What is a Light Dependent Resistor? Complete Guide to LDR Working and Uses
Author:admin Date: 2025-09-28 10:12 Views:25
परिचय
ए light-dependent resistor, or LDR, is an electrical component whose resistance changes in response to changes in incident light intensity. Basically, it works as a variable resistor that is sensitive to light. It will have high resistance in darkness and low resistance when there is a bright light.
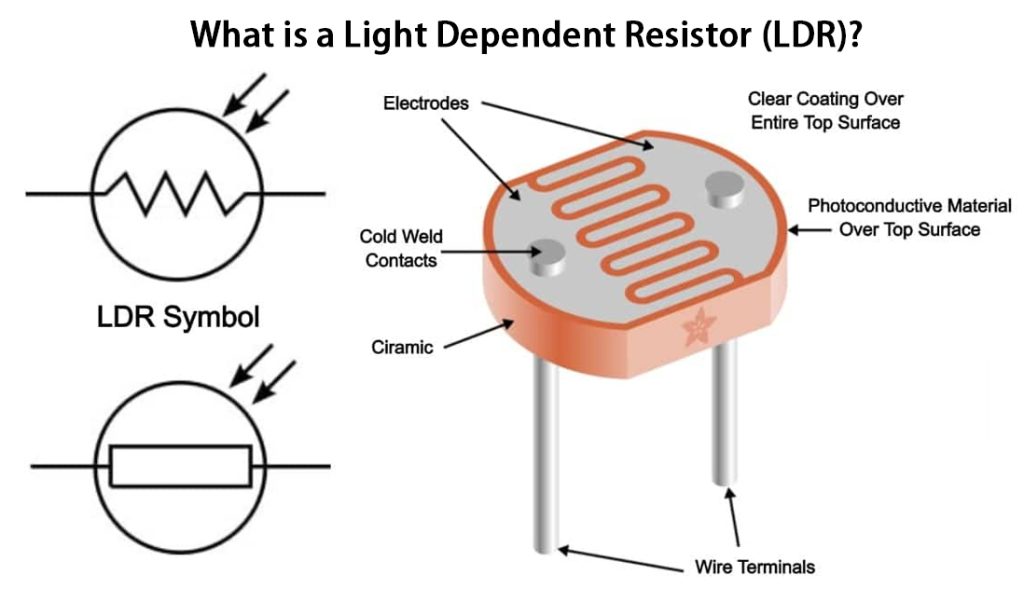
An LDR is also called a photoresistor or photocell. Thanks to its workings, it has many applications, such as light sensors, light-sensitive circuits, and measurement & instrumentation. Let’s learn more about them below.
How a Light Dependent Resistor Works
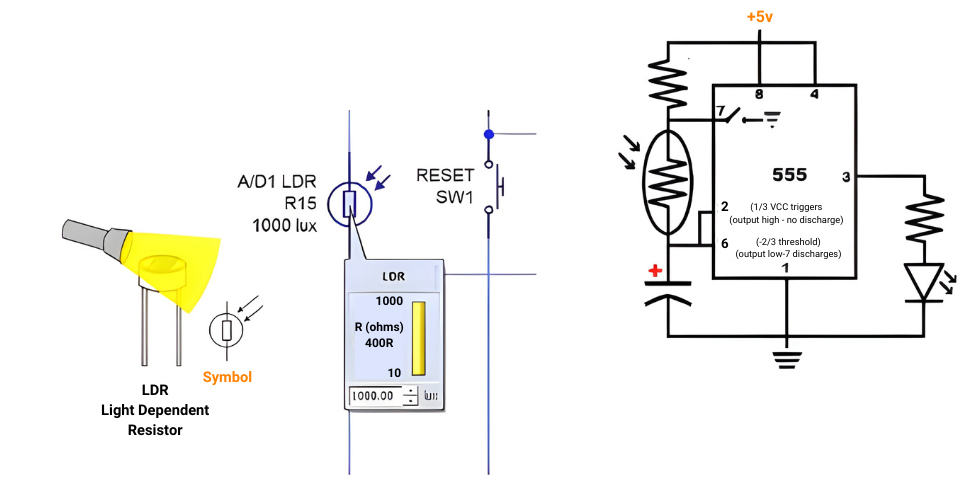
अब जब आप जानते हैं what are light dependent resistors, let us see how they work. We have already seen that their resistance changes based on the amount of light they receive. When more light shines on the light dependent resistor, the resistance decreases, but when it is dark, the resistance increases.
