रिले क्या है? इलेक्ट्रिकल रिले के लिए एक संपूर्ण शुरुआती गाइड
Author:admin Date: 2025-06-11 09:28 Views:302
परिचय
ए relay is a type of electronic switch that turns on or off a circuit based on a signal from an outside source. It can be considered an electric lever that is activated by a small current to control a larger current.
From the relay meaning, we can see it can open and close circuits depending on the signal. This means it can block or allow the flow of electricity. Expect to come across different types of relays to help you achieve different applications.
Some notable applications for relays include power control, detecting overload or overcurrent, and switching smaller currents. We will learn more about relays, including using a relay tester in case the model is not working as expected.
How Does a Relay Work
To understand the question of how does a relay work, we first need to know the components of a relay. They include an electromagnet, armature, and contacts. These work together to realize the functionality of a relay.
The relay features a magnetic core with a wire wrapped around it. This core functions as the electromagnet, and a magnetic field is created whenever current flows through the coil.
The armature is a movable part attached to the coil. Whenever current passes through the coil, a magnetic field attracts the armature. This armature movement leads to the opening or closing of the contacts. That is how switching the circuit open or closed happens.
Under the types of contacts, we have the normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contacts. For NO, these contacts are open whenever the coil is not energized, or there is no current going through it. They will only close when the coil is energized.
For NC, the contacts are closed when the coil is not energized and open when it is energized.
We will also look at how to tell if a relay is bad so that you can troubleshoot better to have it working as expected.
Types of Electrical Relays
Expect to come across different types of electrical relays. However, they mostly fall under electromechanical, solid state, and reed relays. The relays can also be classified based on the number of poles and switches, function, and construction.
Electromechanical Relays
These are relays with an electromagnet vital for moving a set of contacts, which then switches the circuit on or off. Such relays are built with robustness in mind and can handle high currents. Their simple design also makes them more affordable.
Solid State Relays
These relays use semiconductors such as MOSFETs for switching circuits. Because of this construction, they now offer faster switching speeds and have a longer lifespan than electromechanical relays. Also, since they lack moving parts, they are more reliable and less prone to wear and tear.
रीड रिले
These types of relays use two reeds made of ferromagnetic blades encased in a glass tube. An electromagnet moves these reeds to provide the switching mechanism. Expect them to be fast in terms of switching and also offer long lifespans. They can handle sensitive signals better than some other options.
Common Applications of Relays
Relays have multiple applications. Here is what you can expect to find while researching relay applications.
Industrial Automation
In this case, a relay switch can be handy for machinery control. This includes starting, stopping, or switching between different operating modes. The same switch can also activate safety mechanisms if certain conditions are met.
We also find them necessary for process automation. Examples include controlling pumps, conveyor belts, and other related equipment.
Home Automation
Lighting control, security alarms, and smart home devices all use relays to control the functionalities of other devices. For example, relays can be used to switch on or off the lights. The same is true for activating alarms whenever the security system is triggered.
Automotive Systems
Relays help control vehicle functions, including fuel pump operations, wiper control, and headlight switching.
We also find relays in the safety systems of the vehicles. Such include the anti-lock braking systems and airbags. Without relays, such systems will not work. That is why you need to know how to check if a relay is bad.
Telecommunications
Yes, you will come across relays in telecommunications as well. We are talking about signal routing, line protection, and network management functions.
Relays can switch and route signals in the telecommunications network for signal routing. They still help protect lines from power surges and similar damage.
They can also be used for network management, such as connecting and disconnecting lines.
Power Systems
This is another popular field where relays are used in various capacities. We have circuit protection, load shedding, and system monitoring applications.
In circuit protection, relays protect electrical power systems from faults such as short circuits and overloads. Then, we also have load shedding, where the relays can be used to shed load during peak demand periods. This is to prevent cases of system overloads.
Electrical Relay Symbol and Pinout
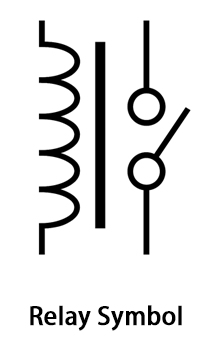
A relay symbol usually consists of a rectangle or box with coils and contacts represented by lines and circles. The symbol will slightly change depending on the type of relay.
