BC858B | ON Semi | 215 | datasheet Diotec Semiconductor
- Transistor Type: PNP
- Current-Collector(Ic)(Max): 100 mA
- Voltage-Collector Emitter Breakdown (Max): 30 V
- Package: TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
BC858B
The BC858B is a common PNP transistor in an SOT-23 surface-mount package, perfect for low-voltage, low-current amplification or switching tasks. It handles up to -30V and -100mA, which makes it ideal for controlling LEDs or other small loads. With a gain (hFE) between 110 and 800, it’s reliable for signal amplification or level shifting. Plus, it has a decent frequency response up to about 150 MHz, so you can comfortably use it for mid-to-high-frequency small-signal applications. Its tiny package is excellent for saving board space. Just keep in mind it’s a PNP type, meaning the current control direction is opposite to NPN types you’re probably more familiar with, so keep an eye on that during layout.
BC858B Pinout
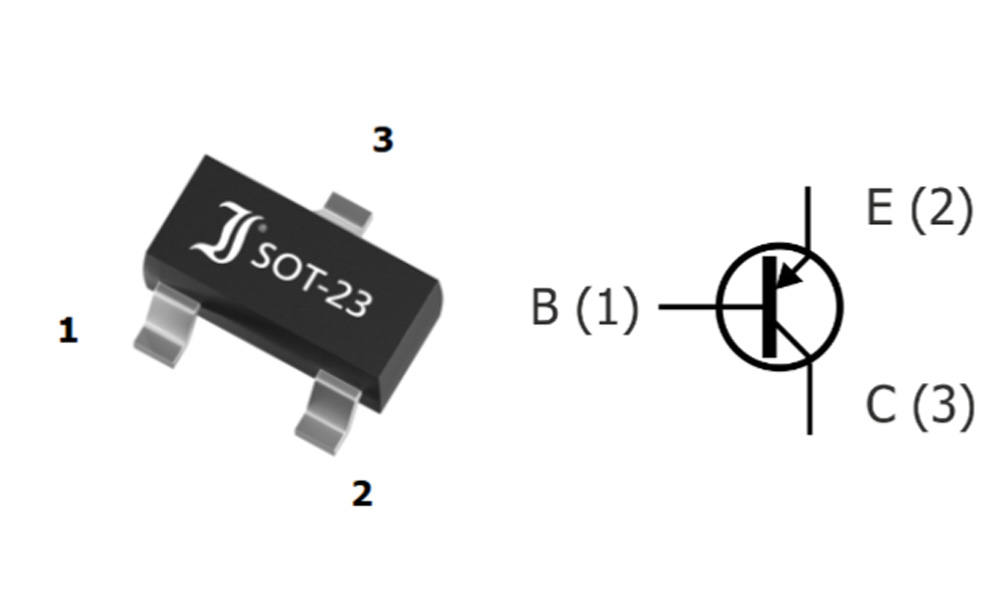
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Function Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base (B) | Input terminal for controlling current |
| 2 | Emitter (E) | Current output terminal (outflow) |
| 3 | Collector (C) | Load current input terminal |
When you’re using the BC858B transistor, keep in mind it’s a PNP type. So, the base voltage should typically be around 0.7 volts lower than the emitter to make it conduct properly. Also, double-check the pin order carefully when soldering surface-mount transistors like this one—it’s easy to get confused by PCB markings or tricky angles, and accidentally connecting pins incorrectly can damage the transistor or make your circuit malfunction. It’s perfect for small-signal control, inverting switches, or basic level shifting. Once you’ve understood these basics, using it becomes straightforward.