To make it all possible, it comes down to how the LDRs are made. They are made of semiconductor materials such as cadmium selenide and cadmium shuffle. When there is darkness, these materials have high resistance because of limited free electrons.
When light shines on the LDR, photons transfer their energy to electrons in the semiconductor. This energy exceeds the material band gap, creating more free electrons.
When you have more free electrons, there is increased conductivity, thus the resistance decreases.
Light and Resistance Relationship
The resistance of a light-dependent resistor is inversely proportional to the light intensity. A higher light intensity results in more electrons being freed, leading to a lower resistance and a higher current flow.
It is the opposite when you have lower light intensity. This leads to fewer electrons and a higher resistance. As a result, you also end up with a lower current flow.
It is worth noting that the relationship between the resistance and light intensity is not linear but tends to follow a hyperbolic curve.
LDR Construction
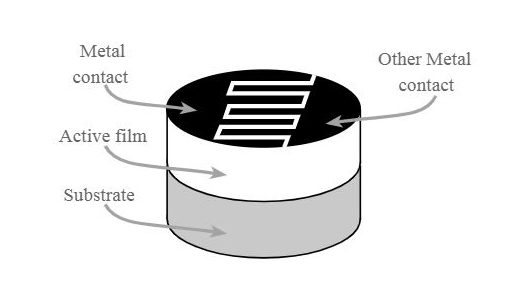
ए light dependent resistor sensor is made up of several components. The first one is the insulating substrate. This is a non-conducting material such as ceramic whose job is to hold the other LDR components.
Next, we have the photoconductive material. This is a strip of light-sensitive material, such as Cds, that is deposited on the substrate in a zigzag pattern. The idea of a zigzag pattern is to increase the surface area exposed to light. This helps maximize light absorption and influences resistance.
You also get the ohmic contacts. These are basically the metal contacts found on either side of the zigzag pattern. They are used to connect the LDR to an external circuit.
Encapsulation is also essential. This is when the entire structure is covered with a transparent material such as glass or plastic for protection from the environment. This allows light to reach sensitive materials.
Electrical Characteristics of LDR
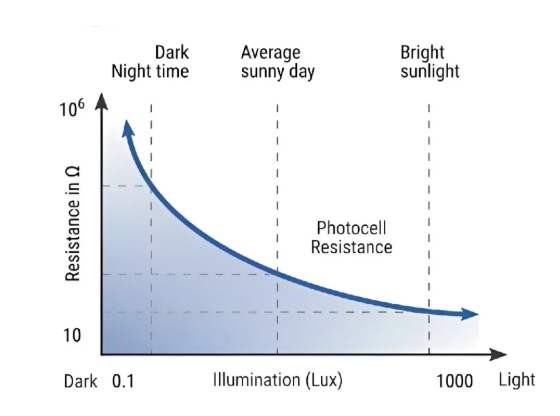
There are a couple of electrical characteristics of LDR that help us understand how light dependent resistors work. Such include:
Resistance Range
Dark – the resistance of the LDR can be as high as several megaohms when there is complete darkness.
Bright light – in bright light, the resistance drops drastically to only a few hundred ohms.
The typical values for an LDR will be more than 1 MΩ in darkness and less than 1 kΩ when the light intensity is high.
Response Time
Rise time – this indicates the time the LDR resistance decreases when exposed to light. It usually ranges from 2 to 50 milliseconds.
Fall time – this is the time it takes for an LDR resistance to return to the initial dark resistance value once the light is removed. This takes longer compared to the rise time. It may take up to a few seconds.
Spectral Response
Wavelength dependence—light-dependent resistors are generally more sensitive to certain wavelengths of light. For example, a material such as cadmium sulfide is more sensitive to green light.
Material dependence—The spectral response is determined by the semiconductor material used to make the LDR. Cadmium sulfide, for example, has a peak sensitivity at around 550 to 600nm.
Types of Light-Dependent Resistors
There are two main ways of categorizing the light-dependent resistors. Such include the intrinsic and extrinsic photoresistors.
Intrinsic Photoresistors
These photoresistors are made of pure, undoped semiconductor materials such as germanium and silicon.
Whenever light shines on the material, it excites the electrons to move from the valence band to the conduction band, increasing conductivity and reducing resistance.
In terms of sensitivity, this type of LDR is less sensitive to light than the extrinsic type.
You will come across them in applications where quick response and high sensitivity are not critical. You are likely to find them in basic light-sensitive circuits such as automatic door openers.
