrict how much data you can transmit. This limits radio frequency in cases of high data rates such as video streaming.
Conclusion
Radio frequencies remain important for many applications right now. Some people even search for radio frequency skin tightening near me to find help for their skin. As you can see, the technology has many applications in addition to communication, which is the most popular. As always, make sure you also follow guidelines to limit your exposure to radio waves to keep you healthy.
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a difference between RF and microwave frequencies?
Microwaves are a subset of radio frequencies, falling in the frequency range from 300MHz to 300GHz. So, microwaves are radio frequencies, but not all radio frequencies are microwaves because of the frequency range.
Is radio frequency safe for humans?
It all depends on the power level. Low-power radio frequencies, such as those used in consumer applications, are considered safe. However, continuous exposure to high-intensity RF equipment, such as industrial-grade machines, can lead to health implications.
Can radio frequency treatment be used in skincare?
RF treatment for skincare is possible. It is a noninvasive procedure that uses RF energy to heat the skin and stimulate collagen production. The result is reduced wrinkles and tightened skin.
Does RF treatment hurt?
No. Most people describe it as a slight discomfort because of the warm sensation. However, most devices now come with cooling mechanisms to help protect the skin.