डिजिटल इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स में फ्लिप फ्लॉप: वे क्या हैं और कैसे काम करते हैं
Author:admin Date: 2025-06-11 07:38 Views:279
परिचय
A flip flop is a type of circuit that has two stable states and can be used for storing and managing digital information. The two main states are in binary, which means 0 and 1.
ए flip-flop can work as a basic memory element in sequential circuits. It can retain some data until a circuit trigger changes it.
We will look into all about flip flops. This includes how it works, the types, applications, and so much more. This is to help you have a better understanding of what a flip flop is all about.
How Flip Flops Work
How flip flops such as D flip flop work is quite easy since they are basic memory elements with two stable states. The state of the memory varies from low (0) to high (1) depending on the input signal. It can be a clock or data input signal.
T flip flops or any other types are triggered based on the clock signal. This dictates when the flip flop changes its status. The data is then synchronized with the clock signal. As such, the output is dependant on the clock pulse.
Well, you can also have flip flops that are independent of the clock pulse. For such types, they have the “set” and “reset” inputs that help change the flip flop state at any time.
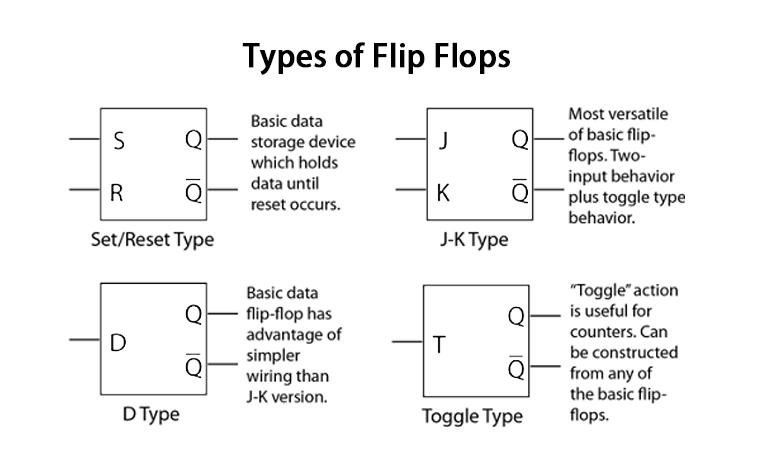
Types of Flip Flops
You are likely to come across different types of flip flops in the market. They are usually categorized based on how the work, dependency on the input signal, and more. Here are the most common options.
SR Flip Flop
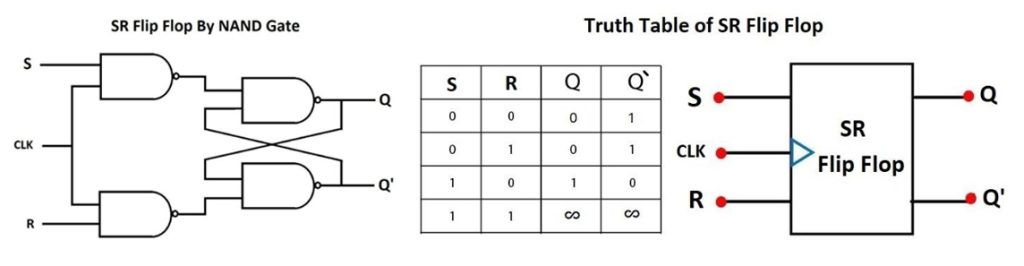
The SR flip flop is the most common flip flop in the market. It comes with a set input labeled as (S) and a reset input labelled as ( R ). When you set S as active, expect the output Q to be high while the Q’ to be low.
Expect these outputs to remain the same until S goes to high or the power to the circuit is turned off. The SR flip flop truth table below shows what to expect in each case with the changes in the input.
| एस | आर | क्यू | Q′ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | ∞ | ∞ |
JK Flip Flop
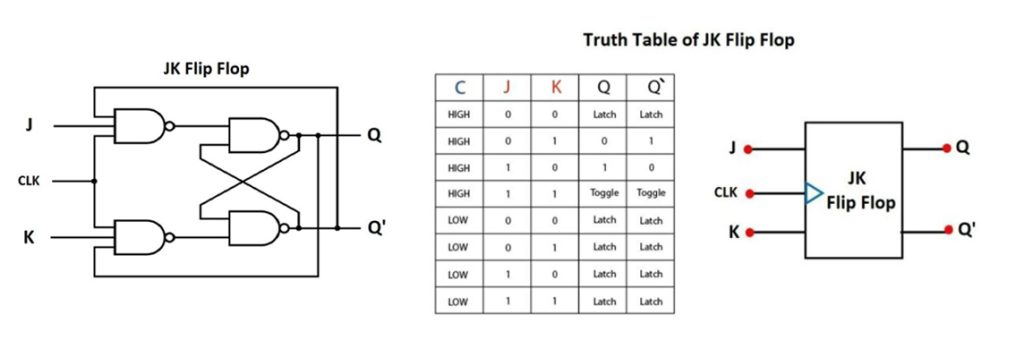
This is another popular flip flops used in digital electronics. You can say it is an improvement of the SR flip flop in many ways. You remember when we got infinity with S=R not in this case.
