Amplificateur différentiel : comprendre ce que c'est, ses types et ses applications
Author:admin Date: 2025-05-22 07:38 Views:493
Introduction
Because of their many applications, differential amplifiers remain a common circuit in electronics today. However, those who have yet to interact with such a circuit might ask, what is a differential amplifier?
We can define a differential amplifier as a circuit designed to take two inputs and only amplify the difference between the two inputs. At the same time, it rejects the common mode signals in the two inputs.
Le differential amplifier is more focused on the difference or the change between the signals rather than amplifying the overall voltage levels that each input presents.
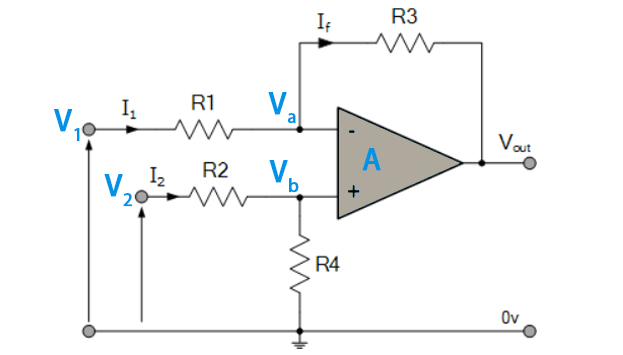
How Does a Differential Amplifier Work?
Le differential operational amplifier has two input terminals. We can label them as Vin+ and Vin-. The work of the amplifier is to amplify only the difference between these voltages which are the inputs of the circuit.
Other than amplifying the difference in the input signals, the circuit also has a common-mode rejection. This is where any interference or noise that is on both the input terminals is attenuated or rejected by the amplifier.
At the output, you get the amplified difference which is also called the differential signal.
Key Characteristics and Parameters of Differential Amplifiers
You should know a few characteristics of a differential amplifier. Such include:
- The differential amplifiers offer impressive noise rejection performance as they only amplify the difference between two input signals.
- Expect to also get high gain. As such, they can offer better amplification even for small voltage differences as per the differential amplifier equation.
- The resulting signal is more accurate since the differential amplifier BJTcan reject the common-mode noise. You can now get your desired signal even better.
Some of the key parameters to keep in mind include:
- Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR): This is what quantifies the ability of the amplifier to reject the common-mode signals. Having a higher CMRR is encouraged as it shows better noise rejection.
- Input offset voltage: This is the voltage difference between the two inputs if there are no input signals yet applied to the amplifier. Having a low input offset voltage is recommended to get the best accuracy.
- Differential Gain: It is the amplification factor of the amplifier for the difference between the two input signals.
- Input resistance: It is the impedance present between the two input terminals. When you have a high input resistance, it means you can avoid loading the signal source.
- Bandwidth: It defines the frequency range over which the differential amplifier can operate effectively.
Types of Differential Amplifiers
To find the gain of differential amplifier, you have to understand which type you are working with. There are a couple of ways of categorizing the differential amplifiers. It can be based on the input and output configurations, BJT or Op-amp types.
Input and Output Configurations
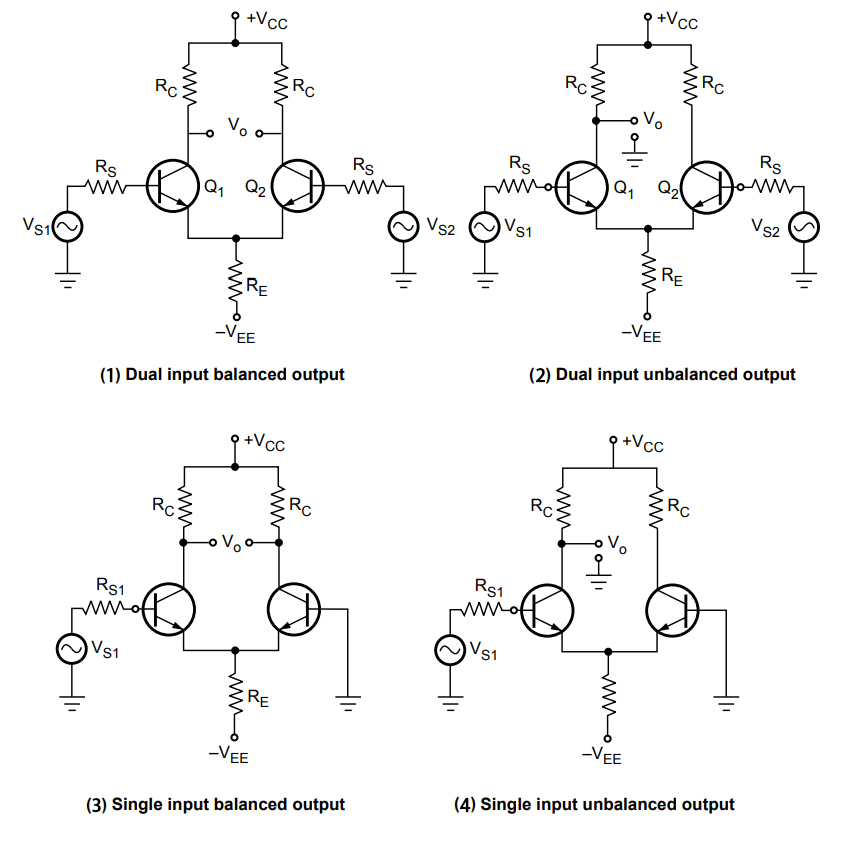
For this one, you can get the following options as the types:
- Dual input, balanced output: This configuration works by amplifying the difference between two input signals, which results in two equal but opposite signals at the output.