Extrinsic Photoresistors
This time, the LDR is made from doped semiconductor materials. Doping means introducing impurities to create additional energy levels in the material.
Doping greatly reduces the energy required for electrons to jump to the conduction band, making the extrinsic photoresistor more sensitive to light.
It is highly sensitive to light, especially in wavelengths such as infrared. Applications that need sensitivity to specific wavelengths or low light intensities are typical uses for this type of LDR.
Examples include infrared detectors, flame sensors, and other applications that need detection at specific light wavelengths.
| विशेषता | Intrinsic LDR | Extrinsic LDR |
| Material | Pure semiconductors | Doped semiconductors |
| Sensitivity | निचला | Higher |
| Wavelength sensitivity | Less specific | Tailored to specific wavelengths |
| Typical applications | General light detection | Specialized light detection |
Applications of Light-Dependent Resistors
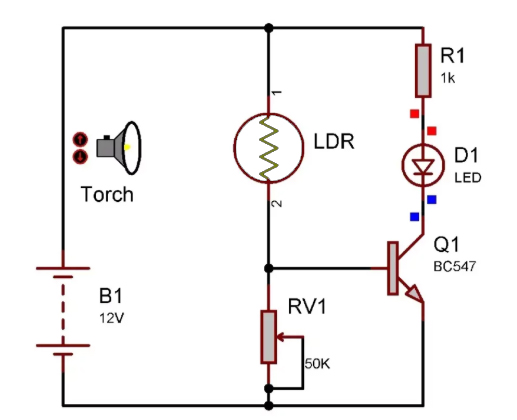
There are several options available when it comes to using light dependent resistors. Such include:
- Automatic street lighting whereby the lights are automatically switched on during the night and off during the day to enhance energy efficiency.
- Solar garden lights also use LDRs to control the process of charging the batteries and ensure the lights turn on automatically at night or off during the day.
- Camera exposure control is a feature that adjusts the camera’s aperture or shutter speed to ensure proper exposure in different lighting conditions.
- Industrial automation and robots also use LDRs in their workspaces and part of robotic systems for reacting to changes in light intensity.
- Light-sensitive switches can also be used in such applications as well. This is where the lights automatically turn on when the ambient light level is low.
Advantages of LDRs
- Low cost and easy to use. You can quickly integrate them into electronic circuits as they need minimal components to set them up.
- They offer energy efficiency if used in automation. LDRs are good for automating lighting systems to ensure the lights are only on when necessary.
- They need no external power source to sense light. They simply use the change in light intensity to do their job.
- High light-to-dark resistance ratio makes them reliable for applications with clear distinctions in light levels.
- They are mostly compact, making integrating them into various systems and devices easy.
Limitations of LDRs
- Compared to photodiodes, the LDRs sometimes take longer to react to changes
- Temperate fluctuations may also affect the resistance of the LDR
- They tend to have limited spectral response, as such they may not accurately detect certain light colors.
Light Dependent Resistors Alternatives
Photodiodes
This is a known alternative to light-dependent resistors because of the fast response times and linear output. This makes them more suitable for applications that require precise and quick light detection.
As much as they are good in terms of sensitivity, they will require a power source. Examples of their use cases include camera light meters, industrial automation, and optical communication.
Phototransistors
The phototransistors offer higher sensitivity than photodiodes, making them a good choice whenever you need better sensitivity.
The only downside is that they are slower in response time than photodiodes and will require voltage biasing.
These characteristics of phototransistors make them suitable for applications with high sensitivity, such as light-sensitive switches.
निष्कर्ष
A light dependent resistor has a simple design but is effective at the same time. That is how we are able to use it in various applications that work through light detection. Examples such as light sensors make seeing the LDR in action possible. As much as there are alternatives, you will still come across other key applications for LDR. Since they are also compact, it becomes easy to integrate into existing electronics and improve their functionality.
Video:What is an LDR? (Light Dependant Resistor)
कृपया आरएफक्यू भेजें, हम तुरंत जवाब देंगे।
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्नों
What are common materials used to make LDRs?
Most LDRs are made using semiconductor materials such as cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. They are highly sensitive to visible light.
Can LDRs work with Arduino or Raspberry Pi?
Yes. A voltage divider circuit can connect LDRs to a microcontroller, such as an Arduino. This capability allows you to build projects such as automatic lamps and light-sensitive alarms.
What is the resistance level of LDR in darkness?
LDR’s resistance in darkness is quite high, sometimes reaching several megaohms. In light conditions, it drops to a few hundred ohms. Of course, it depends on the light intensity.