BC858B Equivalent




| Parameter / Model | BC858B | BC856B | MMBT5401 | BC807-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | PNP | PNP | PNP | PNP |
| Package | SOT-23 | SOT-23 | SOT-23 | SOT-23 |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage Vce | -30V | -65V | -150V | -45V |
| Collector Current Ic | -100mA | -100mA | -600mA | -500mA |
| DC Current Gain hFE | 200–450 | 200–450 | 100–200 | 160–400 |
| Power Dissipation Pd | 250mW | 250mW | 350mW | 250mW |
| Transition Frequency fT (MHz) | 150 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
If you don’t have BC858B handy, you can directly swap it with a BC856B—they’re almost identical, except BC856B can handle higher voltage (-65V). Another alternative is the MMBT5401, also a PNP transistor in an SOT-23 package, but it withstands even higher voltage (-150V) and current (-600mA). It’s great if your circuit involves heavier loads or higher voltages, though its gain (hFE) is lower. So, if your design depends on specific gain values, test carefully before switching. BC807-25 is also solid—it can handle currents up to -500mA, making it suitable for inductive loads or moderate-power switching. Just remember its gain levels vary based on suffixes like -16/-25/-40, so pick the right one for your needs.
BC858B Amplifier Circuit Example
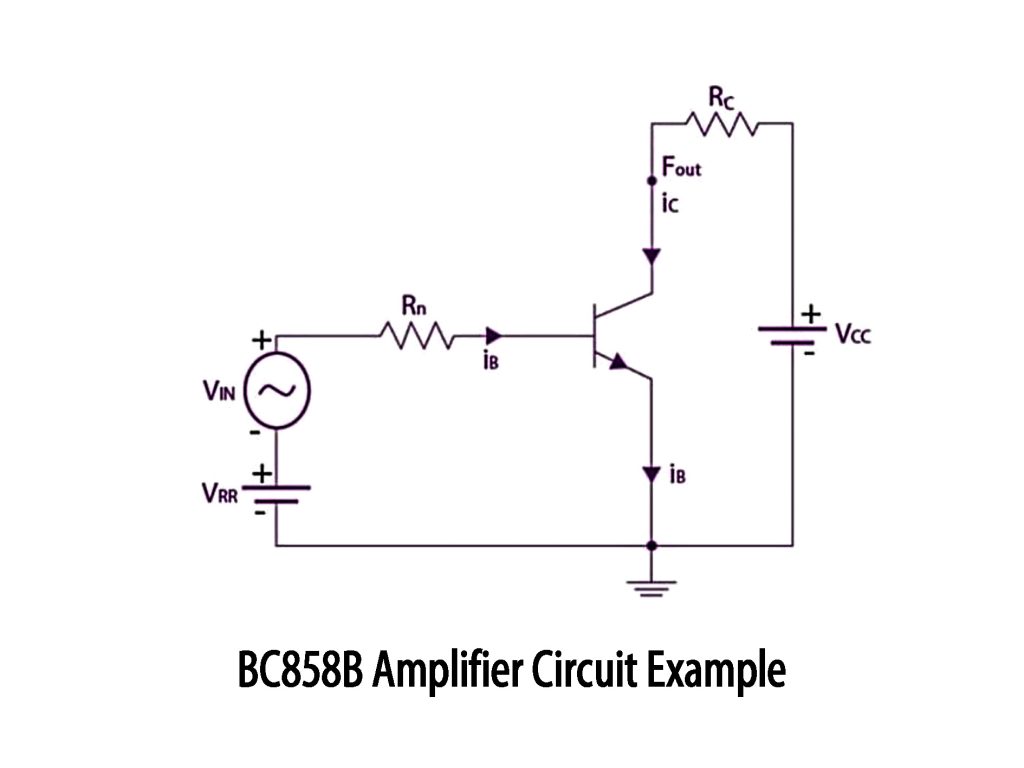
When you feed your small input signal (Vin) through resistor Rn to the base of the BC858B transistor, keep in mind it’s a PNP type, so the base needs a slightly lower voltage compared to the emitter. Usually, this means your signal should have a negative swing or you can use a negative bias voltage (VRR) to help out.
As soon as there’s base current, the transistor switches on and allows a larger current through resistor RC from the collector side to your positive supply voltage (Vcc). This creates a voltage variation across RC, giving you an amplified signal at the output.