- Dual input, unbalanced output: This configuration amplifies the difference between the two input signals, but this time, the output is single-ended.
- Single input, balanced output: This type of configuration has one input signal, which produces two balanced output signals.
- Single input, unbalanced output: This configuration type features one input signal with a single-ended output.
BJT Differential Amplifier
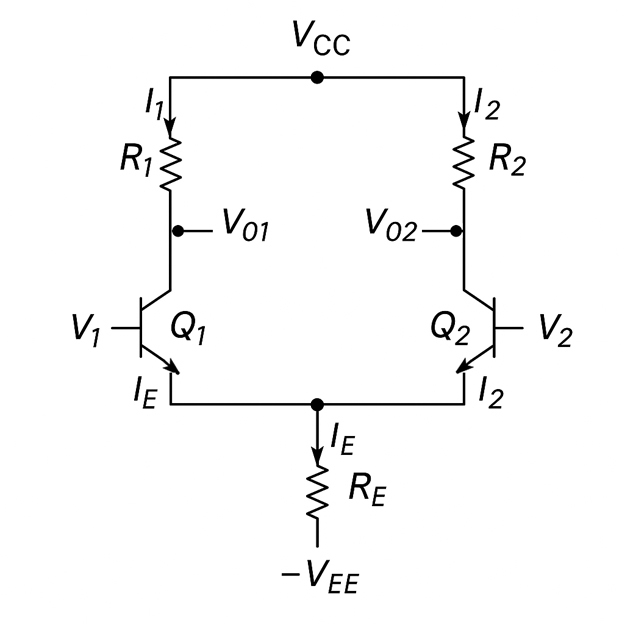
This type of differential amplifier amplifies the difference between two input signals. It is considered a fundamental building block in various analog circuits.
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Differential Amplifier
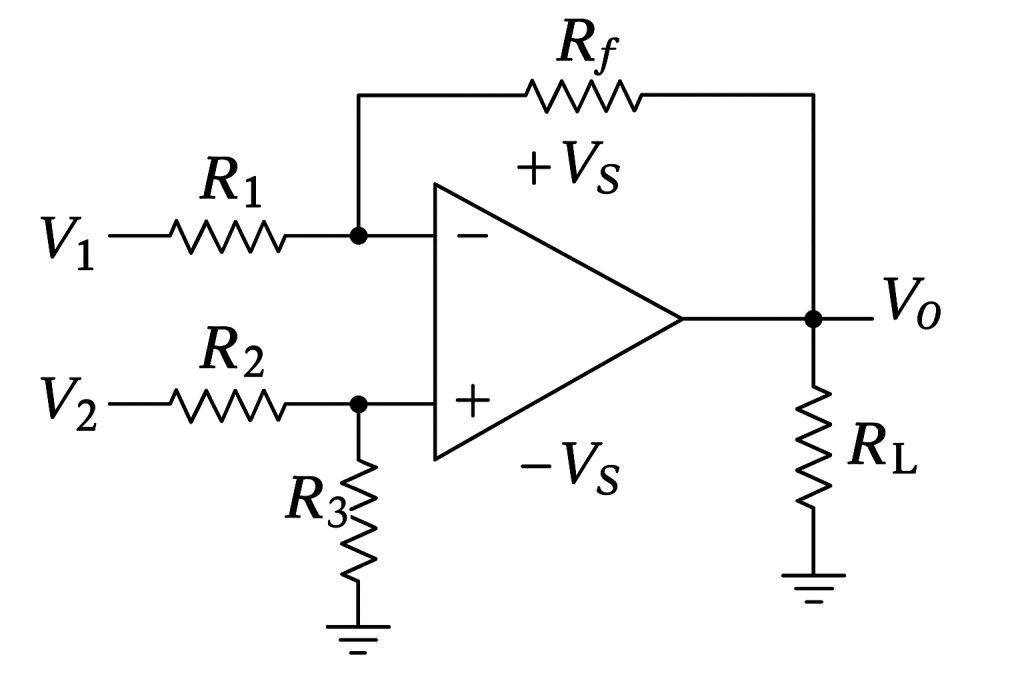
This is another important type of differential amplifier whose job is to amplify the difference between two input voltages. It features two inputs with one output. The main function is to amplify the voltage differential between the two inputs by using a differential operational amplifier circuit.