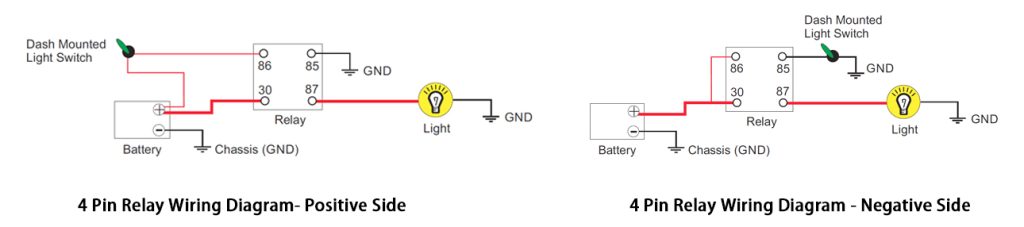
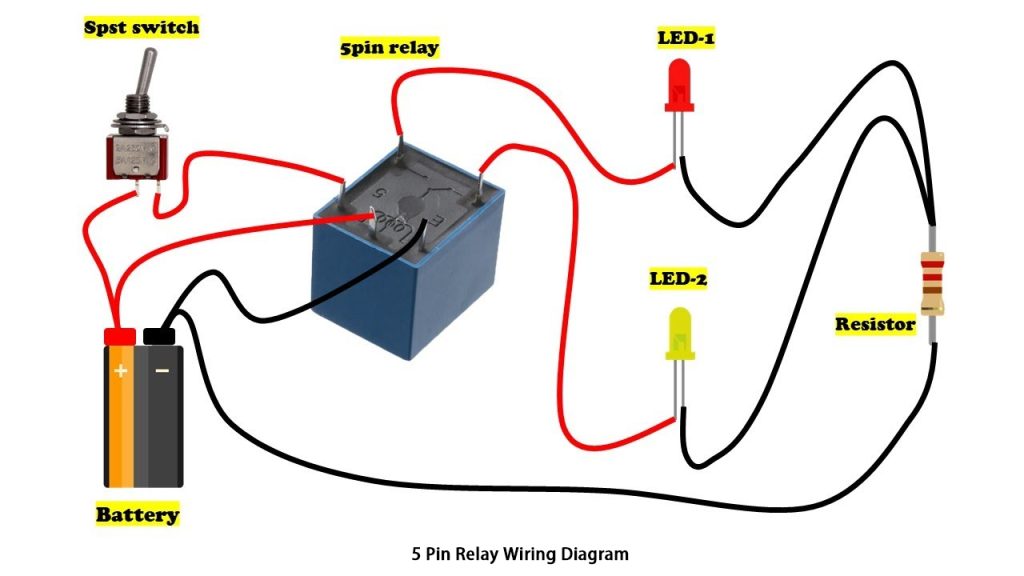
When you look at a relay wiring diagram, you will notice there are two main types. The standard wiring diagrams are 4-pin and 5-pin. The main difference between the two is that a 4-pin relay is used for controlling a single circuit, while the 5-pin relay can switch power between two circuits.
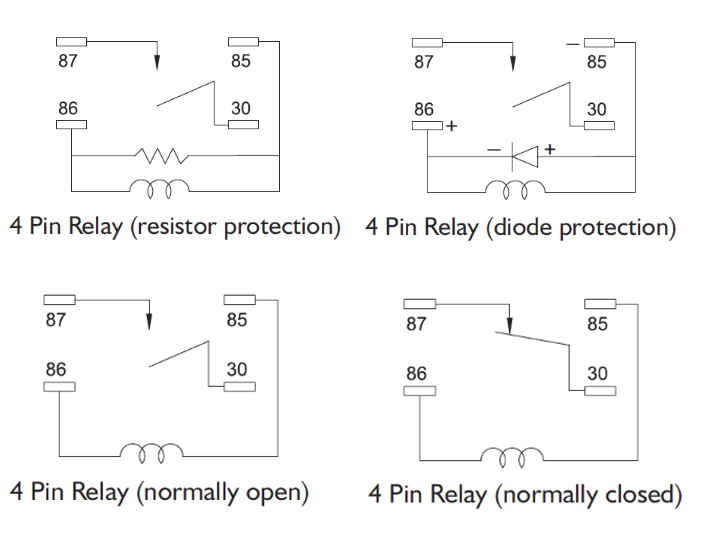
4 Pin Relay Schematic Diagram
In the 4-pin relay wiring diagram, 30 and 87 are used for the main power input and output. 85 and 86 are the control terminals for the relay coil.
In the 5-pin relay diagram, 30 is the common or input terminal for the power source, 87 and 87a are the contacts, and 85 and 86 are the control terminals for the relay coil.