The JK flip flops have the inputs J and K which affect the outputs just as in the D flip flop mentioned above. However, when J = K = 1, the output of the flip flop will be the inverted input.
From a JK flip flop truth table, we can see that if the J and K inputs are different, expect the output Q to take the value of J for the next clock edge. If both inputs are low, then there is no change.
How about when both inputs are high at the clock edge? In such a situation, the output toggles from one state to another. That is how the JK flip flops can work as Set and Reset flip flops.
| जे | क | क्यू | Q′ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
D Flip Flop
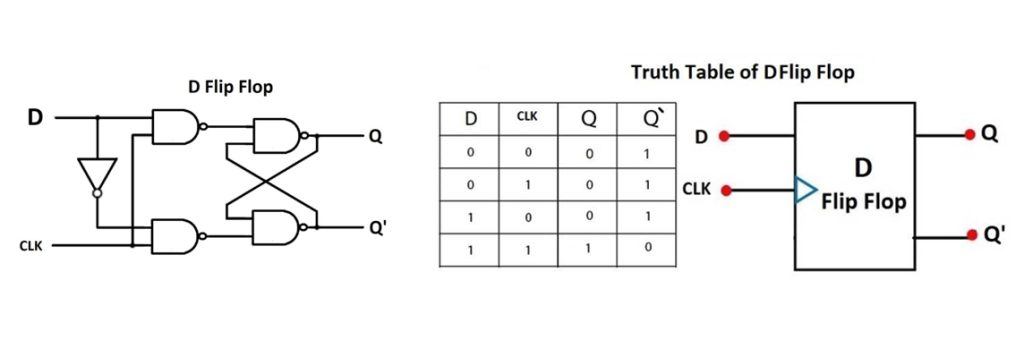
The D flip flop is another important circuit in digital electronics as it can act as a storage element to hold a single bit of data. This is maintained until there is a change in the clock signal.
The flip flop has a single data input labelled as D and a clock input signal labelled as CLK. The output Q of this flip flop mirrors the input signal D only when the clock is on a rising edge, else it stays the same. As such, it is a versatile unit that works for various applications such as counters, memory, and shift registers.
Below is the D flip flop truth table.
| घड़ी | डी | क्यू | Q’ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 (rising edge) | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 (rising edge) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
T Flip Flop
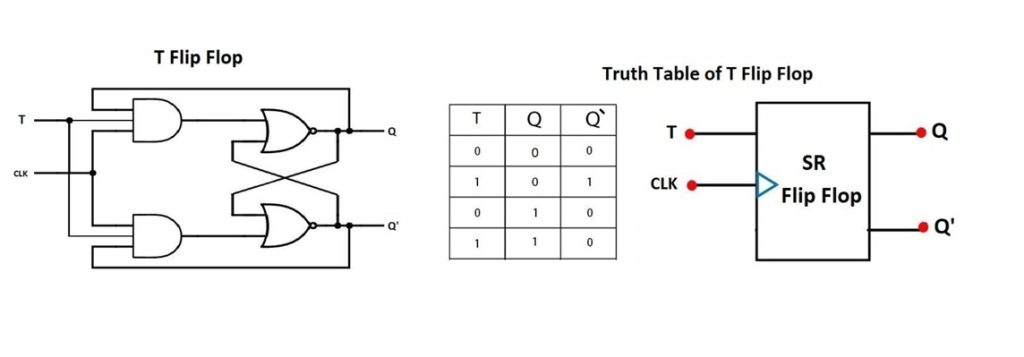
This is also called a toggle flip flop. It is a type of flip flop that toggles its output state depending on the clock pulse when T input is high. In case the T input is low, then the flip flop holds its previous state.
Sometimes this is referred to as a simplified JK flip flop where its inputs J and K are connected. This is because in the T flip flop, you only get a single input.
The T flip flop truth table below will help us understand more in detail how the circuit works.
| टी | क्यू | Q(t + 1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Applications of Flip Flops
There are many applications of flip flops. It all depends on the flip flop working mechanism. Here is what to expect as the applications of flip flops.
- Data storage and registers in memory units for holding and retrieving information.
- The JK and T flip flops work as binary counters. As such, they can be used for counting events or changes in a system.
