बीएसएस123 | Datasheet, Application Circuit, Equivalent & Pinout Yangzhou Yangjie Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd
- ब्रांड: यंग्ज़हौ यांगजी इलेक्ट्रॉनिक प्रौद्योगिकी कं, लिमिटेड
- डाउनलोड करना: BSS123 Datasheet PDF
- कीमत: जाँच करना
- स्टॉक में: 3,179
- एफईटी प्रकार: n- चैनल
- ड्रेनटू सोर्स वोल्टेज (Vdss): 100 वी
- वर्तमान-निरंतर निकासी(आईडी)@25°C: 200mA (टीए)
- पैकेट: एसओटी-23

HK$250.00 से अधिक ऑर्डर पर निःशुल्क डिलीवरी

त्वरित प्रतिक्रिया, त्वरित उद्धरण

फ्लैश शिपमेंट, बिक्री के बाद कोई चिंता नहीं

मूल चैनल, प्रामाणिक उत्पादों की गारंटी
Electronics: LED switching circuit using N-Channel(BSS123) MOSFET (4 Solutions!!)
Bss123
The बीएसएस123 is a small N-channel MOSFET that’s perfect for low-power switching and small current handling applications. Here’s why it stands out:
With a 50V drain-source voltage और 100mA drain current, it’s great for low-power circuits. The Rds(on) of 1.3Ω ensures minimal power loss, which is crucial for energy-efficient designs. Plus, it works with ±20V gate-source voltage, making it ideal for logic-level control in systems like microcontrollers.
You’ll often find the BSS123 in low-power switches, level shifting, and signal amplification applications. It’s widely used in small electronic devices, switch-mode power supplies, and audio circuits.
Bss123 Pinout
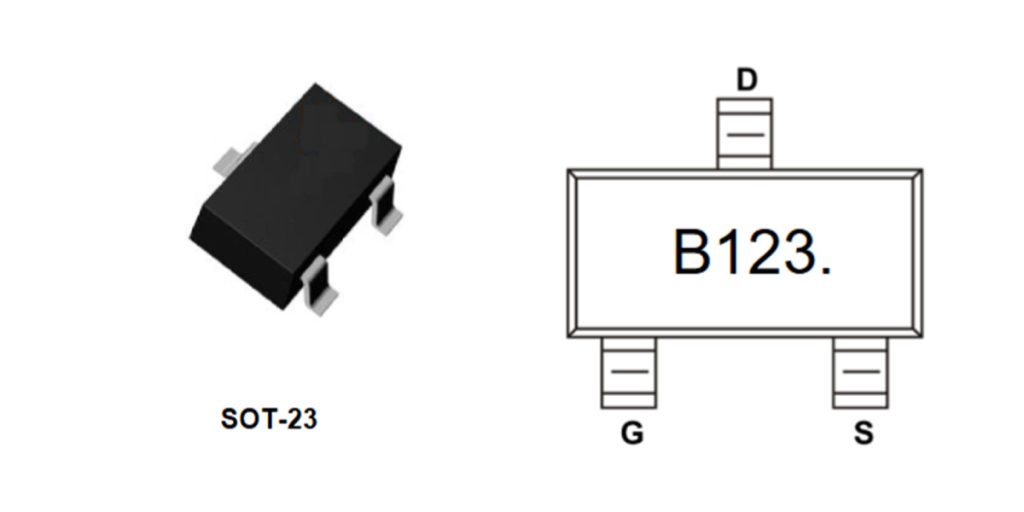
| पिन नंबर | पिन नाम | Function Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | स्रोत | Connected to the load end, usually connected to the lower potential side. |
| 2 | दरवाज़ा | Controls the MOSFET’s switching state, usually connected to the control signal. |
| 3 | नाली | Connected to the positive side of the load or the power source, controlling current flow. |
Here’s a quick breakdown of the BSS123 MOSFET pinout and important things to keep in mind:
-
स्रोत: This is usually connected to ground or a low-voltage signal. It’s where current flows out of the MOSFET, so make sure it’s connected properly in your design.
-
दरवाज़ा: The gate controls the MOSFET’s switching. When the gate voltage is high enough, the MOSFET turns on. But don’t exceed ±20V on the gate, or you risk damaging the MOSFET.
-
नाली: This is where the current flows into the MOSFET, either from your load or power source. Control the current by adjusting the gate voltage.
A few extra tips: Watch the gate voltage, ensure the drain-source voltage stays under 50V, and keep an eye on heat dissipation if you’re handling higher currents.
Bss123 Equivalent Mosfet





| Parameters | बीएसएस123 | IRLML6344 | 2एन7000 | एओ3400ए | IRLML6402 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| पैकेज का प्रकार | एसओटी-23 | एसओटी-23 | एसओटी-23 | एसओटी-23 | एसओटी-23 |
| Max Source-Drain Voltage (Vds) | 50V | 30 वी | 60 वी | 30 वी | 30 वी |
| Max Drain Current (Id) | 100एमए | 150एमए | 200एमए | 150एमए | 200एमए |
| Gate-Source Voltage (Vgs) | ±20V | ±20V | ±20V | ±20V | ±20V |
| Rds(on) | 1.3Ω | 0.6Ω | 1.2Ω | 0.1Ω | 0.45Ω |
| Power Dissipation (Pd) | 350 मेगावॉट | 500 मेगावाट | 350 मेगावॉट | 400mW | 500 मेगावाट |
| Application | Low-power switching, signal control, logic level conversion | Low-power switching, electronic conversion, logic level conversion | Switching electronics | Small power switching, logic level conversion | Low-power switching, logic level conversion |
Here’s a quick guide on some alternative MOSFET options to the BSS123:
-
पैकेट: All alternatives, like the 2N7000, IRLML6344, and AO3400A, come in the same एसओटी-23 package, so they’re a perfect fit for your design without needing any changes.
-
Drain-Source Voltage (Vds): If you need more voltage, the 2एन7000 offers 60 वी (vs. 50V for the BSS123). For lower-voltage needs, the IRLML6344 और एओ3400ए give you 30 वी.
-
Drain Current (Id): The 2एन7000 supports 200एमए (compared to the BSS123’s 100mA), ideal for higher-current applications. The others offer up to 150एमए.
-
Rds(on): If efficiency is key, the एओ3400ए has a very low Rds(on) of 0.1Ω, much better than BSS123’s 1.3Ω.
-
Power Dissipation: For higher-power use, IRLML6344 और IRLML6402 can handle 500 मेगावाट, which is great for more demanding circuits.
Bss123 Load Switch Circuit