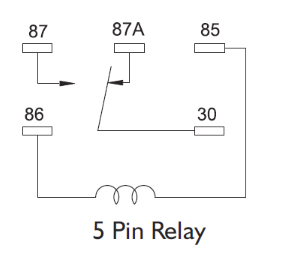
5 Pin Relay Schematic Diagram
How to Pick the Right Relay for an Application
There are several things to consider when picking the right relay. Here is what you need to do.
Understand the Application Requirements
Different systems operate at different levels. So, first, look at the load type. It is essential to determine the right relay type to handle its inrush current and arc suppression.
You will need to understand the relay ratings in terms of voltage and current. This ensures you have the right relay rated for the application.
Operation
Under operation, we are looking at how often the relay will switch on and off. And also, how long it will remain in each state. Depending on the use, sometimes you might need a high-frequency switching relay, while other times it is vice versa. That is why it is important to know this information.
Environmental Conditions
You also have to consider the operating conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances or vibrations. These conditions can determine the type of relay to use so that it can withstand them.
The Relay Type
There are several types of relays in the market. We have the electromechanical and solid-state relays as the main options.
The electromechanical relays are the most common options in the market and are commonly used for general-purpose applications. They are inexpensive but tend to have slower switching speeds. Still, they can have a shorter lifespan compared to the other options.
The solid-state relays offer faster switching speeds, silent operations, and longer lifespans. We can recommend them for applications that need high-frequency switching or if vibration is a concern.
Relay Specifications
We have already mentioned the voltage and current ratings, but there are other important specifications to consider. These include contact rating, switching capacity, operating temperature, and insulation resistance.
The contact rating highlights the maximum current, power, and voltage that the relay can switch. Look at this value to ensure it is enough to work with your load.
As for the switching capacity, it indicates the number of times the relay can switch before its contacts wear out.
Of course the operating temperature indicates the range of temperature where it can still operate normally in your application.
Other Considerations
We also recommend looking at the mounting options. What kind of mounting configuration do you have? Depending on what suits your application, you can opt for a DIN rail, panel mount, or any other type.
The size and shape are also important to look into as they ensure you have a relay that fits into the available space.
How about the cost? Yes, make sure that the relay offers value for money. This means the price should also reflect its performance and reliability.
How to Test a Relay
How do you test a relay? That will be the question in mind if you have not tested relays before, as you would not know where to start. Well, we are here to help with that.
You would mostly use a multimeter to check if the contacts and coil are working as expected.
Start by checking the coil’s resistance. This is to check if it’s open or shorted. Here is how to test a relay with a multimeter for the coil.
- Turn off the power to the relay first and set the multimeter to measure resistance or continuity.
- Connect to the coil terminals, which are typically marked as 85 and 86. Check the resistance across these two terminals.
- For a good coil, it will have a resistance value of 50 to 200 ohms.
- An open or shorted coil will have zero ohms or read “open” on the multimeter, indicating that it is faulty.
Testing the contacts can also be done using a multimeter. Here is how to do it.
- Set the multimeter to the continuity mode first.
- Test for continuity between the common and normally open (NO) terminals. Do the same for the normally closed (NC) terminals.
- Without power in the circuit, the NO contacts will have no continuity, and the NC contacts will show continuity.
- If power is added to the coil, the NO contacts should have continuity, while the NC contacts should have no continuity.
- If the results are different from what is mentioned above, then you know there is a fault in therelay wiring.
निष्कर्ष
We have seen how relays are important in electrical circuits. It comes down to which type you use and how it is used. Make sure that you choose the right type so that it can deliver on the right electrical switching and performance. Buying from top brands is also recommended to ensure performance and longevity. You can always test the relay using the methods we shared above to know when it is time to change the relay or repair it.
कृपया आरएफक्यू भेजें, हम तुरंत जवाब देंगे।
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्नों
Where are relays commonly used?
Depending on the application, relays are commonly used in home appliances, telecommunications, safety circuits, industrial automation systems, and automotive electronics.
How do you read a relay wiring diagram?
The relay diagrams will have coil symbols and contact points such as NO and NC. The standard relay symbol includes a box indicating the coil and the lines for the switch. Make sure to look at a relay’s datasheet to understand more.
What is the difference between a relay and a contactor?
They are both electrically operated switches, but they have some differences. Relays are mostly used for low-power applications and sometimes signal-level switching, while contactors are made for high-power applications such as industrial loads, lighting systems, and motors.


