What are Load Cells: Types, Applications & Working Principle
Author:admin Date: 2025-07-15 08:35 Views:501
- Introduction
- How a Load Cell Works
- Types of Load Cells
- Tension Load Cell Equation
- Uses of Load Cells
- Factors to Consider When Buying a Load Cell
- How to Install and Calibrate Load Cells
- Troubleshooting and Maintaining Load Cells
- Conclusion
- Load cells installation, capacity, support plates, mounting surfaces, single point load cells
Introduction
A load cell is a type of sensor or transducer that works by converting a force or weight into a measurable electrical signal. The output signal can be a voltage or current, which is used to indicate the magnitude of the weight or force being applied.
Load cells tend to have many applications, especially in industries and testing equipment. You can also find them in weighing scales as well. Below, we look further into load cells, understand the types, how they work, and how to choose one.
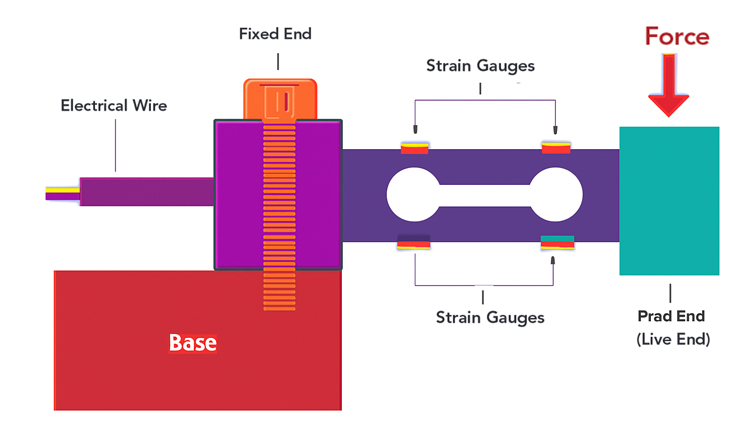
How a Load Cell Works
Whenever a force or weight is applied to a load cell, it deforms slightly. This deformation is quite small and is not visible to the naked eye. Strain gauges, which are basically small resistors, are attached to the deformed surface. The resistance of the strain gauges changes depending on how the surface is stretched or compressed.
Whenever the load cell structure deforms, the strain gauges also deform, which changes their electrical resistance. This change in resistance is proportional to the deformation amount and, therefore, to the applied force.
A Wheatstone bridge circuit is used for measuring the change in resistance, which is then converted into a voltage signal. The electronic circuitry, such as an amplifier and microcontroller, in the structure of the load cell sensor amplifies and processes this voltage signal.
The processed signal is now displayed on a digital display for you to understand the change. The same can be sent to a computer or other systems for additional analysis.
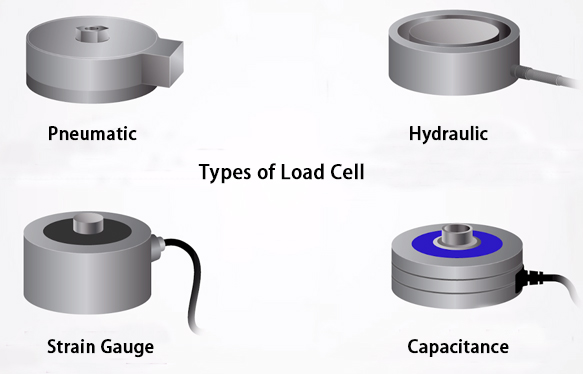
Types of Load Cells
Since you already know what is a load cell, it is time to look at the various types available. The most common types include strain gauge, pneumatic, capacitive, and hydraulic.
Strain Gauge Load Cells
The strain gauge load cell measures the change in the resistance of the strain gauge whenever the load cell deforms under a load. Such load cells are popular because of their accuracy and reliability in different types of applications.
Additional categorizations of the same include beam, single point, S-beam, and beam load cells.
Common applications include process weighing, scales, and measuring forces in several industrial applications.
Hydraulic Load Cells
In this case, the load cell uses hydraulic pressure for measuring the force. Such types are known for being robust and resistant to harsh environments.
Such performance makes them suitable for applications where resistance to overloads or high capacity is needed. Examples include weighbridges and platform scales.
Pneumatic Load Cells
Other than a load cell using strain gauges, we also have those using pressure to measure force, and are called pneumatic load cells. The advantages are that they can offer clean environments since they are explosion-proof and offer a contamination-free nature.
Such load cells are mostly used for measuring small weights, such as in food processing and pharmaceutical applications.
Capacitive Load Cells
These load cells measure the force by detecting the changes in capacitance between two plates, unlike strain gauges, which use resistance. Capacitive load cells are generally known for high sensitivity and precision.
The common applications for such a load cell include cases where high accuracy is needed, such as medical devices and precision scales.
Tension Load Cell Equation
The tension load cell equation is important to help us understand the measured output voltage based on the applied force or tension.
The fundamental equation for a load cell is F = S * V. This is where indicates the F measured in pounds or Newtons, S is the sensitivity of the load cell measured in mV/V, and V is the output voltage measured in millivolts.
To get the load cell output, you need to measure the output voltage when a force is applied. Next is to look at the load cell datasheet to understand its sensitivity. Now that you have both the sensitivity and voltage, you can use the equation to calculate the force.
Uses of Load Cells
Whether it is a bending beam load cell or any other type, there are quite a number of applications that can be done by a load cell. Here are some of them.