Applications of Differential Amplifiers
When you do a simple differential amplifier calculation, you may see there are several ways you could use such a circuit. If you are unsure how, below are the top common applications of differential amplifiers.
Signal Conditioning for Analog to Digital Converters
This is a common application for fully differential amplifiers. They are great for driving differential ADC inputs. They offer a simple way of implementing anti-aliasing filtering properties, and they can be suitable for signal acquisition in noisy environments.
Measuring Differential Signals
These amplifiers can measure the differential signals more accurately. They are ideal for voltage and current monitoring, where accuracy is essential.
Signal Integrity and Noise Rejection
Since the differential amplifiers have a common-mode rejection feature, they are robust to common-mode interference and external noise. This feature is important for applications where noise may corrupt a signal.
Instrumentation and Sensors
Features such as high input impedance, low noise, and high common-mode rejection ratio make differential amplifiers good instrumentation amplifiers. They can acquire weak signals and amplify them to the required level.
Power Supply Applications
Yes, the differential amplifiers can also be suitable for power supply applications where they can reject power supply noise together with the common mode noise in a signal.
Pros and Cons of Differential Amplifiers
Pros
- The differential amplifiers are highly effective at rejecting noise in the input signals
- Expected balanced outputs, which are important for signal integrity and noise reduction applications
- We also find the differential amplifier good for noise-sensitive environments. This makes it good for applications with sensors and instrumentation.
- Reduced harmonic distortion improves the signal quality thanks to the use of differential amplifiers.
- These amplifiers are good for data transmission, audio, and telephone systems because they can reject noise.
Cons
- Differential amplifiers are more complex to design compared to single-ended amplifiers. This is because of increased size, which can increase the circuit cost.
- These amplifiers generally need more space on a chip or circuit board compared to when working with single-ended amplifiers.
- You may also experience impedance mismatch issues depending on your setup. This may reduce the common-mode rejection ratio.
Differential Amplifier vs. Single-Ended Amplifiers

By now, we already know how the differential amplifier formula and how it works. How about the single-ended amplifier?
A single-ended amplifier has one input signal and a ground reference. The output signal is amplified relative to the ground. In this setup, we find that it is more susceptible to noise, as the common-mode noise is also amplified with the input signal.
Even with its limitations, the single-ended amplifier still has applications. It is used where noise is not a big issue, such as for basic audio amplification.
The main difference between the two is that differential amplifiers are built to reject common-mode noise, while single-ended amplifiers amplify it.
Also, the cost is different. The differential amplifiers are more complex and need more components to build. As such, you end up spending more on such amplifiers.
How about signal integrity? The differential amplifiers offer better signal integrity by suppressing noise. Because of this, there are some applications where the single-ended amplifiers will not do a good job.
| Fonctionnalité | Single-Ended Amplifier | Differential Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Inputs | One | Two |
| Outputs | One | One or Two |
| Amplification | Signal relative to the ground | Difference between the two input signals |
| Noise Immunity | Low | Haut |
| Common-mode rejection | Low | Haut |
Conclusion
When you work with a differential amplifier circuit diagram, you will quickly notice several parameters are better than some other amplifier types. This is not to say it does not have limitations, but the overall functionality is quite good. You end up with better noise immunity, increased dynamic range for the voltage, reduced harmonic distortion, and much more. If you were to design a differential amplifier today, use the right tools to simulate it first to find where you need to optimize it for the best performance.
Veuillez envoyer une demande de devis, nous vous répondrons immédiatement.
Questions fréquemment posées
Why is a differential amplifier good for noise rejection?
This is because the differential amplifier can ignore the common-mode signals and effectively cancel them out to give you an output signal free from such issues.
Can you design and build a differential amplifier?
Yes. It is possible to build a differential amplifier by using a standard op-amp combined with a few resistors. This setup is the most common in many analog circuit designs.
What should you consider when designing a differential amplifier?
We recommend features such as resistor matching, power supply stability, the desired gain, and input impedance. Having precise resistor ratios is important for getting a good CMRR and better signal amplification accuracy.