FQP27P06 datasheet & pinout, Arduino | price UMW
- Supplier Device Package: -
- FET Type: -
- Drain to Source Voltage (Vdss): -
- Package: -

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
P-MOSFET27A-C64 | P-Channel MOSFET 60V 27A FQP27P06 TO-220
fqp27p06
If you’re looking for a powerful MOSFET to handle heavy loads or high-current switching, the FQP27P06 could be exactly what you need. It’s a P-channel power MOSFET, perfect for high-side switching applications where efficiency matters.
One of the best things about this MOSFET is its impressive current handling—it can comfortably carry up to 27 amps continuously, so driving larger loads isn’t a problem. Plus, with a low on-resistance (around 0.07Ω), it helps keep your circuit efficient and your heat dissipation low.
The FQP27P06 also offers robust voltage handling, safely managing up to -60 volts, making it ideal for automotive and industrial environments. Its fast switching capability lets you use it in high-frequency circuits without issues.
You’ll appreciate its standard TO-220 package, which makes it easy to mount on heat sinks and integrate into power supplies, motor controllers, or DC/DC converters. Overall, it’s a reliable and efficient choice for your power management and heavy-load switching projects.
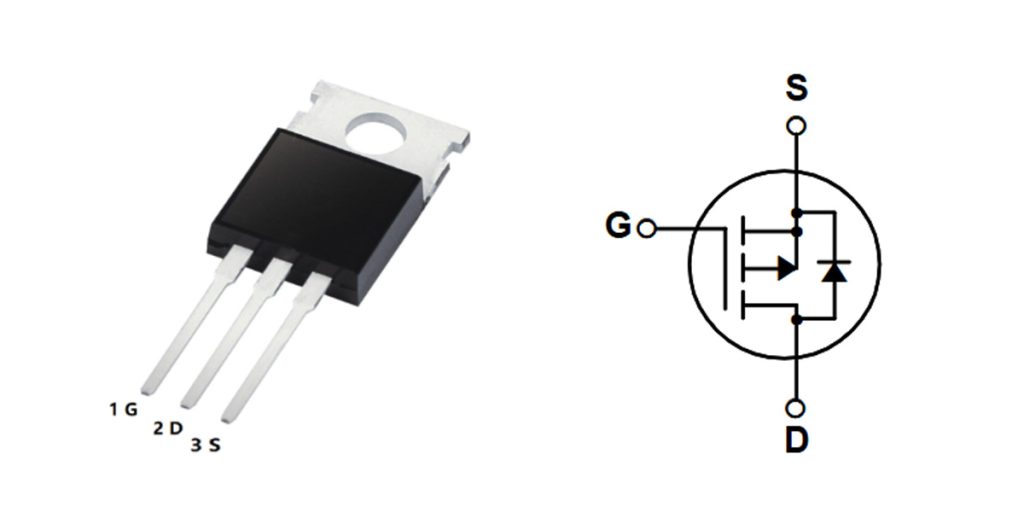
fqp27p06 pinout and package
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gate (G) | Gate, Controls MOSFET switching state |
| 2 | Drain (D) | Drain, Connects to load or negative terminal of the power supply |
| 3 | Source (S) | Source, Typically connected to the positive terminal or load |
When you’re using the FQP27P06 MOSFET in your projects, you’ll find it packaged in the popular TO-220 format. This makes it simple to mount securely and attach a heatsink, helping handle those higher currents without overheating.
Here’s a quick tip on handling its pins: the Gate controls the MOSFET’s switching, so keep your control signals clean and steady. Adding a small resistor (around 100Ω) in series, or using a dedicated MOSFET driver, can prevent oscillations and protect against damaging gate currents.
Remember, as it’s a P-channel MOSFET, your Drain usually connects to the load or negative side of the power supply, while the Source connects to the positive side—perfect for high-side switching setups. Double-check your polarity connections carefully.
Since this MOSFET can handle high currents, don’t forget a proper heatsink to keep it cool. And always use anti-static precautions, like wearing an ESD wrist strap, because MOSFETs can be easily damaged by static discharge.
fqp27p06 equivalent mosfet
| Parameter / Model | FQP27P06 | IRF9540N | IRF4905 | IRF9Z34N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Type | P-Channel Enhancement | P-Channel Enhancement | P-Channel Enhancement | P-Channel Enhancement |
| Max Drain-Source Voltage (V_DS) | -60 V | -100 V | -55 V | -55 V |
| Max Continuous Drain Current (I_D) | -27 A | -23 A | -74 A | -19 A |
| R_DS(on) (Typical) | 0.07 Ω | 0.117 Ω | 0.02 Ω | 0.10 Ω |
| Gate Threshold Voltage (V_GS) | -2 V to -4 V | -2 V to -4 V | -2 V to -4 V | -2 V to -4 V |
| Package Type | TO-220 | TO-220 | TO-220 | TO-220 |
If you’re thinking about replacing the FQP27P06 MOSFET, here’s some practical advice. The IRF4905 can handle much higher currents, which makes it great if your circuit demands more power. But if you consider IRF9540N or IRF9Z34N, keep in mind their current ratings are a bit lower—double-check your load to ensure you’re staying within safe limits.
