KOSTENLOSE Lieferung für Bestellungen über HK$250.00

Schnelle Reaktion, schnelles Angebot

Blitzversand, keine Sorgen nach dem Verkauf

Originalkanal, Garantie der authentischen Produkte
IB100
The IB100 optical encoder sensor is perfect for accurately detecting position in motion control systems. It gives you high resolution for precise position feedback and control. With its quadrature output, you get A and B channels to detect direction and speed, making it great for measuring rotation. The compact design makes it easy to fit into tight spaces, while its durability ensures reliable performance in tough industrial environments. Plus, it’s energy-efficient, consuming minimal power during use. If you need to reset or calibrate the system, the optional Z-channel index pulse provides a zero-position reference.
IB100 Encoder Sensor Pinout

| PIN-Nummer | Pin-Name | Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vcc | Power supply pin (typically 5V or 3.3V, depending on the application) |
| 2 | Masse | Ground pin |
| 3 | A (Output) | A channel output (usually a square wave, for encoding position) |
| 4 | B (Output) | B channel output (quadrature signal for position decoding) |
| 5 | Z (Output) | Z channel output (optional, for indexing or zero reference pulse) |
| 6 | Vout | Voltage output pin, used for some models to send analog signals |
The Vcc and GND pins power the sensor, while the A and B outputs provide the quadrature signal for determining the direction and position. If the Z pin is available, it gives a unique index pulse to help with precise referencing. When wiring this encoder, connect the outputs to the correct inputs on your microcontroller or decoder. It’s also important to keep the signal cables as short as possible. Longer cables can weaken the signal, affecting performance, so minimizing cable length is a good practice for better results.
IB100 Equivalent Hall Encoder
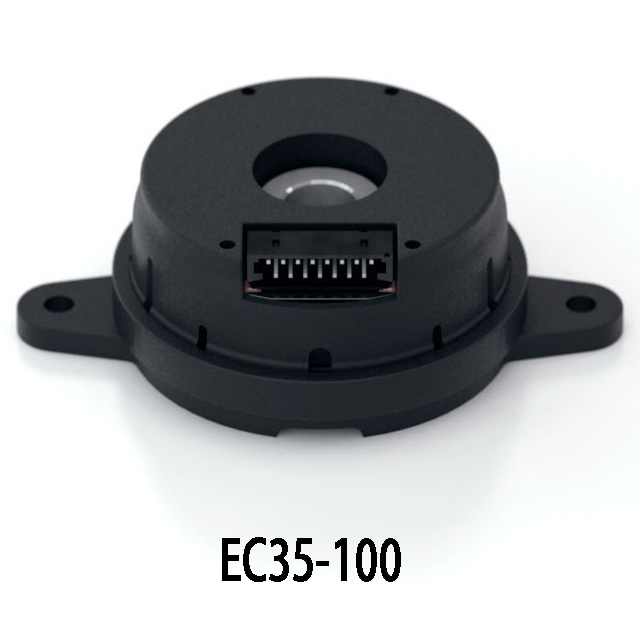
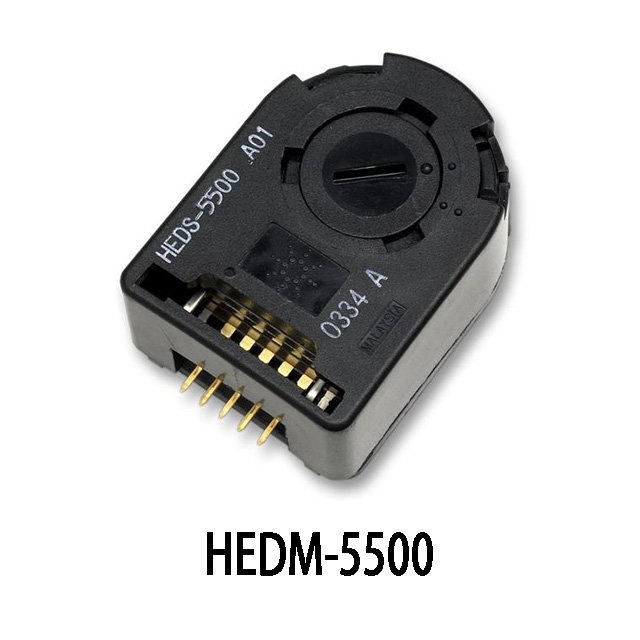



