SZNUP2105LT1G datasheet | price | SOT23
- Voltage-ReverseStandoff(Typ): 24V (Min)
- Voltage-Breakdown(Min): 26.2V
- Voltage-Clamping(Max)@Ipp: 44V
- Package: TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
sznup2105lt1g
SZNUP2105LT1G is a dual N-channel MOSFET in a tiny SOT-363 package. It’s perfect for situations where space is tight but you still need two independent channels for switching, like in battery management, level shifting, or load switching. With a maximum drain-source voltage of 20V and a current rating of about 1.3A, it can handle a decent load while keeping energy consumption low thanks to its low Rds(on) of just 0.11Ω. The gate drive voltage works well with low-voltage controllers like STM32 or ESP32, making it a great fit for portable devices like phones, headphones, or battery packs. It’s all about saving space and power while keeping your circuit’s performance intact.
sznup2105lt1g pinout
| Pin Number | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | Drain (First MOSFET) |
| 2 | Gate (First MOSFET) |
| 3 | Source (First MOSFET) |
| 4 | Source (Second MOSFET) |
| 5 | Gate (Second MOSFET) |
| 6 | Drain (Second MOSFET) |
For the pinout of the SZNUP2105LT1G, you’ll have three key pins:
-
Drain (D): This is where you connect the load or the power supply. Each MOSFET has its own Drain pin, so you can control each one separately.
-
Gate (G): This pin controls whether the MOSFET is on or off. Applying a positive voltage turns it on. Both MOSFETs have independent Gate pins for separate control.
-
Source (S): Usually connected to ground or the negative side of the power source. The voltage difference between the Source and Drain determines the MOSFET’s state.
Make sure the Gate voltage is high enough (around 2.5V or more) to turn on the MOSFET.
sznup2105lt1g equivalent schottky diode
| Parameter | SZNUP2105LT1G | 1N5819 | SS14 | BAT54 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Package | SOT-363 | DO-41 | SMA | SOT-23 |
| Maximum Reverse Voltage (V) | 20V | 40V | 40V | 30V |
| Maximum Forward Current (A) | 1.3A | 1.0A | 1.0A | 0.3A |
| Forward Voltage Drop (V) | 0.11V | 0.45V | 0.45V | 0.3V |
| Operating Temperature Range (°C) | -55 to 150 | -40 to 125 | -55 to 125 | -55 to 150 |
| Features | Dual-channel MOSFET, suitable for battery management | Low forward voltage, high temperature resistance, commonly used for low-power applications | Suitable for battery management and DC-DC converters | Small package, suitable for high-frequency circuits |
When you’re swapping out the SZNUP2105LT1G, keep a few things in mind:
-
Package Size: The SZNUP2105LT1G uses SOT-363, but others like BAT54 and SS14 may have different sizes, so double-check they fit your circuit.
-
Maximum Reverse Voltage: This part handles 20V, but if you need something higher, 1N5819 and SS14 go up to 40V, which is great for higher voltage systems.
-
Forward Voltage Drop: The SZNUP2105LT1G has a low drop (0.11V), but if you’re after something similar, BAT54 works well for low-power applications.
BAT54 is great for small designs but can’t handle high currents, while SS14 is better for higher voltages and medium-current applications.
sznup2105lt1g rectifier circuit example
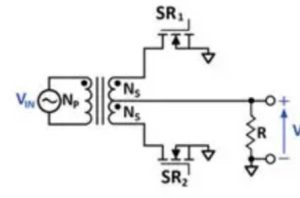
If you’re thinking of using SZNUP2105LT1G in a rectifier circuit, this example is exactly what you’re looking for. This circuit shows synchronous rectification using MOSFETs instead of traditional diodes. MOSFETs like SR₁ and SR₂ significantly boost your efficiency in rectifying applications, especially at lower voltages. Since SZNUP2105LT1G provides two independent N-channel MOSFETs in one tiny package, it fits perfectly here, simplifying your design. It’s a classic setup for DC output scenarios where efficiency and compact size matter.
sznup2105lt1g reverse polarity protection
If you’re using the SZNUP2105LT1G, here’s what you should know: It’s a compact TVS diode that protects your CAN bus from voltage spikes and static electricity. It handles quick surges (up to 350W), clamps around 44V at high currents, and has a low capacitance (≤30pF), ideal for fast CAN signals. But remember, it’s not designed for continuous reverse polarity—don’t rely on it if someone connects the battery backwards. You’d usually pair it with a diode or MOSFET to handle reverse connections properly. Perfect for automotive CAN setups needing strong surge protection in tough conditions.
sznup2105lt1g power supply diode usage
If you’re thinking of using the SZNUP2105LT1G as a regular power diode, hold on—that’s not its purpose. It’s actually a TVS diode, designed mainly to handle sudden voltage spikes, not to rectify power or block current. The right way to use it is placing it across your power lines, like from VBUS to ground, so it can quickly clamp down voltage surges and protect your circuits. But remember, it won’t stop current flow like a regular diode. For that, you’ll still want a dedicated diode or a MOSFET-based circuit.




~~2-Top.jpg)