In terms of voltage, the IRF9540N can handle up to -100 volts, giving you extra headroom for applications with higher voltage spikes. The others, like IRF4905 or IRF9Z34N, have similar or slightly lower ratings, so make sure the voltage stays within your safety margin.
Lower R_DS(on) means your MOSFET stays cooler and more efficient—IRF4905 typically has the lowest resistance, but might cost a bit more. Higher resistance models can generate more heat, so you’ll need to plan accordingly for cooling.
Good news is, they’re all in the standard TO-220 package, making swaps straightforward and easy.
fqp27p06 mosfet switching circuit
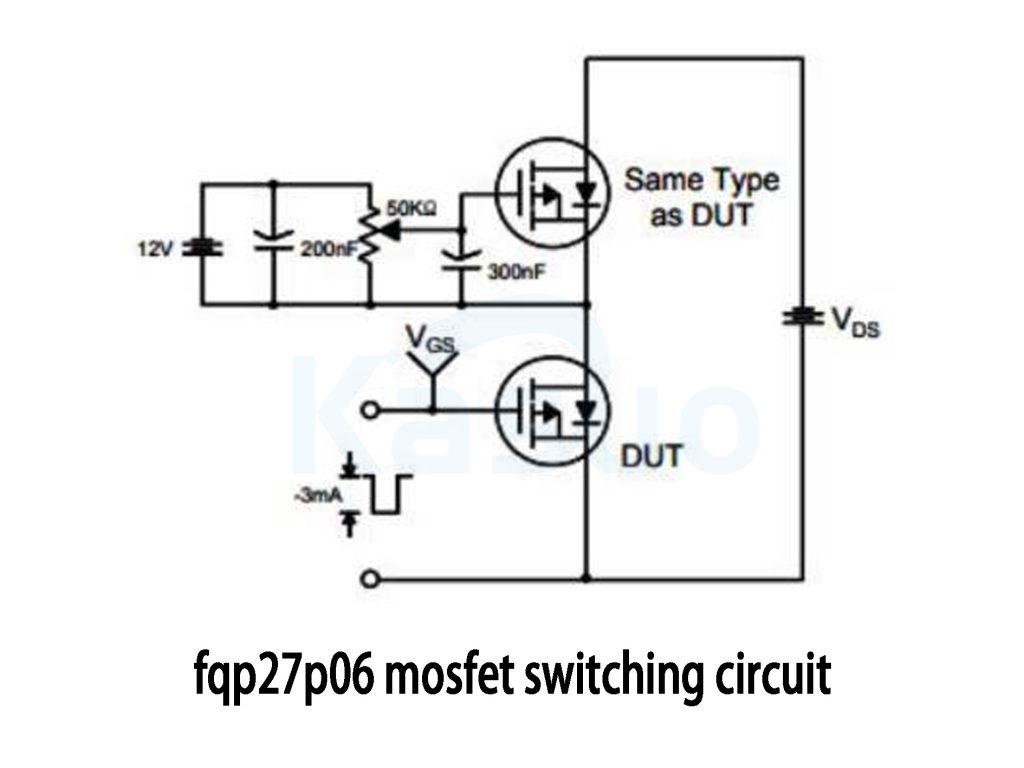
Here’s a practical look at how you can test the switching performance of a MOSFET like the FQP27P06. The setup uses two identical P-channel MOSFETs—one labeled “DUT” (Device Under Test) and another as a reference device. You’re powering the circuit from a stable 12V DC supply.
There’s also a simple RC network involved: a 50kΩ adjustable resistor and capacitors of 200nF and 300nF. These components help control how quickly your MOSFET switches on and off by shaping the gate voltage waveform.
You’ll apply an external pulse signal (marked “-3mA”) to the gate of your test MOSFET, triggering its switching action. By monitoring the voltage across its drain-source terminals (“V_DS”), you can precisely measure things like switching speed, rise and fall times, and how effectively it turns on (R_DS(on)).
Keep in mind, this circuit isn’t meant for direct load driving in your applications—it’s ideal for checking and optimizing your MOSFET’s switching behavior during the design stage.
fqp27p06 high current mosfet application
If you’re looking for a reliable MOSFET to handle heavy-duty switching, the FQP27P06 is a great choice. It’s a powerful P-channel MOSFET rated for up to 27 amps with a low on-resistance of just 0.07Ω, perfect for controlling large loads and high-side switching tasks.
You’ll find it handy for high-current applications like motor drivers, DC-DC converters, battery protection circuits, and even powerful LED lighting setups.
Here’s how you’d typically set it up: Connect the MOSFET on the high-side, placing the source pin to your positive supply (like 12–48V). Your load goes between the drain pin and ground. When the gate voltage drops sufficiently below the source voltage, your MOSFET switches on, powering the load.
Remember, always use a proper driver to quickly switch the MOSFET, preventing overheating. Include solid heat dissipation solutions like heat sinks or fans, and ensure your working voltage stays well within the -60V rating. Protect your circuit with fuses or TVS diodes to guard against voltage spikes.












SOT223-1.jpg)