| Parameter | IB100 | EC35-100 | HEDM-5500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encoder Type | Optical Encoder | Optical Encoder | Optical Encoder |
| Power Supply (Vcc) | 5 V | 5 V | 5 V |
| Output Type | Quadrature (A, B, Z) | Quadrature (A, B, Z) | Quadrature (A, B, Z) |
| Auflösung | 500 PPR | 360 PPR | 500 PPR |
| Output Channels | 3 (A, B, Z) | 3 (A, B, Z) | 3 (A, B, Z) |
| Betriebstemperatur | -40°C bis +85°C | -40°C bis +85°C | -40°C to +100°C |
| Größe | Compact (28mm x 22mm) | Similar (30mm x 25mm) | Slightly Larger (35mm x 28mm) |
| Mounting Type | Through-Hole / Panel Mount | Through-Hole Mount | Through-Hole / Panel Mount |
| Output Signal | TTL | TTL | TTL |
If you’re looking for alternatives to the IB100, both the EC35-100 and HEDM-5500 are good options. They offer the same quadrature outputs (A, B, and Z), so they can easily replace the IB100 in most setups.
The EC35-100 has a lower resolution (360 PPR) compared to the IB100 and HEDM-5500 (500 PPR), which may matter if you need high precision. The HEDM-5500 is slightly bigger, so if space is tight, the EC35-100 could be a better fit. On the other hand, the HEDM-5500 has a wider temperature range, which makes it a better choice for harsh environments.
IB100 Industrial Sensor Circuit Example
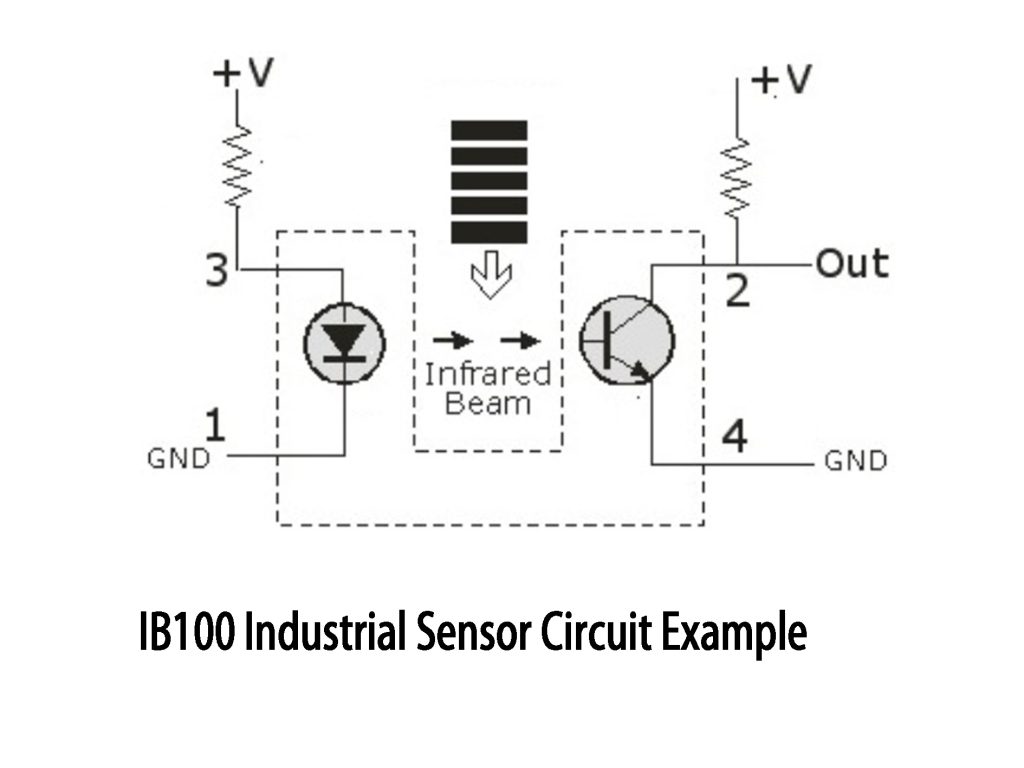
This circuit uses an IR LED to emit infrared light, which is common in industrial sensors for things like proximity detection or object sensing. On the opposite side of the LED, you’ve got a phototransistor that picks up the infrared light reflected from objects or obstacles. When the IR beam is clear, the phototransistor stays in one state—either conducting or not. But when something interrupts that beam, the phototransistor changes state, and that’s when you get a signal output. Pin 2, labeled “Out,” is where you get the sensor’s signal, indicating whether there’s an object in the way or not. This type of setup is useful in industrial applications like automation or safety systems, where detecting objects or movement is key.
IB100 Hall Effect Sensor Wiring
To wire the IB100 Hall Effect sensor, start by connecting the Vcc pin to your power supply, usually 5V or 12V depending on your sensor’s requirements. Then, connect the GND pin to the ground of your power supply. The OUT pin is where the sensor gives a digital signal, either HIGH or LOW, based on the magnetic field it detects. You’ll want to connect this pin to a digital input on your microcontroller or logic circuit. If needed, you can add a small capacitor (around 0.1µF) between the Vcc and GND to filter out any power supply noise. This setup will give you a reliable digital signal to detect magnetic fields, but remember to double-check the datasheet for exact voltage and current specs.
IB100 Proximity Sensing Application
Rotary encoders like the IB100 are used in various systems. For example, in motor control, a Hall Effect sensor detects the motor shaft’s rotation, sending pulses to the microcontroller to track position, speed, and direction. These sensors are contactless, which reduces mechanical wear. In robotics, Hall Effect sensors can detect proximity to objects, making them ideal for assembly or precise placement tasks. They’re durable and reduce wear since they don’t need to touch the objects they detect. In cars, Hall Effect sensors are used to measure wheel speed for ABS and traction control systems, working well in tough environments. Similarly, in conveyor systems, these sensors monitor the speed of rollers and help track motion direction, ensuring precise control in high-speed manufacturing processes.