Weighing
The load cells are core in scales used for weighing raw materials, process materials, and finished products in different industries.
Manufacturing
The load cells can also be used in the manufacturing sector, where they can monitor tension in conveyor belts and ensure there is precise filling of the containers in bottling plants.
Aerospace and Automotive
Yes, you will also come across the load cells in the testing and validation of components. They are used in such industries to assess performance and durability.
Food and Beverage
You may also use load cells in the food and beverage sector for portion control, filling operations, and batching. This ensures accurate measuring for ingredients and packaging.
Pharmaceuticals
You can also find the S-type load cell being used in medical devices and pharmaceuticals for accurate ingredient mixing, tablet compression, and other types of formulation processes.

Factors to Consider When Buying a Load Cell
You might be considering a crane load cell or digital load cell, but do you know what to keep in mind before buying? It is important to have the following in mind before committing to buy a load cell type.
Capacity
The load cell you choose should have a slightly higher capacity than the expected maximum load it can handle. This helps to prevent potential damage and also ensures you get accurate readings.
Typical load cells will come with an overload protection, which is often around 1.5 times their rated load capacity.
Accuracy Requirements
The accuracy is usually indicated as a percentage of the full scale output. Expect it to vary largely depending on the type of load cell and application.
For accuracy, consider what would be the acceptable error margin depending on the specific application. Some applications do not work well with high errors. They need the best accuracy.
Operating Environment
The operating environment, such as temperature fluctuations, may affect how a load cell works. It is best to choose a load cell that offers appropriate temperature compensation or is designed to work in such a temperature environment.
Moisture, dust, and corrosive substances may also lead to damage to the load cell. Make sure to choose a load cell that has the appropriate IP rating and material.
Still consider the possibility of physical damage and choose a load cell with suitable protection and rugged construction.
Direction of Loading
Yes, you will come across load cells being designed for either tension or compression loading. It is vital to choose the type of load cells based on the application. Take note that some load cells can handle both tension and compression forces, but check with the product specifications to be sure.
Mounting Options
Still, consider how load cells can be mounted. Are the mounting options compatible with your application? This is crucial, as proper mounting is vital for accurate measurement and error prevention.
The Output Type
The output of a button load cell or pancake load cell also matters. The output can be analog or digital. You have to choose based on the system’s requirements.
Digital outputs are often preferred as they make it easy to integrate with modern systems and have more flexibility. However, they might come at a higher cost.
Certifications and Standards
Consider the standards and certifications depending on the application. It is vital to have a load cell that meets all the necessary industry standards.
How to Install and Calibrate Load Cells
Installing and calibrating the load cells is usually not hard. You just need the right procedure to do it right. Let us start with the installation process.
1. Mounting
Make sure that the load cell is correctly mounted on a stable flat surface for it to handle the expected load. Also, use the appropriate mounting hardware and still follow the instructions given by the manufacturer.
2. Alignment
You have to ensure that the load cell is correctly aligned in the direction of the applied force. This is to help prevent side loads or misalignment, which often affects the accuracy.
3. Wiring
Connect the load cell to the data acquisition system, such as an amplifier or a Wheatstone bridge. The manufacturer’s wiring diagram should give you an idea of what to do. Always use shielded cables and proper grounding to help minimize interference.
How about the calibration of a load cell? Here is how you would do it.
- Set the system to read zero with no load applied. This gives you the baseline reading.
- Apply known weights, ensuring they are within their limit. Record the corresponding readings.
- Compare the recorded readings with the known weights. You can adjust the calibration parameters, such as offset and gain, to ensure accurate measurements.
- Verify that the load cell responds linearly with a wide range of weights and that the readings are repeatable.
Troubleshooting and Maintaining Load Cells
Troubleshooting load cells is quite important to ensure performance is maintained. It is the same thing with the proper maintenance of the load cells.
Visual inspection is encouraged to check for any physical damage, such as cracks, corrosion, dents, and excessive wear in the loading area. Check the cables and connectors for crimps and cuts.
Electrical testing can also be done to measure the resistance and output voltage to ensure they are within the specifications. Check for open or short circuits in the wiring system as well.
Do a calibration check as well. This is done by applying known weights to verify if the load cell has an output that is within the manufacturer’s specifications. Also, check if there are linearity issues at different load points.
Make sure the unit is also cleaned properly to remove anything that might affect how it works. Use a gentle, non-corrosive cleaning agent to ensure the load cell sensors are kept in good condition.
Conclusion
Getting the best load cells from the load cell manufacturers should now be easy since we have covered what you need to know about load cells. It is best to always choose one from a top brand, as you are assured of the best performance. Look at the type as well, as it determines where best to use the load cell. Do not forget to maintain the load cell unit as recommended to keep it in good working condition.
Conclusion
Load cells installation, capacity, support plates, mounting surfaces, single point load cells
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a difference between compression and tension load cells?
The compression load cells are used for measuring the force pushing down on them, while the tension load cells measure the force pulling away from them. It is possible to get some load cells that can measure both tension and compression.
Are load cells accurate?
It depends on how they are built. If you can get high-quality load cells, then you will like their accuracy. They are known for being extremely accurate with very low error margins.
Is it necessary to calibrate load cells?
Yes. Calibration is key in ensuring accurate and consistent readings. This should be done during installation, after doing repairs, or after maintenance. Some units come with auto-calibration features.