Here’s a simple breakdown of how this circuit works:
The 3.3V power supplies energy to the circuit. The LED (D1) has a forward voltage of 2.3V and operates at 70mA. The R2 resistor (330Ω) limits the current to prevent the LED from burning out.
The MOSFET (Q3, BSS123) acts as a switch. When the gate voltage (controlled by R1) is high enough, the MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow through the LED and light it up. When the gate voltage drops below a certain threshold, the MOSFET turns off, and the LED goes dark. This setup keeps the LED safe and controlled.
Bss123 Smd Mosfet Application
The बीएसएस123 is a small N-channel MOSFET that’s great for low-power circuits, especially when you need something compact and efficient. It’s commonly used in SMD (surface-mount device) designs for its low resistance and high switching efficiency. Here are some common uses:
-
Low-Power Switching: It’s perfect for controlling small loads, like in battery-powered devices या relay drivers for low-current devices.
-
Level Shifting: BSS123 is often used to convert between 3.3V and 5V logic levels in circuits like microcontroller I/O interfaces or communication protocols like आई2सी.
-
Signal Amplification: It can amplify small signals, like in audio circuits or low-noise analog applications.
-
Load Driving: It’s widely used to drive LEDs या small motors in embedded systems.
-
Voltage Regulation: Ideal for LDOs (low-dropout regulators) in portable electronics for stable voltage output.
-
Protection Circuits: Used for overcurrent protection या reverse voltage protection.
With its versatility, the BSS123 is great for a wide range of compact, low-power designs.
Bss123 Arduino Logic Level Switch
The बीएसएस123 N-channel MOSFET is a great choice for low-power switching, especially in logic level shifting setups with आर्डुइनो. Here’s how you can use it:
Schematic:
-
कनेक्ट करें दरवाज़ा of the MOSFET to an Arduino digital output pin (like D3).
-
The स्रोत goes to जीएनडी.
-
The नाली connects to the input pin of the device you’re controlling (for example, a 5V device).
-
Place a 10kΩ pull-up resistor between the 5V power supply and the नाली to ensure the signal goes HIGH when the MOSFET is off.
How It Works:
-
Low (0V): When the Arduino pin is LOW, the MOSFET stays off, and the pull-up resistor pulls the drain to 5 वी, sending a HIGH signal to the target device.
-
High (3.3V or 5V): When the Arduino pin is HIGH, the MOSFET turns on, pulling the drain to जीएनडी and sending a LOW signal.
This setup is perfect for shifting 3.3V logic to 5V or the other way around, making it ideal for low-power applications.
Bss123 Gate Threshold Voltage
The BSS123 MOSFET has a threshold voltage (V_GS(th)) ranging from 1.3V to 3.0V. This means the MOSFET starts to conduct when the gate-source voltage (V_GS) reaches this level, allowing a small current to flow.
However, to fully turn on the MOSFET and get it into its “saturated” state (or “fully on”), you’ll usually need a V_GS of 3V to 5V. This higher gate voltage ensures you get a low R_DS(on), meaning lower resistance and better performance for your circuit.
So, remember, for the best results, aim for a gate voltage of around 3V to 5V to ensure the MOSFET operates efficiently.
Bss123 Reverse Polarity Protection
Using a BSS123 MOSFET for reverse polarity protection is a smart and efficient way to safeguard your low-power circuits. Here’s how it works:
-
स्रोत is connected to जीएनडी, and the नाली goes to the load (the circuit that needs power).
-
The दरवाज़ा is tied to the वीसीसी through a resistor, ensuring the MOSFET turns on when the power is correctly connected.
-
ए Schottky diode prevents reverse current from flowing when the polarity is wrong.
How it works:
When the polarity is correct, the MOSFET conducts and powers the load. If the polarity is reversed, the MOSFET turns off, preventing any damage.
Advantages:
-
Low voltage drop compared to regular diodes, making it more efficient.
-
No power loss during normal operation, which improves efficiency.
Bss123 Mosfet for Led Control
The BSS123 MOSFET is a great choice for controlling LEDs, especially when used as a low-side switch. Here’s how it works:
-
नाली connects to the LED’s negative side, and the स्रोत connects to जीएनडी. The दरवाज़ा is controlled by a signal (like from a microcontroller).
-
When the signal is high, the MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow through the LED, making it light up.
-
When the signal is low, the MOSFET turns off, and the LED goes dark.
Advantages:
-
Low power consumption due to its small R_DS(on).
-
Works with 3.3V or 5V logic signals.
Limitations:
-
Best for low-current LEDs (up to 170mA).
In short, the BSS123 is an efficient and energy-saving choice for controlling low-power LEDs.


~~3.jpg)




.jpg)

;;2.jpg)






.jpg)