The size of this output signal depends on your supply voltage, resistor RC’s value, and the transistor’s gain. It’s a common way to amplify small signals like audio inputs or sensor outputs. Just don’t forget, PNP transistors behave opposite to the NPN types you’re probably used to.
BC858B Switching Circuit Design
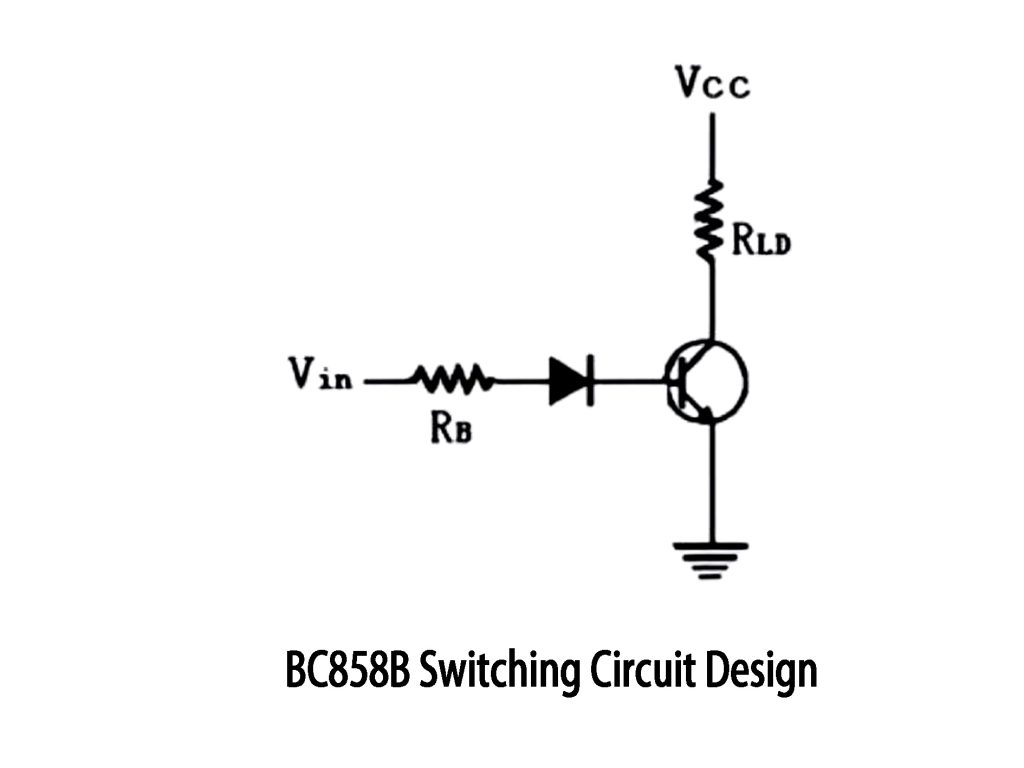
When using a BC858B transistor for switching, connect the emitter to Vcc and collector through your load resistor RLD to ground. Feed your input signal (Vin) to the base via resistor RB, and place a diode for protection.
Here’s how it works: When Vin goes low (e.g., grounded), the diode turns on, making the transistor’s base lower than the emitter. The transistor switches on, current flows through your load, activating it (like an LED or relay). When Vin goes high, the transistor turns off, cutting the load off.
Just make sure resistor RB isn’t too small, to keep base current safe. A diode like 1N4148 is perfect for input protection, and remember to keep load currents under about 100mA to stay safe.
BC858B Usage
When you’re working with the BC858B transistor, there are a few handy ways to use it. For example, if your MCU outputs a low signal, the transistor can switch small loads like LEDs or buzzers. It also works great for amplifying tiny signals, like audio inputs or sensor outputs, making them easier to handle later. Need a simple level inverter to flip high signals into low? A BC858B with a pull-up resistor gets that done easily. You can even control power to different modules using it as a switch controlled by your MCU. It’s perfect for embedded designs—just stay within its 100mA current limit, and you’ll have no trouble at all.








,TO-226_straightlead.jpg)