- D flip flops are commonly used in shift registers for moving data bits serially. This is vital for serial communication and data transfer mostly in digital circuits.
- They can also be used as frequency dividers. This is done by reducing the clock signal frequency by a specific factor.
- Data transfer is another application of flip flops where they can be used in data transfer circuits to move data between different system parts.
- The SR flip flops can be used as part of control systems where they synchronize signals and control how other components operate.
- Flip flops are used as building blocks for different types of memories. Examples include Random Access Memory (RAM).
Edge Triggering and Clocking Mechanisms
Edge triggering of a flip flop simply means the change in the flip flop output state depending on the falling or rising edge of the clock signal.
There are flip flops that are controlled by a clock signal. In this case, when a clock changes from low to high or rising edge or from high to low or falling edge, then it triggers the flip flop to change its output state.
The clock signal works as a synchronous control that ensures all the flip flops in that system change their states at the same time depending on the clock’s edge.
You can have both positive and negative edge triggering. In the positive edge triggering case, the flip flop changes the output when the clock signal changes from low to high. As for the negative edge triggering, it is the vice versa.
Advantages of Edge Triggering
- It leads to precise timing which provides a defined and clear time for data transfer. This makes it more suitable for high speed applications.
- Expect reduced glitches as the flip flops only respond to the edge trigger. This makes them less susceptible to glitches due to unstable input signals or noise.
- There is also improved synchronization within a digital circuit with such a mechanism. This ensures that all the components are coordinated in their operations.
Limitations of Edge Triggering
- The circuits can be more complicated to design and implement
- These circuits need a precise clock signal to work as expected
Flip Flop vs. Latch: Know the Difference
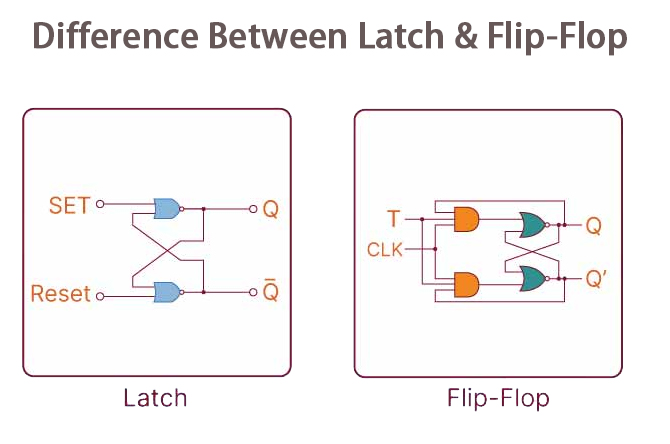
Flip flops and latches are both important in digital electronics especially when it comes to storing information. However, they vary in terms of how they handle input changes and their output timing.
The key differences between the two largely depend on factors such as triggering, timing, stability, structure, and applications.
Latches are level triggered, which means their output changes continuously depending on the input changes. This is so long as the enable signal is maintained active. As for the flip flops, they are edge triggered, meaning that they output changes only during the rising or falling edge of a clock signal.
In terms of timing, the latches continuously reflect the input. As such, the output tracks the input if the enable remain active. In the case of flip flops, the inputs are sampled based on the clock edge. So, the output will only change at that edge.
How about stability? We find that latches are prone to more glitches and metastability issues because of their continuous level-triggered operation. As for flip flops, they are more stable thanks to having the edge triggered operation. This ensures synchronization which reduces glitches.
Latches are best suited for applications where the quick changes in output are needed. This is for mostly simple memory elements such as asynchronous circuits. You would want flip flops in the synchronous circuits where the controlled state depends on the clock signal.
निष्कर्ष
Flip flops remain key in how digital electronics work. That is why understanding their working principles is important so that you can know how best to use them. We have seen how the different types of flip flops work above and their expected outputs. You should always keep this in mind to find the best flip flop based on your application. Also, their characteristics come in handy for those who might be interested in how the flip flop works and their implementation in various circuit designs.
कृपया आरएफक्यू भेजें, हम तुरंत जवाब देंगे।
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्नों
Why is a JK flip flop preferred over using SR flip flop?
In an SR flip flop, it enters the invalid state when both inputs are high. This is not the same for JK flip flop. What it does is to toggle its output in such a condition, thus making more reliable.
Why do you need edge triggering in flip flops?
Edge triggering is essential in flip flops as it ensures that the flip flop only responds to the input changes at a specific moment. This is vital to help in synchronizing the digital circuits and avoid having unintended changes in the flip flop states.
What tools can be used for simulating flip flop circuits?
You can consider software such as Multisim, Logisim, and more to build and test the flip flop circuits virtually before implementing them.


